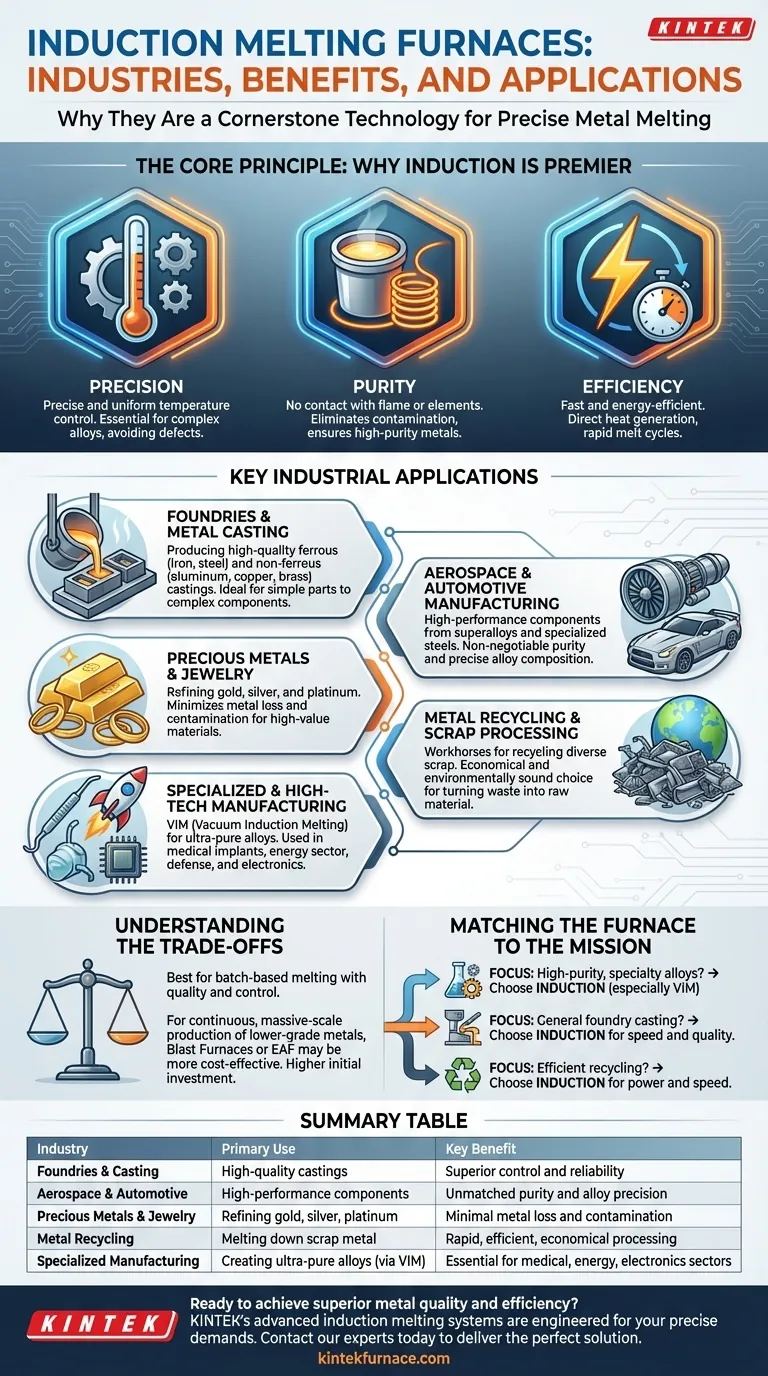
In short, induction melting furnaces are a cornerstone technology in nearly every industry that requires the precise melting of metals. Their use is widespread in metal foundries, aerospace and automotive manufacturing, precious metal refining for jewelry, and large-scale metal recycling operations due to their unparalleled control, speed, and efficiency.
The core reason for their broad adoption is not just that they melt metal, but how they melt it. Induction furnaces offer superior control over temperature and chemistry, resulting in higher-purity, higher-quality metal essential for high-performance and high-value applications.
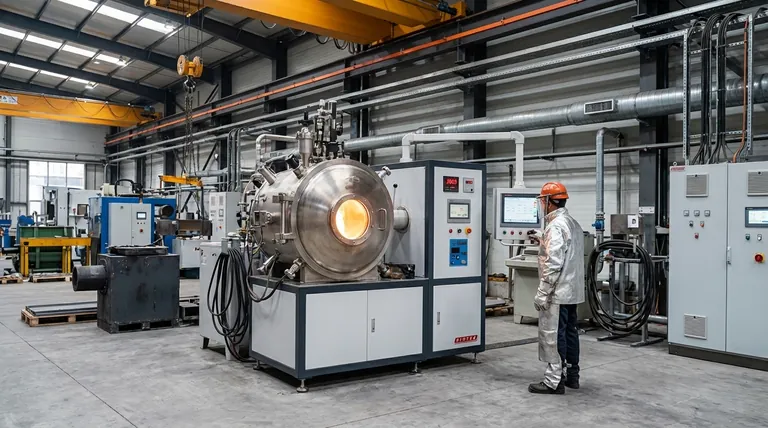

The Core Principle: Why Induction is a Premier Melting Technology
Before listing the industries, it's crucial to understand why this technology is so valued. Unlike traditional fuel-fired furnaces, an induction furnace uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal itself. This fundamental difference provides three key advantages.
The Advantage of Precision
The electromagnetic process allows for extremely precise and uniform temperature control. This is critical when working with complex alloys where small temperature deviations can ruin the entire batch, leading to defects and material failure.
The Advantage of Purity
Because the heat is generated within the metal, there is no contact with a flame or heating element. This eliminates contamination from combustion byproducts, ensuring the production of very high-purity metals and alloys.
The Advantage of Efficiency
Induction melting is exceptionally fast and energy-efficient. Heat is generated instantly and directly where it's needed, minimizing thermal loss to the surrounding environment and enabling rapid melt cycles that boost productivity.
Key Industrial Applications: From Raw Metal to Advanced Components
These advantages make induction furnaces the preferred choice across a spectrum of industries, each leveraging a specific benefit of the technology.
Foundries and Metal Casting
This is the most fundamental application. Both ferrous foundries (iron and steel) and non-ferrous foundries (aluminum, copper, brass) rely on induction furnaces for producing high-quality castings. Their reliability and control make them ideal for creating everything from simple parts to complex industrial components.
Aerospace and Automotive Manufacturing
These high-stakes industries demand materials that perform flawlessly under extreme stress. Induction furnaces are used to produce high-performance engine components, turbine blades, and other critical parts from superalloys and specialized steels. The purity and precise alloy composition achieved are non-negotiable.
Precious Metals and Jewelry
When melting gold, silver, and platinum, minimizing metal loss and ensuring absolute purity is paramount. The clean, contained melting process of an induction furnace is perfectly suited for these high-value materials, preventing losses and contamination.
Metal Recycling and Scrap Processing
Induction furnaces are workhorses in the recycling industry. Their ability to rapidly and efficiently melt down a wide variety of scrap metal—from shredded cars to aluminum cans—makes them an economically and environmentally sound choice for turning waste back into valuable raw material.
Specialized and High-Tech Manufacturing
In advanced sectors, specialized versions of this technology are used. Vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnaces operate in a vacuum to produce the ultra-pure alloys required for:
- Medical industry: Creating surgical instruments and biocompatible implants.
- Energy sector: Forging components for power generation equipment.
- Defense and Electronics: Producing superalloys for rockets, missiles, and sensitive electronic parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite their numerous benefits, induction furnaces are not a universal solution. Their primary strength lies in batch-based melting where quality and control are the main drivers.
For the continuous, massive-scale production of lower-grade metals like basic construction steel, a blast furnace or an electric arc furnace (EAF) is often more cost-effective. The initial capital investment for a large induction furnace system can also be higher than for some traditional alternatives. The choice depends entirely on the required scale, speed, and final metal quality.
Matching the Furnace to the Mission
Your choice of melting technology is dictated by your final goal. An induction furnace is an investment in quality and precision.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or specialty alloys: An induction furnace, particularly a vacuum model, is the industry standard for aerospace, medical, and electronics.
- If your primary focus is general foundry casting: An induction furnace provides the speed, flexibility, and quality control needed for competitive ferrous and non-ferrous casting.
- If your primary focus is efficient recycling: An induction furnace offers the power and speed to profitably convert diverse metal scrap into reusable material.
Ultimately, the induction furnace is a tool that empowers industries to transform raw or recycled metal into highly engineered, high-value products with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Foundries & Metal Casting | Producing high-quality castings | Superior control and reliability |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Manufacturing high-performance components | Unmatched purity and alloy precision |
| Precious Metals & Jewelry | Refining gold, silver, platinum | Minimal metal loss and contamination |
| Metal Recycling | Melting down scrap metal | Rapid, efficient, and economical processing |
| Specialized Manufacturing | Creating ultra-pure alloys (via VIM) | Essential for medical, energy, and electronics sectors |
Ready to achieve superior metal quality and efficiency?
KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including our robust induction melting systems, are engineered to meet the precise demands of your industry. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide the control and purity you need for high-performance applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can deliver the perfect melting solution for your unique requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















