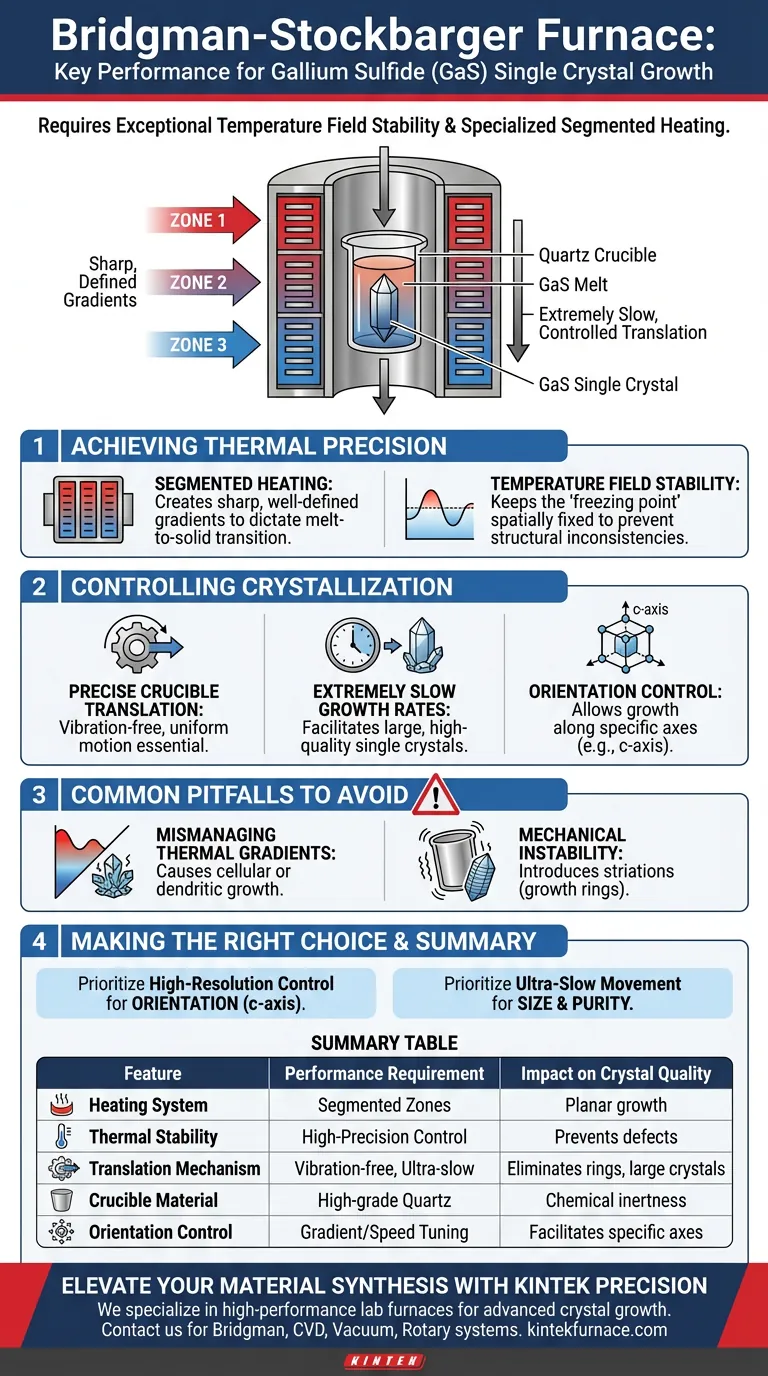
To successfully synthesize Gallium Sulfide (GaS) single crystals, a Bridgman-Stockbarger growth furnace requires exceptional temperature field stability and a specialized segmented heating system. This configuration is essential to create precise temperature gradients while allowing the quartz crucible to move through the crystallization zone at a controlled, extremely slow rate.
The success of GaS crystal growth relies on the furnace's ability to decouple temperature generation from the crystallization position. By utilizing segmented heating and precise crucible translation, the system ensures the slow solidification rates necessary for obtaining large, high-quality crystals with specific c-axis orientations.
Achieving Thermal Precision
The Role of Segmented Heating
Standard heating elements are insufficient for this specific synthesis. The furnace must employ a segmented heating configuration.
This design divides the furnace into distinct zones, allowing for the creation of sharp, well-defined temperature gradients. These gradients are the driving force that dictates exactly where and when the material transitions from melt to solid.
Temperature Field Stability
Beyond creating gradients, the furnace must maintain exceptional field stability.
Fluctuations in the thermal environment can interrupt the crystal lattice formation. A stable field ensures that the "freezing point" remains spatially fixed relative to the heaters, preventing structural inconsistencies in the final crystal.
Controlling the Crystallization Mechanism
Precise Crucible Translation
In a Bridgman-Stockbarger setup for GaS, the thermal profile is generally static while the sample moves.
The furnace must support the physical movement of the quartz crucible through the established thermal zones. The mechanical system responsible for this translation must be vibration-free and capable of uniform motion to prevent physical disturbances to the melt.
Extremely Slow Growth Rates
The speed of the crucible's movement directly correlates to the quality of the crystal.
The system must be capable of extremely slow translation rates. Rapid movement entraps impurities and creates stress; a slow, controlled pace allows the Gallium Sulfide molecules to arrange themselves perfectly, facilitating the growth of large, high-quality single crystals.
Orientation Control
The combination of specific gradients and slow movement is required to control the crystal's physical orientation.
Properly tuning these parameters allows for growth along specific crystallographic directions, such as the c-axis. This directional control is critical for applications requiring specific anisotropic properties.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mismanaging Thermal Gradients
If the temperature gradient between segments is too shallow, the crystallization interface becomes unstable.
This often leads to "constitutional supercooling," resulting in cellular or dendritic growth rather than a single, unified crystal. The gradient must be steep enough to force planar growth.
Mechanical Instability
Even minor vibrations in the crucible translation mechanism can ruin the batch.
If the movement is jerky or uneven, it introduces striations (growth rings) into the GaS crystal. The mechanical drive system requires the same level of precision as the thermal control system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting or configuring a Bridgman-Stockbarger furnace for Gallium Sulfide, prioritize features based on your specific output requirements:
- If your primary focus is Crystal Orientation (e.g., c-axis): Prioritize a furnace with high-resolution segmented control to shape the thermal gradient precisely.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Size and Purity: Prioritize a translation mechanism capable of ultra-slow, vibration-free movement to minimize internal stress and defects.
Ultimately, the quality of your Gallium Sulfide crystal is defined by the furnace's ability to maintain absolute thermal and mechanical stability over long growth periods.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Performance Requirement | Impact on Crystal Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Heating System | Segmented Heating Zones | Enables sharp, well-defined temperature gradients for planar growth. |
| Thermal Stability | High-Precision Field Control | Prevents lattice defects by keeping the crystallization zone spatially fixed. |
| Translation Mechanism | Vibration-free, Ultra-slow Movement | Eliminates growth rings and ensures large, high-purity single crystals. |
| Crucible Material | High-grade Quartz | Provides chemical inertness and structural integrity during translation. |
| Orientation Control | Gradient/Speed Tuning | Facilitates growth along specific axes (e.g., c-axis) for anisotropic needs. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving perfect Gallium Sulfide crystals requires more than just heat—it requires absolute thermal and mechanical control. At KINTEK, we specialize in the R&D and manufacturing of high-performance lab furnaces tailored for advanced crystal growth.
Whether you need customized Bridgman systems, CVD, Vacuum, or Rotary furnaces, our expert team delivers the stability and precision necessary for your most demanding research applications.
Ready to refine your crystallization process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique project requirements and discover how our customizable high-temperature solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
References
- Danil Bukhvalov, Antonio Politano. Self‐Assembled Gallium Sulfide (GaS) Heterostructures Enabling Efficient Water Splitting and Selective Ammonia Sensing. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202507388
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
People Also Ask
- What conditions does a laboratory tube furnace provide for PtS/Ti3C2Tx preparation? Master 300°C Thermal Decomposition
- How does a multi-tube pyrolysis furnace achieve precise temperature control? Advanced Hardware & PID Logic Explained
- What is a laboratory tube furnace and how is it designed? Master Precise Heating for Your Lab
- What is the Purpose of Carbon Coating Quartz Tubes? Enhance Crystal Growth via Bridgman Method
- What advanced materials research applications involve tube furnaces? Unlock Precision for Next-Gen Materials
- Why is a tube furnace with multiple zones required for MoSe2 selenization? Achieve Precision Gradient Control
- How does a tube furnace differ from a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What are the unique features of a multi station vacuum tube furnace regarding atmosphere control? Unlock High-Purity Parallel Experiments



















