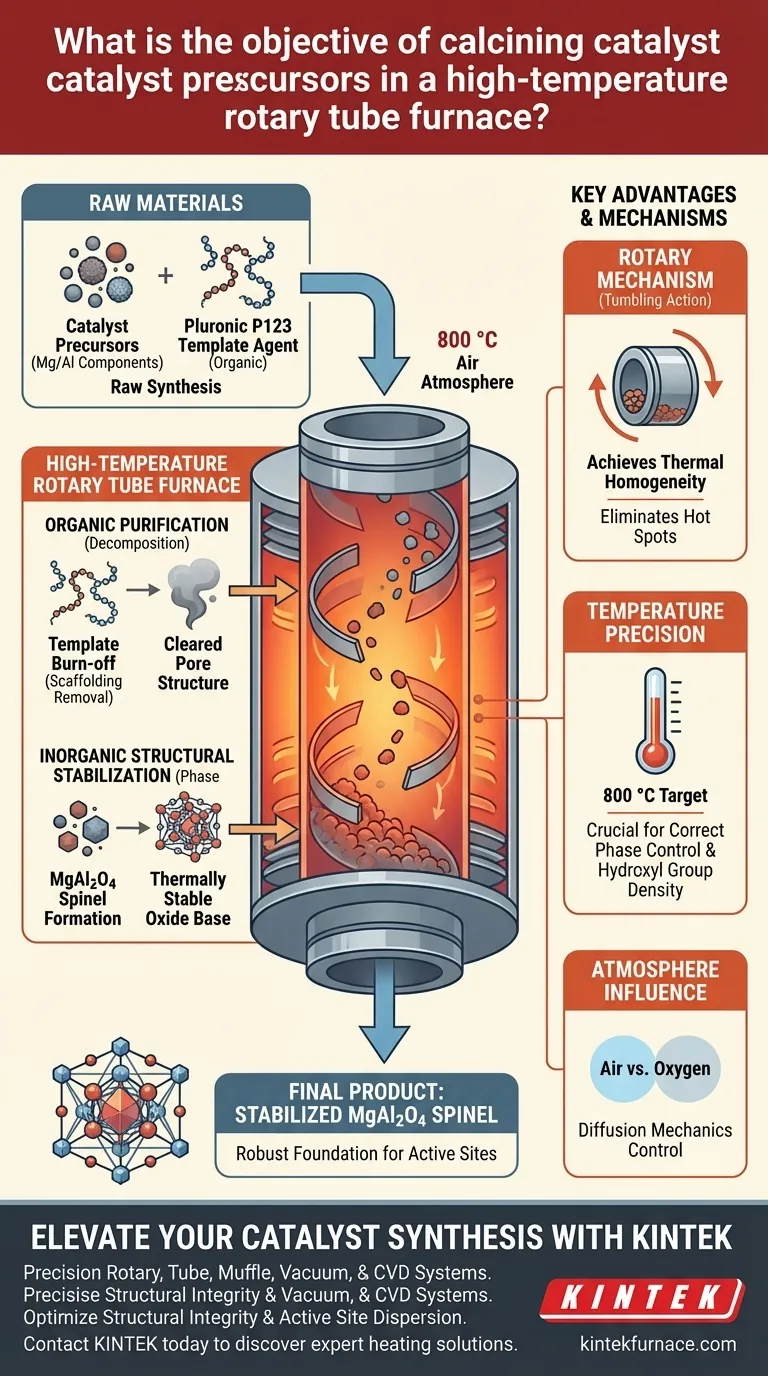
The primary objective of this process is to achieve simultaneous organic purification and inorganic structural stabilization. Specifically, calcining precursors at 800 °C in an air atmosphere serves to thermally decompose the Pluronic P123 template agent and induce a phase transition. This transforms the raw components into a thermally stable magnesium-aluminum spinel (MgAl2O4) mixed oxide, creating a robust foundation for the deposition of active metallic components.
The calcination process acts as a critical bridge between raw synthesis and functional utility, stripping away organic templates to reveal a crystallized, stable spinel structure capable of supporting catalytic activity.

The Chemical Transformation Process
Removal of Template Agents
The initial function of the high-temperature environment is the complete removal of the Pluronic P123 template agent.
Through thermal decomposition at 800 °C, the organic polymer network acts as a sacrificial framework. Once this template is burned off, the internal pore structure of the material is cleared. This is similar to removing scaffolding from a building once the concrete has set, leaving behind the desired architecture.
Inorganic Phase Transition
Beyond simple purification, the heat treatment drives a chemical phase transition within the inorganic components.
The precursors are converted into a magnesium-aluminum spinel (MgAl2O4) mixed oxide base. This specific crystalline phase is chemically and thermally stable. Establishing this stability is vital, as it prevents the catalyst support from degrading under future operating conditions.
Foundation for Active Sites
The formation of the MgAl2O4 spinel provides a necessary structural foundation.
This stabilized oxide base allows for the subsequent uniform precipitation of metallic components. Without this pre-stabilized surface, the active metals applied in later steps would not disperse correctly, leading to uneven catalytic performance.
The Mechanical Advantage of Rotation
Achieving Thermal Homogeneity
While the chemistry dictates the temperature, the rotary mechanism of the tube furnace ensures consistency.
Static furnaces can suffer from "hot spots" and "shadow areas," leading to uneven calcination. The continuous rotation of the tube tumbles the powder, exposing every particle to the heat source evenly. This eliminates thermal gradients and ensures the entire batch achieves the same high-quality spinel structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Precision and Phase Control
It is critical to note that higher temperatures are not always better; they must be precise.
If the temperature deviates significantly from the target (e.g., 800 °C), you risk altering the phase incorrectly or sintering the material too aggressively. As seen in similar alumina processes, specific temperatures determine the density of surface hydroxyl groups, which dictates how well the support can hold active metals later.
Atmosphere Influence
The choice of atmosphere (air vs. oxygen) fundamentally changes diffusion mechanics.
While air is standard for general decomposition, using pure oxygen can inhibit volume diffusion while promoting surface diffusion. This trade-off can lead to smaller particle sizes and better dispersion, but it requires specialized atmosphere control equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your calcination process, align your parameters with your specific catalytic requirements:
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Ensure the temperature is maintained strictly at 800 °C to guarantee the complete formation of the MgAl2O4 spinel phase.
- If your primary focus is active site dispersion: Prioritize the rotary function to ensure every particle is equally exposed, preventing agglomeration that hampers metal precipitation.
The success of your final catalyst depends entirely on the rigorous control of this thermal purification and crystallization stage.
Summary Table:
| Process Objective | Mechanism | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Organic Purification | Thermal decomposition of P123 template | Cleared internal pore structure |
| Structural Stabilization | Phase transition at 800 °C | Formation of stable MgAl2O4 spinel |
| Thermal Homogeneity | Tube rotation and tumbling | Elimination of hot spots and gradients |
| Surface Preparation | Precise temperature/atmosphere control | Optimized foundation for metal deposition |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a failed precursor and a high-performance catalyst. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Rotary, Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for rigorous lab and industrial needs.
Our customizable high-temperature furnaces ensure the thermal homogeneity and atmosphere control required for perfect MgAl2O4 spinel formation and template removal. Don’t settle for uneven calcination—Contact KINTEK today to discover how our expert heating solutions can optimize your material's structural integrity.
Visual Guide
References
- Kyung Hee Oh, Ji Chan Park. Scalable Exsolution‐Derived E‐Ni/m‐MgAlO <sub>x</sub> Catalysts with Anti‐Sintering Stability for Methane Dry Reforming. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202508028
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of rotary tube furnaces in fuel compatibility? Boost Efficiency and Cut Costs
- What types of materials and processes can the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace accommodate? Unlock Versatile Heat Treatment Solutions
- How does a rotary kiln differ from a shuttle kiln in terms of material transport? Compare Continuous vs. Batch Processing
- What is the role of a Rotary Chemical Vapor Deposition (Rotary CVD) system? Optimize Hollow Silica Particle Coating
- What advantages does a Rotary Kiln Reactor offer? Unlock Superior Uniformity for Graphene-Coated CaO Composites
- What are the main advantages of rotary kilns for industrial applications? Boost Efficiency and Quality in Your Processes
- What types of heating elements are commonly used in rotary tube furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Processing
- How does the tilting design of some rotary furnaces benefit operations? Boost Efficiency and Throughput



















