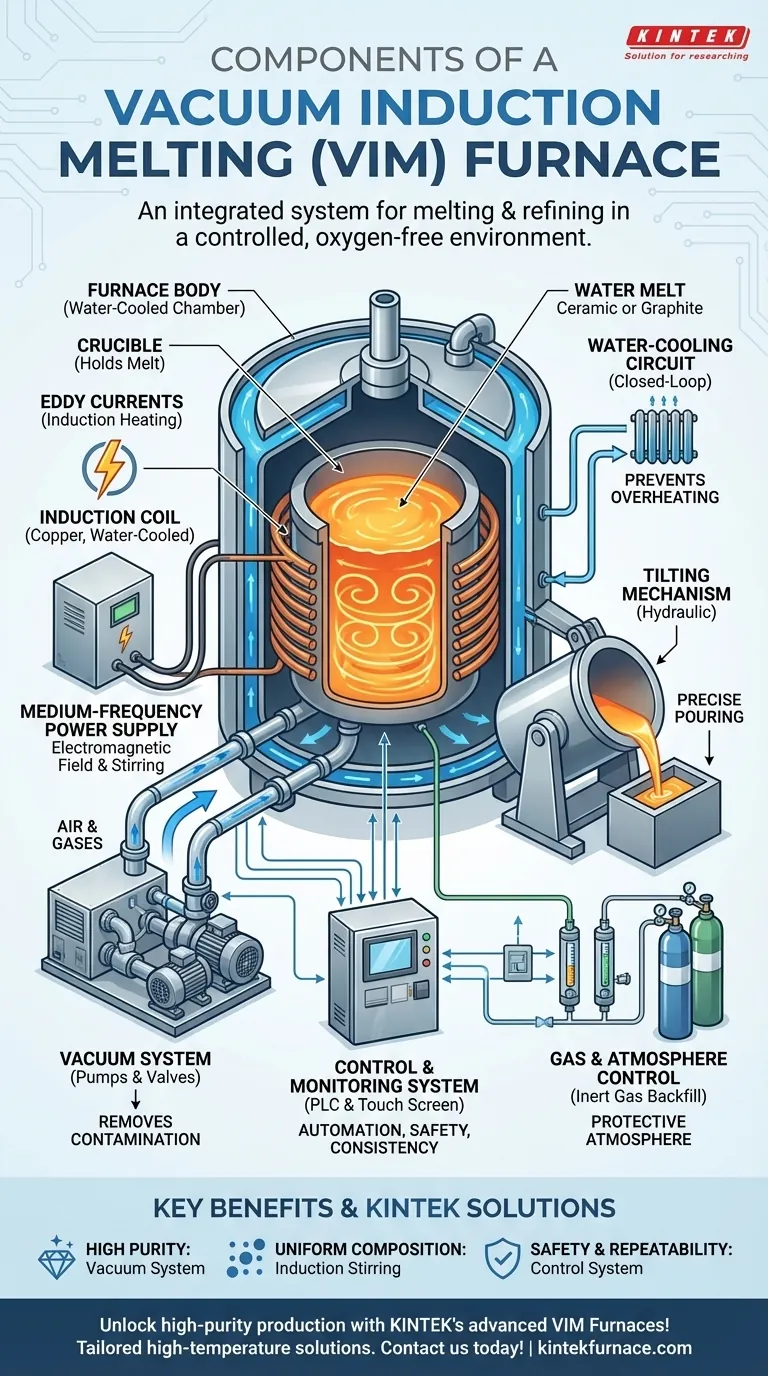
At its core, a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is an integrated system designed for a single purpose: melting and refining metals in a highly controlled, oxygen-free environment. Its primary components are the furnace body which houses the melt, a vacuum system to create the controlled atmosphere, an induction coil and power supply for heating, and a control system to manage the entire process.
A VIM furnace is best understood not as a collection of parts, but as two primary systems working in unison: an induction heating system to melt the metal and a vacuum system to protect it from contamination, ensuring maximum purity and quality.

The Core Systems: Melting and Environment Control
A VIM furnace's effectiveness comes from its ability to precisely manage both the thermal energy and the atmospheric conditions of the melt. This is achieved through several interconnected systems.
The Furnace Body and Crucible
The furnace body is the main steel chamber, often double-walled and water-cooled, that contains the entire melting process. It is built to withstand both extreme internal temperatures and the high vacuum pressure.
Inside the body sits the crucible, a ceramic or graphite vessel that directly holds the metal charge. The crucible material is chosen based on its ability to resist the high temperatures and avoid reacting with the specific metal being melted.
The Induction Heating System
This is the engine of the furnace. It consists of two key parts: a medium-frequency power supply and the inductor.
The power supply converts standard utility power into high-current, medium-frequency electricity. This power is then sent to the inductor, a water-cooled copper coil that wraps around the crucible without touching it.
When energized, the inductor generates a powerful, alternating magnetic field. This field penetrates the metal inside the crucible, inducing strong electrical "eddy currents" that generate intense heat and melt the charge. A key benefit of this process is that the magnetic field also creates a natural stirring action, ensuring the molten metal is homogenous.
The Vacuum System
The vacuum system is what differentiates a VIM furnace from a standard induction furnace. It is responsible for removing air—specifically oxygen and nitrogen—from the furnace chamber before and during melting.
This system is comprised of a series of pumps and valves that work to create and maintain a high-vacuum environment. By eliminating atmospheric gases, it prevents the molten metal from oxidizing and removes dissolved gases like hydrogen, resulting in exceptionally clean, high-purity alloys.
The Mechanical Systems
To pour the molten metal, the furnace utilizes a tilting mechanism. This system, often hydraulic, allows the entire furnace body to be precisely tilted, pouring the refined metal into a mold or ladle without breaking the vacuum seal.
Ancillary Systems and Operational Considerations
Beyond the core components, several support and safety systems are critical for reliable and safe operation. These systems are not optional extras; they are integral to the furnace's function.
The Water-Cooling Circuit
Induction heating generates immense heat, not just in the metal but also in the copper coils and furnace chamber. A closed-loop water-cooling system continuously circulates water through the inductor coil and the walls of the furnace body.
This system is essential for preventing the components from overheating and failing, ensuring the furnace can operate reliably for extended periods.
Gas and Atmosphere Control
While the primary function is to operate under a vacuum, some processes require backfilling the chamber with a specific gas. An integrated gas flow control system allows for the precise introduction of inert gases like argon.
This provides an alternative protective atmosphere for specific alloys or can be used to control pressure during certain stages of the melting process.
The Control and Monitoring System
The entire operation is managed by an electrical control system, typically run by a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) and operated via a touch screen interface.
This system allows operators to precisely regulate power levels, monitor temperature and pressure with sensors, and automate the melting cycle. It is the brain of the furnace, ensuring process repeatability and consistent quality. It also manages critical safety interlocks, such as overpressure and short-circuit protection.
How Each Component Contributes to the Final Product
Understanding the components is key to leveraging the furnace to achieve specific metallurgical goals.
- If your primary focus is achieving high purity and low gas content: The Vacuum System is your most critical component, as it is directly responsible for removing contaminants.
- If your primary focus is ensuring precise composition and homogeneity: The Induction Heating System is key, as its electromagnetic stirring action guarantees a uniform mix of alloying elements.
- If your primary focus is maximizing safety and repeatability: The Control and Monitoring System is paramount, as it automates the process and enforces safety limits.
Ultimately, the power of a VIM furnace lies in the precise integration of these components to create a superior metallurgical tool.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Body & Crucible | Houses and contains the metal melt | Double-walled, water-cooled; ceramic/graphite crucible |
| Induction Heating System | Melts metal via electromagnetic induction | Medium-frequency power supply; inductor coil with stirring |
| Vacuum System | Creates oxygen-free environment | Pumps and valves for high vacuum; removes contaminants |
| Tilting Mechanism | Pours molten metal | Hydraulic system; maintains vacuum seal |
| Water-Cooling Circuit | Prevents overheating | Circulates water through coils and body |
| Control & Monitoring System | Manages and automates operations | PLC-based with sensors; ensures safety and repeatability |
Unlock high-purity metal production with KINTEK's advanced Vacuum Induction Melting Furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our VIM furnaces can enhance your metallurgical processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















