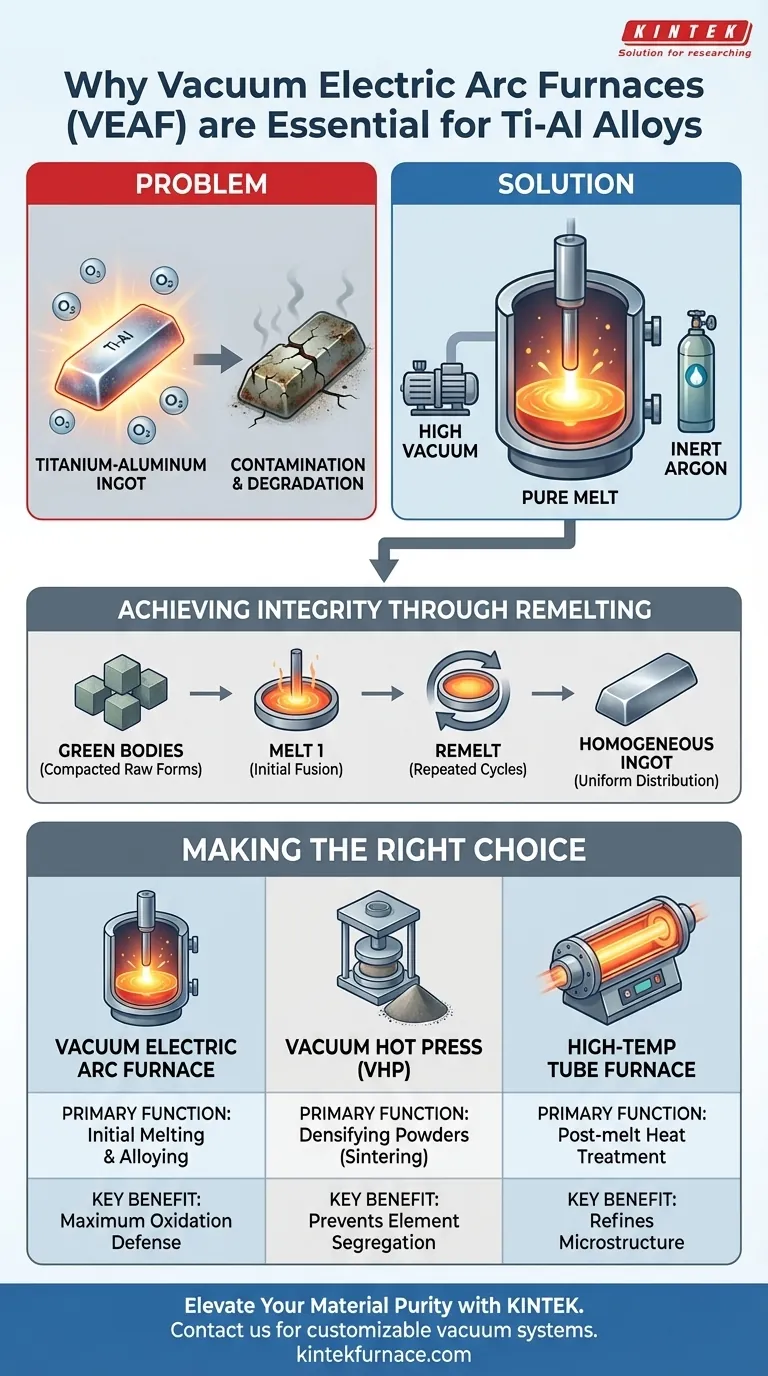
A vacuum electric arc furnace acts as the primary defense against oxidation for reactive metals. For titanium-aluminum (Ti-Al) alloys specifically, this equipment is essential because it provides the strictly controlled environment necessary to melt and remelt material without compromising its chemical integrity. Because these metals possess an extreme affinity for oxygen, the furnace’s combination of a vacuum and protective argon atmosphere is the only way to process them effectively.
Core Takeaway Titanium-aluminum alloys react aggressively with oxygen at high temperatures, which can permanently ruin their mechanical properties. The vacuum electric arc furnace solves this by isolating the melt in an inert environment, enabling the high-temperature processing and repeated remelting cycles required to achieve chemical homogeneity.

The Chemistry of Contamination
The Oxygen Affinity Problem
Titanium and its aluminides are highly reactive materials. They possess a very high affinity for oxygen, meaning they will absorb it instantly if exposed to air during heating.
The Consequence of Exposure
If this oxidation occurs, the alloy suffers from contamination that degrades its final properties. Standard open-air furnaces are effectively useless for these materials because they cannot prevent this chemical degradation.
The Protective Shield
The vacuum electric arc furnace counters this by creating a specialized atmosphere. By utilizing a high vacuum or a protective argon gas environment, it completely isolates the metal from oxygen, ensuring the material remains pure during the transition from solid to liquid.
Achieving Structural Integrity
Processing "Green Bodies"
The furnace creates the extreme high temperatures required to thoroughly melt "green bodies." These are the compacted, raw forms of the metal that must be fused into a solid, cohesive alloy.
Homogenization Through Remelting
Melting the material once is rarely sufficient for advanced alloys. The vacuum arc process is designed to facilitate remelting. This repetition is critical for ensuring high chemical homogeneity, ensuring the elements are evenly distributed throughout the ingot.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Segregation
While the vacuum electric arc furnace is essential for melting, it is not without challenges. Compared to sintering methods like Vacuum Hot Pressing (VHP), electric arc melting can sometimes result in element segregation or compositional non-uniformity if not managed correctly.
The Mitigation Strategy
To counter segregation, the remelting process mentioned in the primary methodology becomes vital. Operators must often melt the alloy multiple times to mix the elements thoroughly and eliminate the macroscopic defects that can occur in a single-pass melt.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The vacuum electric arc furnace is a specific tool for a specific phase of material production. Depending on your current stage of development, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is creating bulk alloys from raw materials: You must use a Vacuum Electric Arc Furnace to handle the initial melting and remelting while preventing oxidation.
- If your primary focus is densifying powders below the melting point: Consider a Vacuum Hot Press (VHP), which applies pressure to prevent the segregation issues sometimes seen in arc melting.
- If your primary focus is post-melt heat treatment: Utilize a High-Temperature Tube Furnace to relieve casting stresses and refine the microstructure without melting the material.
Mastering the atmosphere is the only way to master the alloy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Electric Arc Furnace | Vacuum Hot Press (VHP) | High-Temp Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Initial melting & alloying | Densifying powders (Sintering) | Post-melt heat treatment |
| Atmosphere Control | High Vacuum / Argon Shield | Vacuum / Controlled Atmosphere | Vacuum / Inert Gas |
| Material State | Fully Molten (Liquid) | Solid State (Below melting point) | Solid State |
| Key Benefit | Maximum oxidation defense | Prevents element segregation | Refines microstructure |
| Best For | Bulk alloy production | Precision powder densification | Stress relief & annealing |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK
Don't let oxidation compromise your Ti-Al alloys. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing. Whether you require Vacuum Electric Arc systems, Vacuum Hot Pressing, or customizable Tube and Muffle furnaces, our technology is designed to meet your strictest metallurgical standards.
Ready to optimize your alloying process? Contact us today to discuss how our customizable vacuum systems can ensure the chemical integrity and homogeneity of your advanced materials.
Visual Guide
References
- Steven Magogodi, A.S. Bolokang. The effect of hot corrosion on mechanical properties of the tin-doped titanium aluminide alloy. DOI: 10.1007/s00170-024-14935-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace in superalloys? Secure Purity and Chemical Precision
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- Why is induction heating faster than traditional methods? Achieve Instantaneous, Internal Heat Generation
- Importance of Induction Heating System and Coil Design in ODS Steel Bonding: Optimize Your Thermal Profile
- Why are crucible furnaces important in industrial applications? Versatile, Cost-Effective Melting Solutions
- What advantages does an electron beam melting furnace offer? Superior Purification for Zirconium Refining
- Why is the melting process for AlCoCrFeNi HEAs repeated 3 times? Achieving Pure Chemical Homogeneity
- What industries commonly use induction melting furnaces? Achieve High-Purity Metal Melting



















