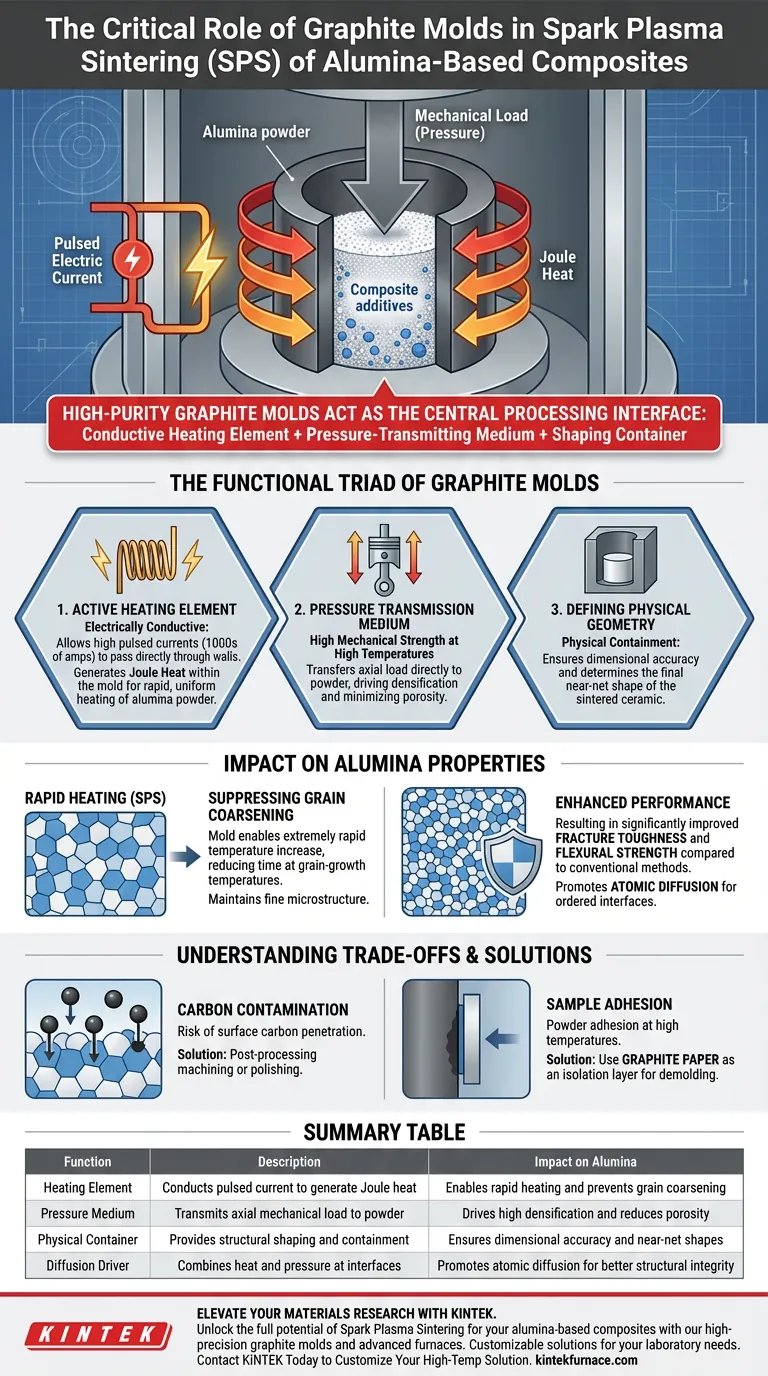
High-purity graphite molds act as the central processing interface in Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), simultaneously serving as the conductive heating element, the pressure-transmitting medium, and the shaping container. By converting pulsed electric current directly into Joule heat while applying mechanical load, these molds enable the rapid thermal and mechanical coupling necessary to sinter alumina-based composites.
Core Takeaway The unique advantage of graphite molds in SPS is their ability to facilitate extremely rapid heating rates. This fast thermo-mechanical processing suppresses grain coarsening in alumina ceramics, which is directly responsible for significantly enhanced fracture toughness and flexural strength compared to conventional sintering methods.
The Functional Triad of Graphite Molds
Acting as an Active Heating Element
Unlike conventional furnaces that heat from the outside in, graphite molds are electrically conductive.
They allow high pulsed currents (often thousands of amperes) to pass directly through the mold walls. This current generates Joule heat within the mold itself, transferring thermal energy immediately to the alumina powder for highly efficient, uniform heating.
Transmitting Mechanical Pressure
Graphite possesses high mechanical strength even at elevated sintering temperatures.
This allows the mold to act as a pressure transmission medium, transferring axial loads (external pressure) directly to the powder particles. This pressure is essential for driving the densification of the alumina composite and minimizing lattice thermal conductivity.
Defining Physical Geometry
At the most basic level, the mold provides physical containment for the powder.
It ensures the dimensional accuracy of the sample during the high-pressure consolidation process. This shaping capability determines the final near-net shape of the sintered ceramic.
Impact on Alumina Properties
Suppressing Grain Coarsening
The most critical role of the graphite mold in this context is enabling rapid temperature increases.
Because the mold heats so quickly, the alumina spends less time at critical grain-growth temperatures. This suppresses the "coarsening" (enlarging) of grains, maintaining a fine microstructure that is superior to materials processed slowly.
Enhancing Mechanical Performance
The preservation of a fine grain structure has a direct correlation to mechanical limits.
By preventing grain growth, the process significantly boosts the fracture toughness and flexural strength of the final alumina ceramic. The mold’s ability to facilitate fast sintering is the primary driver of these improved mechanical characteristics.
Promoting Atomic Diffusion
The combination of direct heat and pressure creates an environment conducive to atomic diffusion.
This leads to the formation of ordered interfaces with semi-coherent characteristics between the composite materials. These interfaces are vital for structural integrity and optimizing thermal properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Carbon Diffusion and Contamination
Graphite molds are carbon-based, creating a risk of carbon atoms penetrating the surface of the alumina composite.
This can alter the mechanical properties of the exterior. It is standard practice to machine or polish away the surface layer of the sintered sample to remove this contamination before performance testing.
Sample Adhesion
At high temperatures and pressures, ceramic powders can adhere or react with the mold walls.
To prevent this, graphite paper is often used as an isolation layer between the mold and the powder. This liner ensures the sample can be demolded without damage and maintains a uniform current distribution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of graphite molds in your SPS process, consider your specific material objectives:
- If your primary focus is High Strength: Prioritize rapid heating rates facilitated by the mold's conductivity to suppress grain growth and maximize flexural strength.
- If your primary focus is Surface Purity: Account for the necessary post-processing removal of the carbon-contaminated surface layer, or utilize coated graphite paper liners.
- If your primary focus is Density: Leverage the mold's high-temperature strength to apply maximum allowable pressure, driving atomic diffusion and closing porosity.
The graphite mold is not just a container; it is the active engine that drives the unique microstructural benefits of the SPS process.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description | Impact on Alumina Composites |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Conducts pulsed current to generate Joule heat | Enables rapid heating and prevents grain coarsening |
| Pressure Medium | Transmits axial mechanical load to powder | Drives high densification and reduces porosity |
| Physical Container | Provides structural shaping and containment | Ensures dimensional accuracy and near-net shapes |
| Diffusion Driver | Combines heat and pressure at interfaces | Promotes atomic diffusion for better structural integrity |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of Spark Plasma Sintering for your alumina-based composites. KINTEK provides high-precision graphite molds and advanced high-temperature furnace systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern material science.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are looking to suppress grain coarsening or maximize fracture toughness, our technical team is ready to assist you.
Contact KINTEK Today to Customize Your High-Temp Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Yufei Sun, Dairong Chen. Recent Advancements in Alumina-Based High-Temperature Insulating Materials: Properties, Applications, and Future Perspectives. DOI: 10.70322/htm.2025.10001
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does the choice of high-purity ceramic crucibles impact glass phantoms? Unlock Optical Precision in Sintering
- How do a brass cap and a cooling element work together? Ensuring Reliable High-Temperature Experimental Seals
- What is the primary role of laboratory furnaces in manufacturing and scientific processes? Unlock Precision Thermal Control
- What is the function of an in-situ heating holder in the study of Peierls transitions in NaRu2O4? Dynamic Lab Insights
- What is the purpose of using a high-purity argon system for AlCoCrFeNi melting? Preserve Alloy Stoichiometry
- What are the primary functions of the vacuum pump system and inert gases? Achieve High-Purity Atomization
- Why are evaporators and condensers required for zirconium tetrachloride purification? Mastering Nuclear-Grade Standards
- Why are vacuum filtration devices and specific cellulose filter papers used in hydrothermal synthesis recovery?



















