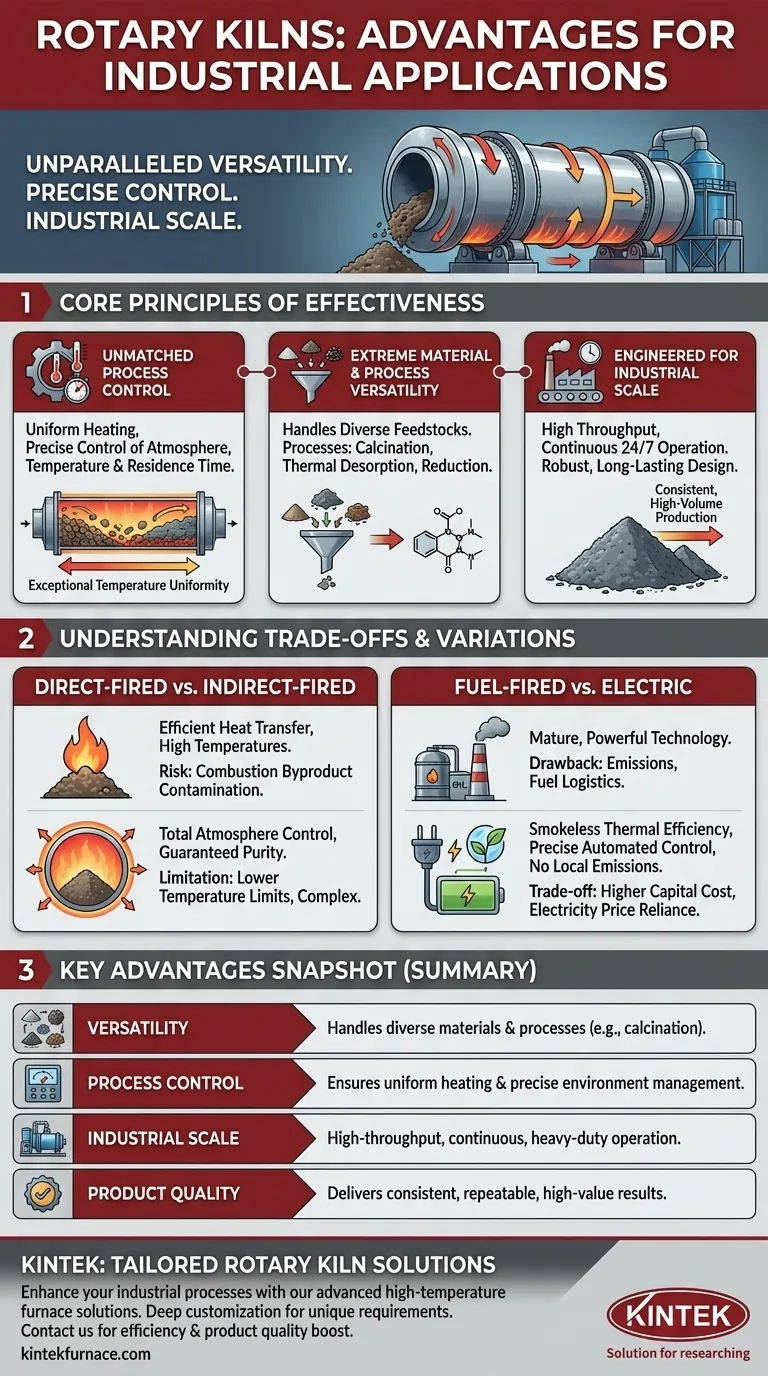
The primary advantages of a rotary kiln are its unparalleled versatility in handling diverse materials, its ability to achieve uniform processing at extremely high temperatures, and its robust design for high-volume, continuous industrial operation. This combination allows for consistent, repeatable product quality at a scale that few other thermal technologies can match.
A rotary kiln should be understood not merely as a furnace, but as a dynamic and continuous chemical reactor. Its fundamental advantage is the ability to reliably transform a wide range of raw feedstocks into high-value, uniform products by precisely controlling the processing environment at an industrial scale.
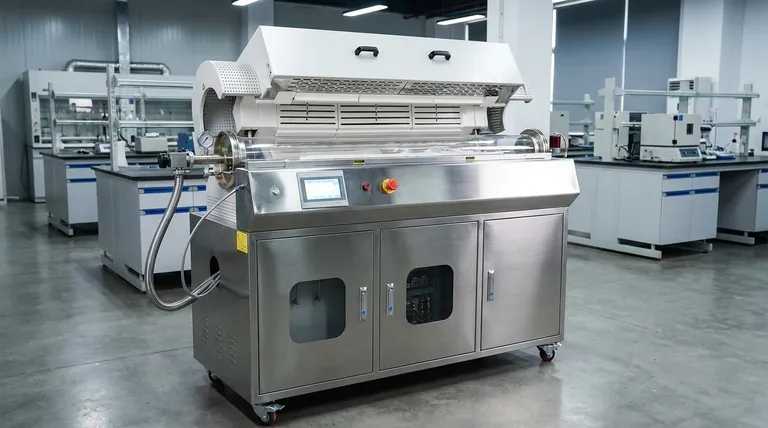

Why Rotary Kilns Excel: The Core Principles
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln stems from a few key operational principles that make it a cornerstone technology in industries from cement and minerals to chemical manufacturing and waste recycling.
Principle 1: Unmatched Process Control
The rotating-drum design is central to its success. This gentle tumbling action constantly exposes new material surfaces to the heat source, ensuring exceptional temperature uniformity throughout the material bed.
Modern kilns, particularly indirect-fired and electric models, offer precise control over the internal atmosphere, temperature profile, and residence time (the duration the material spends in the kiln). This level of control is critical for driving specific chemical reactions or phase changes, guaranteeing a consistent final product.
Principle 2: Extreme Material & Process Versatility
Rotary kilns are renowned for their ability to process an incredibly wide variety of feedstocks. They can effectively handle everything from fine powders and ores to bulk solids, filter cakes, and sludges.
This physical versatility is matched by process versatility. Kilns are used for numerous thermal treatments, including calcination (heating to drive off volatiles), thermal desorption (removing contaminants), reduction (removing oxygen), and other complex chemical transformations.
Principle 3: Engineered for Industrial Scale
Rotary kilns are designed for high-throughput, continuous operation. Their heavy-duty construction ensures a long service life even under the most demanding conditions, 24/7.
This capacity for large-volume processing makes them highly efficient for industries like cement and metallurgy, where producing vast quantities of material is a core business requirement. High-speed cycles allow for rapid processing while maintaining the repeatable, high-quality results essential for industrial applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While powerful, a rotary kiln is not a universal solution. The choice of kiln type involves critical trade-offs between cost, process purity, and efficiency.
Direct-Fired vs. Indirect-Fired
In a direct-fired kiln, the flame and combustion gases are in direct contact with the process material. This is a very efficient way to transfer heat and can achieve the highest temperatures, but it risks contaminating the product with byproducts of combustion.
An indirect-fired kiln heats the material through the shell of the rotating drum, keeping the material completely isolated from the flame. This allows for total control of the internal atmosphere and guarantees product purity, but it is typically more complex and has lower temperature limits.
Fuel-Fired vs. Electric
Traditional kilns are fuel-fired (gas, oil), which is a mature and powerful technology. However, they produce emissions (like SO2) and require significant fuel storage and management logistics.
Electric rotary kilns offer a significant advantage in control and environmental impact. They provide smokeless thermal efficiency often exceeding 95%, enable highly precise automated temperature control, and eliminate all local emissions and fuel handling costs. The primary trade-off is often a higher capital cost and reliance on electricity prices for operational economy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the optimal rotary kiln requires aligning its specific configuration with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is product purity and precise atmosphere control: An indirect-fired or electric kiln is the necessary choice to prevent contamination and manage the process environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput for bulk materials: A large, direct-fired kiln often provides the most cost-effective and highest-volume solution.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and process simplicity: An electric kiln eliminates local emissions and the complexities of fuel management, offering superior and automated temperature control.
Ultimately, choosing the right rotary kiln is about matching its inherent processing strengths to your specific material transformation and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Versatility | Handles diverse materials and processes like calcination and thermal desorption. |
| Process Control | Ensures uniform heating, precise temperature, atmosphere, and residence time control. |
| Industrial Scale | Designed for high-throughput, continuous operation with robust, long-lasting construction. |
| Product Quality | Delivers consistent, repeatable results for applications in cement, minerals, and chemicals. |
Ready to enhance your industrial processes with a tailored rotary kiln? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can boost your efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















