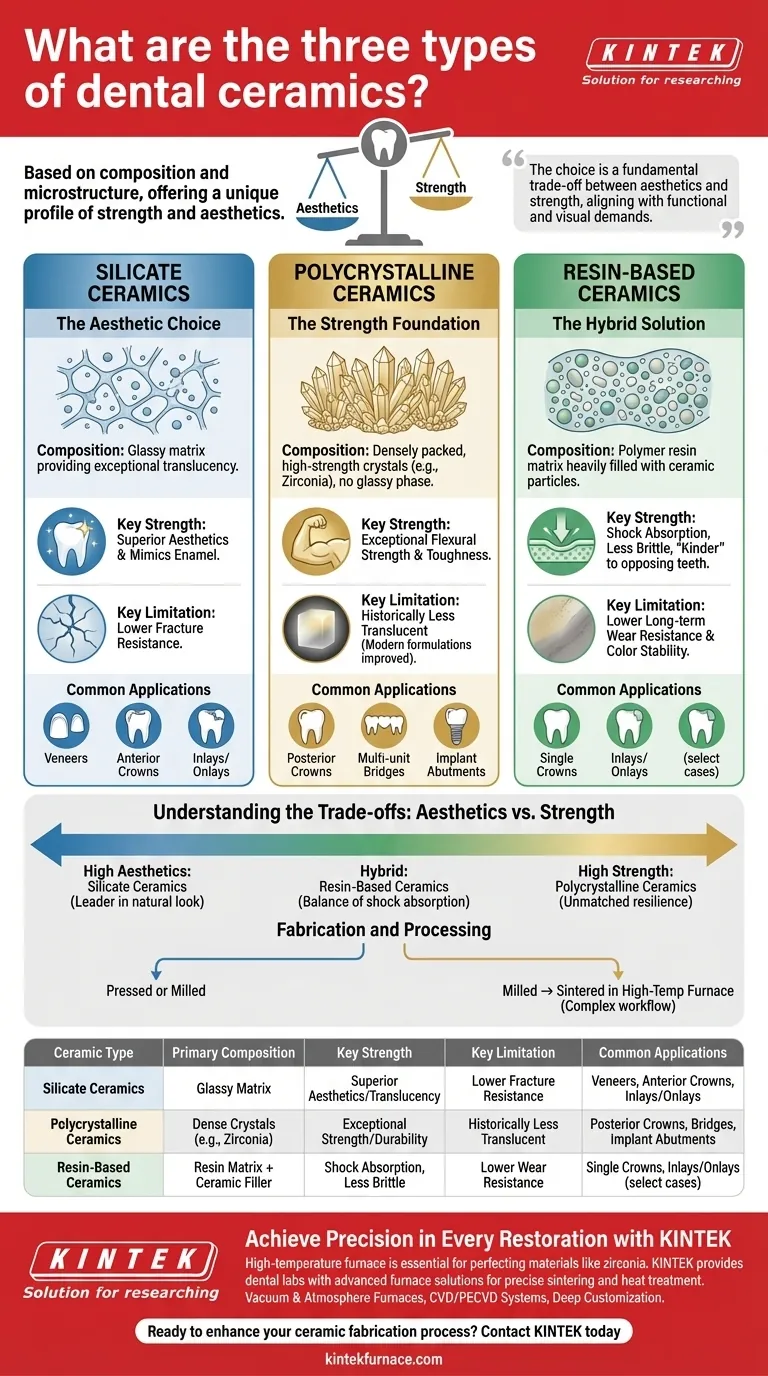
The primary classes of dental ceramics are broadly divided into three distinct categories based on their composition and microstructure. These categories are silicate ceramics (glass-based), polycrystalline ceramics (crystal-based), and resin-based ceramics (hybrid composites). Each class offers a unique profile of strength, aesthetics, and fabrication requirements, dictating its ideal use in clinical restorations.
The choice of a dental ceramic is not about finding a single "best" material, but about understanding the fundamental trade-off between aesthetics and strength. Your selection must align with the specific functional and visual demands of the restoration, from a highly visible anterior veneer to a load-bearing posterior crown.

The Three Core Classes of Dental Ceramics
Understanding the composition of each ceramic class is the key to predicting its clinical performance. The primary difference lies in the ratio of glass to crystalline structures within the material.
Silicate Ceramics: The Aesthetic Choice
Silicate ceramics are defined by a glassy matrix, which gives them exceptional translucency and the ability to mimic the natural appearance of tooth enamel.
These materials, which include feldspathic porcelains and glass-ceramics like lithium disilicate, are the gold standard for highly aesthetic restorations. Their optical properties are unmatched.
However, the glassy phase that provides their beauty is also their structural weakness, making them less resistant to fracture than other classes. They are best suited for veneers, inlays, onlays, and single anterior crowns where cosmetic results are paramount.
Polycrystalline Ceramics: The Strength Foundation
Polycrystalline ceramics, such as zirconia and alumina, contain no glassy phase at all. They are composed of densely packed, high-strength crystals.
This structure gives them exceptional flexural strength and fracture toughness, making them the most durable ceramic materials available. They are the definitive choice for restorations that must withstand significant chewing forces.
Their high strength makes them ideal for posterior crowns, multi-unit bridges, and implant abutments. While historically more opaque, modern formulations of zirconia have significantly improved translucency, expanding their use.
Resin-Based Ceramics: The Hybrid Solution
Resin-based ceramics, also known as hybrid ceramics, are a composite material. They consist of a polymer resin matrix that is heavily filled with ceramic particles.
This combination creates a material that is less brittle than pure ceramics. It absorbs chewing forces rather than directly resisting them, which also makes it "kinder" to the opposing natural teeth by causing less wear.
Hybrid ceramics are easy to mill and polish, and can be repaired in the mouth. However, they have lower long-term wear resistance and color stability compared to pure ceramics, making them a choice for specific situations rather than a universal replacement.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Aesthetics vs. Strength
No single material excels in every category. The selection process is a deliberate balancing act between visual demands and mechanical durability.
The Aesthetic Spectrum
When a restoration must be indistinguishable from a natural tooth, silicate ceramics are the clear leader. Their glass content allows light to pass through them in a way that polycrystalline materials cannot fully replicate.
The Strength Spectrum
For posterior teeth or long-span bridges where fracture is the primary concern, polycrystalline ceramics like zirconia are unmatched. Their all-crystal structure provides the necessary resilience to withstand years of functional load.
Fabrication and Processing
The material's composition dictates its fabrication process. Silicate ceramics can be pressed or milled, while zirconia must be milled and then sintered in a specialized high-temperature furnace to achieve its final strength. This adds a layer of complexity to the manufacturing workflow.
Selecting the Right Material for the Restoration
Your final decision should be guided by the clinical requirements of the specific case.
- If your primary focus is anterior aesthetics: Silicate ceramics like lithium disilicate offer the best combination of translucency and beauty for veneers and single crowns.
- If your primary focus is posterior strength and durability: Polycrystalline ceramics like zirconia provide the highest fracture resistance for crowns and bridges under heavy load.
- If your primary focus is a balance of shock absorption and opposing tooth preservation: Resin-based ceramics are a viable option for inlays, onlays, and single crowns, especially in patients who grind their teeth.
Understanding these fundamental material classes empowers you to make a more informed decision that ensures both the beauty and longevity of every restoration.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Primary Composition | Key Strength | Key Limitation | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicate Ceramics | Glassy Matrix | Superior Aesthetics/Translucency | Lower Fracture Resistance | Veneers, Anterior Crowns, Inlays/Onlays |
| Polycrystalline Ceramics | Dense Crystals (e.g., Zirconia) | Exceptional Strength/Durability | Historically Less Translucent | Posterior Crowns, Bridges, Implant Abutments |
| Resin-Based Ceramics | Resin Matrix + Ceramic Filler | Shock Absorption, Less Brittle | Lower Wear Resistance | Single Crowns, Inlays/Onlays (select cases) |
Achieve Precision in Every Restoration with KINTEK
Just as selecting the right dental ceramic is critical for a successful restoration, having the right high-temperature furnace is essential for perfecting materials like zirconia.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides dental labs with advanced furnace solutions for precise sintering and heat treatment. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your lab's unique workflow requirements.
Ready to enhance your ceramic fabrication process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our reliable, high-performance furnaces can bring consistency and excellence to your dental restorations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- What aspects of a dental restoration are directly impacted by the choice of a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Fit, Strength & Longevity
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- What is the importance of dental furnaces in dentistry? Ensure Strong, Precise Dental Restorations
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns

