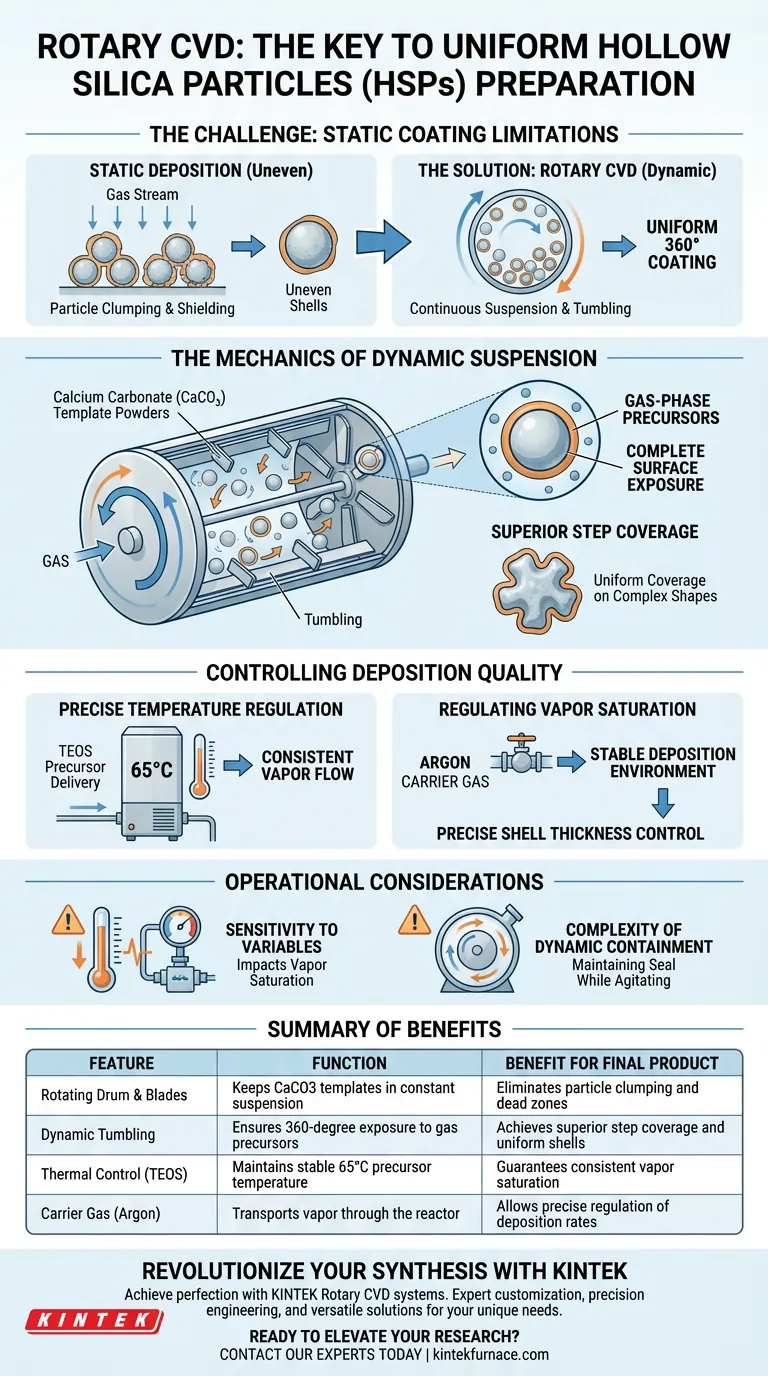
The role of a Rotary Chemical Vapor Deposition (Rotary CVD) system is to ensure the uniform coating of individual particles during the synthesis of hollow silica particles (HSPs). By utilizing a rotating drum reactor with internal blades, the system keeps calcium carbonate (CaCO3) template powders in a constant state of suspension and tumbling, allowing gas-phase precursors to coat the entire surface area of every particle.
By replacing static coating methods with dynamic tumbling, Rotary CVD guarantees that gas-phase precursors achieve comprehensive contact with complex particle shapes. This process is essential for achieving exceptional step coverage and uniform silica shell thickness.
The Mechanics of Dynamic Suspension
The Rotating Drum and Internal Blades
The core of the Rotary CVD system is a specialized reactor designed for particulate processing. It features a rotating drum equipped with internal blades.
These mechanical components function to continuously agitate the calcium carbonate (CaCO3) template powders.
Achieving Complete Surface Exposure
In static deposition, particles often touch or shield one another, leading to uneven coatings. Rotary CVD solves this by maintaining the powder in a state of suspension.
This tumbling action ensures that every side of the template particle is equally exposed to the chemical vapor.
Superior Step Coverage
The dynamic movement of the powder allows for excellent step coverage.
Regardless of the complexity or irregularity of the template particle's shape, the gas-phase precursors can reach and coat the surface uniformly, creating a high-quality silica layer.
Controlling Deposition Quality
Precise Temperature Regulation
Mechanical movement must be paired with chemical stability. The system requires a precursor delivery unit that maintains liquid precursors, such as tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), at a specific temperature (e.g., 65°C).
This thermal control is vital for generating a consistent and stable vapor flow.
Regulating Vapor Saturation
Consistent temperature ensures uniform vapor saturation within the reactor.
When this is combined with a constant flow of a carrier gas like argon, the system creates a highly predictable deposition environment.
Tuning Shell Thickness
The ultimate goal of these controls is the precise regulation of the deposition rate.
By stabilizing the vapor flow and carrier gas, the system allows operators to dictate the final thickness of the silica shell layer with high accuracy.
Understanding the Operational Requirements
Sensitivity to Environmental Variables
The quality of the final HSPs is heavily dependent on the stability of the precursor delivery system.
Fluctuations in the temperature of the TEOS or the flow rate of the argon carrier gas can lead to inconsistent vapor saturation, resulting in uneven shell thickness.
Complexity of Dynamic containment
Unlike static systems, a Rotary CVD setup must maintain a controlled chemical atmosphere while mechanically agitating the substrate.
This adds a layer of operational complexity, as the system must effectively tumble the powder without compromising the integrity of the gas flow or the vacuum environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a Rotary CVD system for HSP preparation, align your process controls with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is shell uniformity: Ensure the rotational speed and blade configuration are optimized to keep the CaCO3 template powders in full suspension, eliminating dead zones where particles might clump.
- If your primary focus is precise shell thickness: Prioritize the thermal stability of the precursor delivery system to maintain TEOS at exactly 65°C (or your target setpoint) for consistent vapor saturation.
Rotary CVD transforms the challenge of coating particulates into a controlled, reproducible process, delivering the uniformity required for high-performance hollow silica particles.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in HSP Preparation | Benefit for Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating Drum & Blades | Keeps CaCO3 templates in constant suspension | Eliminates particle clumping and dead zones |
| Dynamic Tumbling | Ensures 360-degree exposure to gas precursors | Achieves superior step coverage and uniform shells |
| Thermal Control (TEOS) | Maintains stable 65°C precursor temperature | Guarantees consistent vapor saturation |
| Carrier Gas (Argon) | Transports vapor through the reactor | Allows precise regulation of deposition rates |
Revolutionize Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect hollow silica particle requires precision engineering and dynamic control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Rotary CVD systems designed specifically to solve the challenges of particulate coating. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our systems—including Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, and CVD furnaces—are fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory or production needs.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert Customization: Tailor drum speeds and blade configurations to your specific template powders.
- Precision Engineering: Maintain exact thermal stability for consistent shell thickness every time.
- Versatile Solutions: From Rotary to CVD and high-temp furnaces, we cover all your lab heating requirements.
Ready to elevate your research and manufacturing? Contact our technical experts today to discuss your custom project and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Hirokazu Katsui, Mikinori Hotta. Preparation of hollow silica particles by template method via chemical vapor deposition. DOI: 10.2109/jcersj2.23114
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How are indirect-fired rotary kilns utilized in waste management? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Resource Solutions
- What is the significance of rotation in a pyrolysis rotary kiln reactor? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Energy Conversion
- Why are rotary kilns preferred for incineration processes? Versatile, Reliable Waste Destruction
- What are the main applications of rotary tube furnaces? Boost Efficiency in Material Processing
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of fuel can rotary kilns use? Optimize Your Process with the Right Choice
- What role do indirect-fired rotary kilns play in carbonization and activation processes? Unlock Precise Control for High-Purity Carbon Products



















