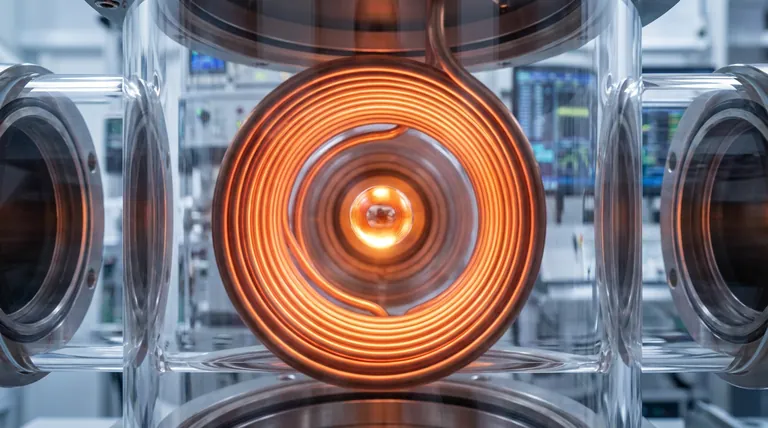
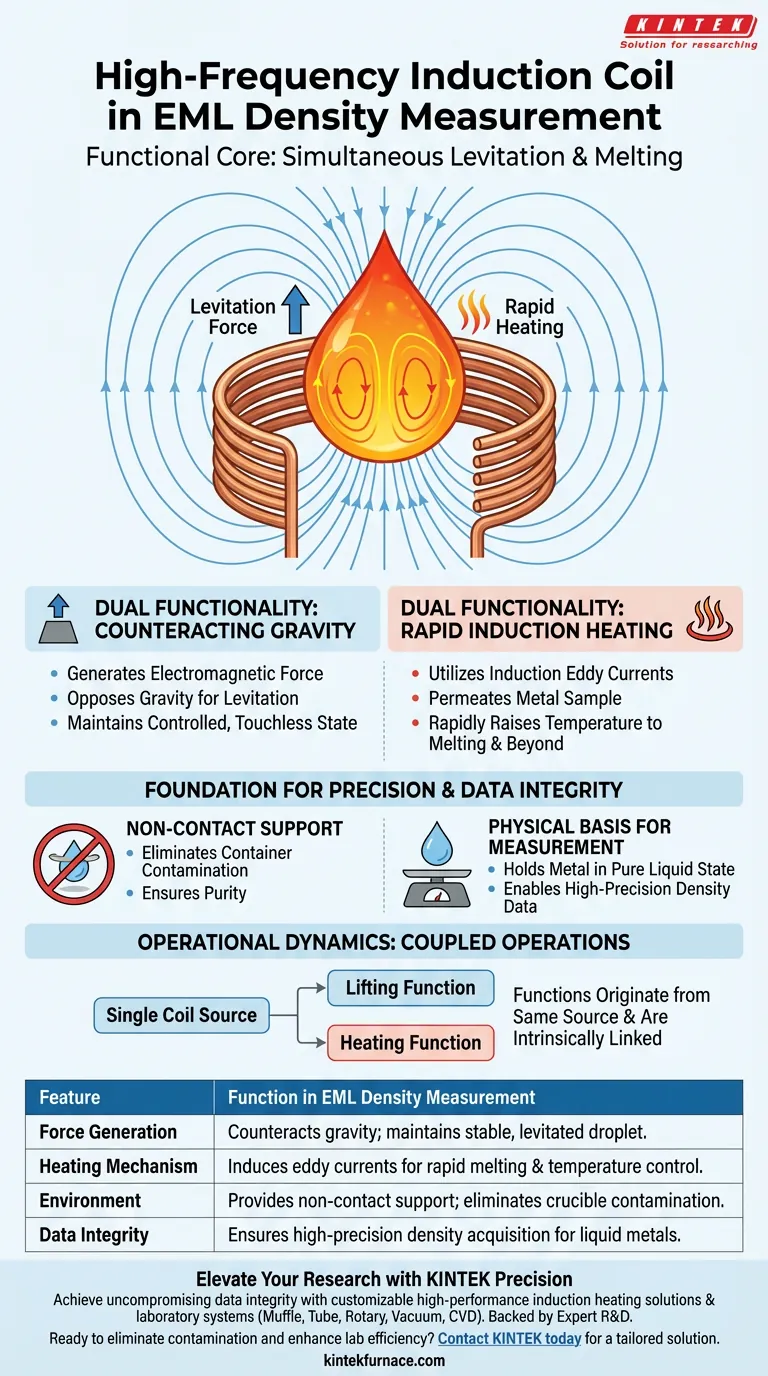
The high-frequency induction coil is the functional core of the Electromagnetic Levitation (EML) system. It simultaneously generates the electromagnetic force required to counteract gravity, maintaining the metal droplet in a suspended state, while inducing the eddy currents necessary to melt the sample.
By combining non-contact support with efficient heating, the induction coil establishes the stable, contamination-free environment required to acquire high-precision density data for liquid metals.

The Dual Functionality of the Coil
The efficacy of EML in density measurement relies on the coil performing two distinct physical tasks at the same time.
Counteracting Gravity
The first critical function of the coil is the generation of electromagnetic force.
This force is directed to oppose gravity, lifting the metal sample.
This allows the droplet to be maintained in a controlled, levitated state without touching any surfaces.
Rapid Induction Heating
The second function is serving as an efficient heat source.
The coil utilizes induction eddy currents to permeate the metal sample.
This mechanism rapidly raises the temperature of the sample to its melting point and beyond, ensuring a complete transition to the liquid phase.
The Foundation for Precision
The interaction between the coil and the sample is not just about suspension; it is about data integrity.
Non-Contact Support
The coil provides a method of support that is entirely non-contact.
This eliminates the need for a crucible or container, which is often a source of contamination or reaction.
Physical Basis for Measurement
By holding the metal in a pure liquid state, the coil provides the physical foundation for measurement.
This stable state allows for the acquisition of high-precision density data that would be difficult to obtain using traditional contact methods.
Understanding the Operational Dynamics
While the coil is highly efficient, understanding the relationship between its two functions is vital.
Coupled Operations
The coil is a single component responsible for two outcomes: lifting and heating.
Because these functions originate from the same source, the generation of lift and the generation of heat are intrinsically linked in this process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage EML for density measurement effectively, you must understand how the coil supports your specific research objectives.
- If your primary focus is sample purity: The coil's non-contact support ensures that your density data is not compromised by container contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature analysis: The coil's use of eddy currents allows you to rapidly reach and exceed the melting point of the metal.
The high-frequency induction coil effectively transforms a single piece of hardware into a comprehensive solution for positioning and processing liquid metals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in EML Density Measurement |
|---|---|
| Force Generation | Counteracts gravity to maintain a stable, levitated droplet. |
| Heating Mechanism | Induces eddy currents for rapid melting and temperature control. |
| Environment | Provides non-contact support to eliminate crucible contamination. |
| Data Integrity | Ensures high-precision density acquisition for liquid metals. |
Elevate Your Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieve uncompromising data integrity in your high-temperature experiments. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance induction heating solutions and laboratory systems—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable to your unique density measurement needs.
Ready to eliminate contamination and enhance lab efficiency? Contact KINTEK today for a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Eleftheria Ntonti, Manabu Watanabe. Reference Correlations for the Density and Thermal Conductivity, and Review of the Viscosity Measurements, of Liquid Titanium, Zirconium, Hafnium, Vanadium, Niobium, Tantalum, Chromium, Molybdenum, and Tungsten. DOI: 10.1007/s10765-023-03305-z
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- High Performance Vacuum Bellows for Efficient Connection and Stable Vacuum in Systems
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a double-layer water-cooled stainless steel chamber used in equipment for preparing ultrafine magnesium powder via the evaporation-condensation method?
- What is the core function of a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Master High-Manganese Steel Preparation
- What components make up a Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace? Discover the Key Systems for Pure Metal Melting
- How do IGBT induction melting furnaces improve precision in material production? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the advantages of using induction melting furnaces? Boost Efficiency, Quality, and Safety
- Why is repeated flipping and remelting necessary when producing Sm-Co-Fe alloy ingots in an arc furnace? Key Insights
- What are the productivity benefits of induction melting furnaces? Transform Your Metal Production Workflow
- Why is a vacuum electric arc furnace essential for Ti-Al alloys? Achieve Superior Metal Purity & Homogeneity



















