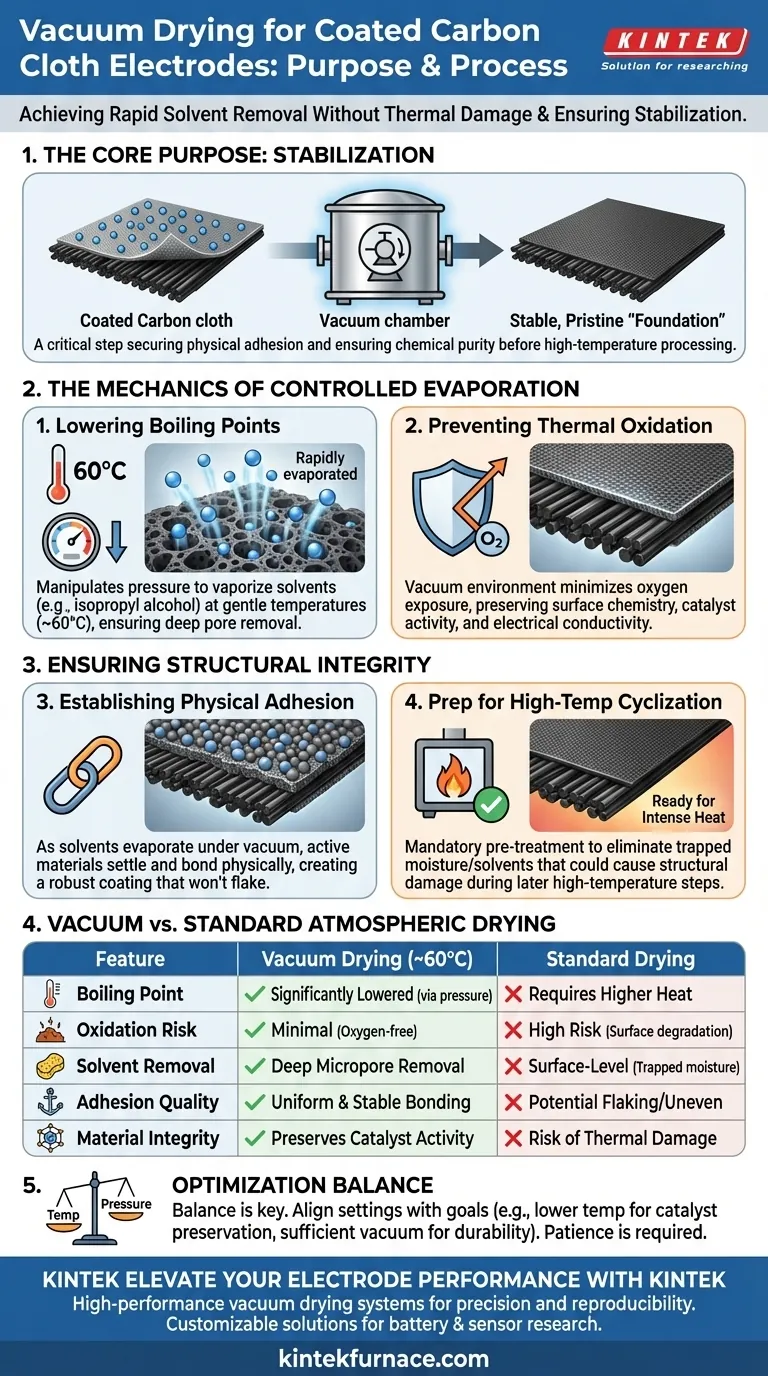
The primary purpose of using a vacuum drying oven for coated carbon cloth is to achieve rapid solvent removal without thermal damage. By operating at reduced ambient pressure and lower temperatures (typically around 60 °C), the oven accelerates the evaporation of solvents like isopropyl alcohol and moisture while preventing the severe oxidation that occurs at higher temperatures.
Core Takeaway The vacuum drying process acts as a critical stabilization step between wet coating and high-temperature processing. It secures the physical adhesion of the catalyst to the carbon fibers and ensures the material is chemically pristine before undergoing subsequent cyclization.

The Mechanics of Controlled Evaporation
Lowering the Boiling Point
The fundamental advantage of this process is the manipulation of pressure to lower boiling points.
By reducing the internal pressure, volatile components like isopropyl alcohol and water vaporize at significantly lower temperatures than they would at standard atmospheric pressure.
This allows for a thorough drying process at a gentle 60 °C, ensuring deep removal of solvents from the porous structure of the carbon cloth.
Preventing Thermal Oxidation
Heat is necessary for drying, but excessive heat in the presence of air degrades carbon materials and catalysts.
Standard drying methods often risk thermal oxidation, which alters the surface chemistry of the active materials and reduces conductivity.
The vacuum environment minimizes oxygen exposure, allowing the coating to set and dry without compromising the chemical integrity of the substrate or the catalyst.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
Establishing Physical Adhesion
The drying phase is not just about removing liquid; it is about structural stabilization.
As the solvent evaporates under controlled vacuum conditions, the active materials settle and bond physically to the carbon cloth fibers.
This creates a robust, uniform coating that will not flake or detach during later handling.
Preparation for High-Temperature Cyclization
This process serves as a mandatory pre-treatment for the next stage of electrode preparation: high-temperature cyclization.
If residual moisture or solvents remain trapped in the pores, they can cause unpredictable endothermic effects or structural damage when the material is later subjected to intense heat.
Vacuum drying ensures the "foundation" is stable, dry, and pure, enabling reproducible results in the final electrochemical testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Balance of Temperature and Pressure
While vacuum ovens allow for lower temperatures, patience is still required.
Attempting to rush the process by raising the temperature (even under vacuum) risks damaging sensitive organic binders or surface functional groups.
Conversely, setting the pressure too low without adequate temperature control may fail to remove solvents deeply adsorbed in the micropores, leading to side reactions later.
Equipment Dependencies
Success relies heavily on the stability of the vacuum pump and the seal integrity.
Fluctuations in pressure can lead to uneven drying rates across the electrode sheet.
This can result in gradients in the coating thickness or adhesion quality, which will negatively impact battery or sensor performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your electrode preparation, align your oven settings with your specific material constraints.
- If your primary focus is preserving catalyst activity: Prioritize lower temperatures (around 60 °C) and extend the drying time to prevent any thermal degradation of surface groups.
- If your primary focus is structural durability: Ensure the vacuum level is sufficient to remove all deep-pore solvents, as this guarantees better physical adhesion for the subsequent cyclization step.
Ultimately, the vacuum drying oven is not just a drying tool, but a stabilization chamber that defines the structural quality of your final electrode.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Drying (at ~60°C) | Standard Atmospheric Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Point | Significantly lowered via pressure reduction | Requires higher heat for same evaporation rate |
| Oxidation Risk | Minimal due to oxygen-free environment | High risk of surface chemistry degradation |
| Solvent Removal | Deep removal from microporous structures | Surface-level removal; risk of trapped moisture |
| Adhesion Quality | Uniform physical bonding & stabilization | Potential for flaking or uneven coating |
| Material Integrity | Preserves catalyst activity and conductivity | Risk of thermal damage to sensitive binders |
Elevate Your Electrode Performance with KINTEK
Precision matters in carbon cloth processing. KINTEK provides high-performance vacuum drying systems designed to ensure stable physical adhesion and chemical purity for your sensitive substrates. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a full range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces, all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of battery and sensor research.
Ready to optimize your drying process? Contact us today to discover how our high-temperature lab solutions can improve your material consistency and experimental reproducibility.
Visual Guide
References
- Yifan Gu, Yi Feng. A Novel Cyclized Polyacrylonitrile Binder Strategy for Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction Catalysts. DOI: 10.3390/polym17182477
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does temperature control precision affect SC-NMNO crystal morphology? Master Thermal Fields for High-Quality Grains
- What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)? Master Thin Film Coating for Enhanced Materials
- What role does a high-pressure reactor play in the production of hydrochar? Optimize Biomass Carbonization
- How do high-temp furnace processes affect carbon nanofiber micro-morphology? Master Precise Structural Control
- Importance of NaH2PO2 Layout in V-Ni3S2/NF Phosphorization: Ensuring Uniform 3D Doping
- What is the function of rapid quenching after high-temperature heat treatment? Master AlSi10Mg Microstructural Control
- Why is a heating device required when evaluating HEAs? Unlocking High-Temperature Material Performance
- What is a crucible furnace used for? Achieve Pure, Controlled Melts for Non-Ferrous Metals



















