At its core, efficient heat transfer is the defining operational advantage of a rotary tube furnace. This efficiency allows for exceptionally rapid and uniform heating of materials, which in turn enables continuous batch processing, minimizes material handling, and ensures a highly consistent and pure final product.
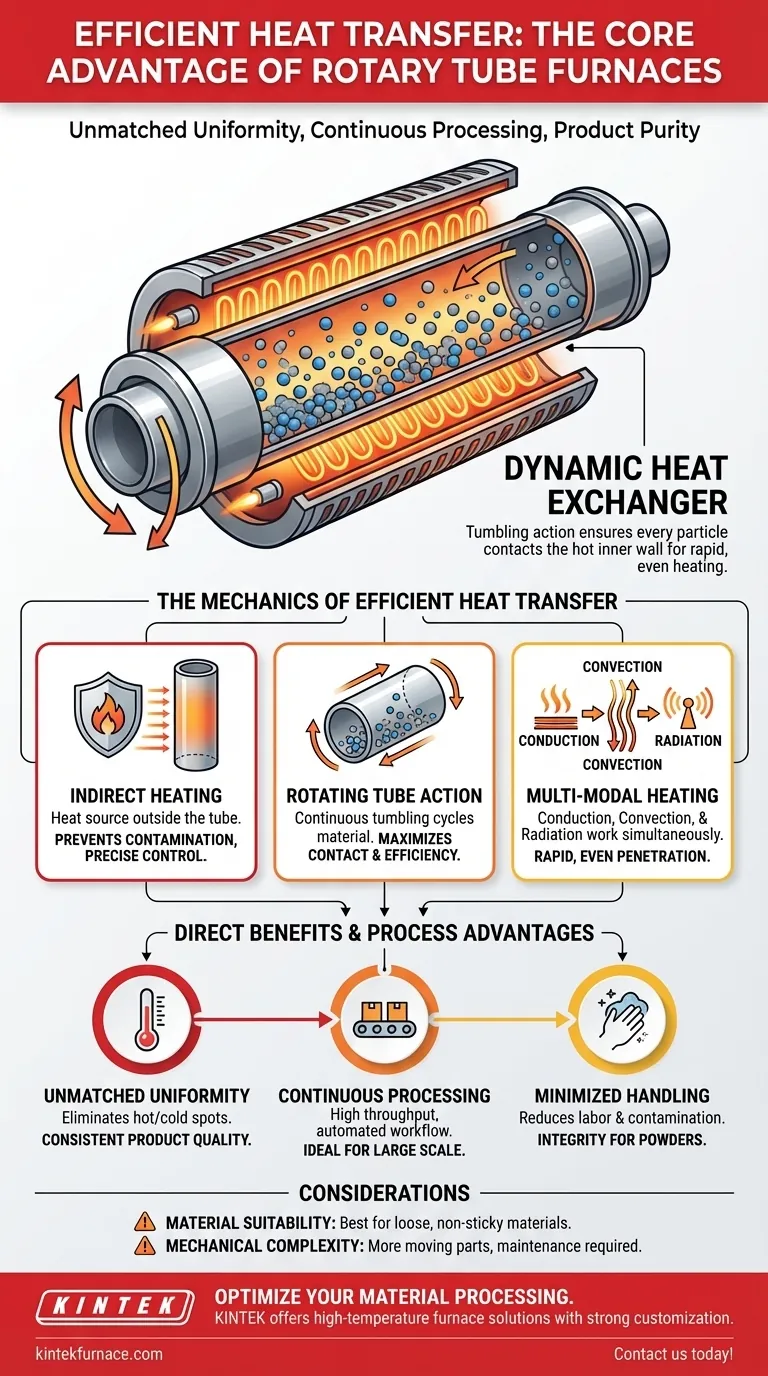
The unique value of a rotary tube furnace comes from its design, which combines indirect heating with constant rotation. This turns the entire tube into a dynamic heat exchanger, ensuring every particle of material is heated evenly and quickly while being protected from contamination.
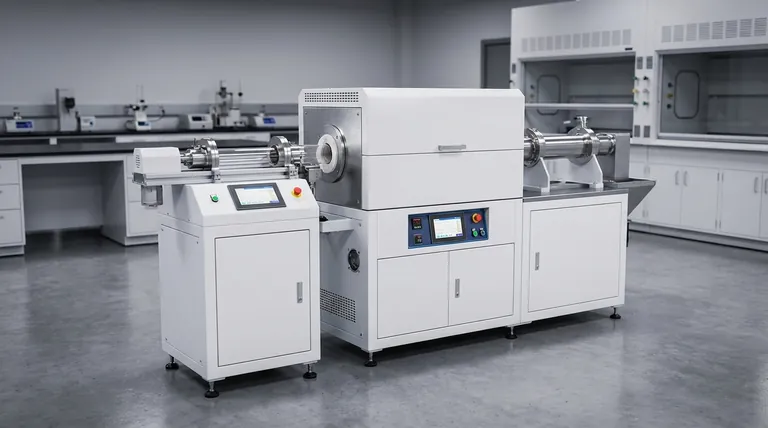

The Mechanics of Efficient Heat Transfer
To understand why this is so important, you must first understand the fundamental principles at work. The furnace's effectiveness is not based on a single factor, but on the interplay of its design and the physics of heat transfer.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
A rotary tube furnace employs an indirect heating method. The heat source, such as electric elements or gas burners, is positioned outside the rotating tube that contains the material.
This design is critical because it prevents any direct contact between the heating source and the material being processed. The primary benefit is the prevention of contamination, ensuring product purity. It also allows for extremely precise temperature control of the environment within the tube.
The Rotating Tube as a Heat Exchanger
The furnace's tube is not merely a container; it is the primary tool for heat transfer. As the external elements heat the tube, the tube wall itself becomes hot.
The longitudinal rotation of the tube then continuously tumbles the material inside. This dynamic motion ensures that the entire bulk of the material is constantly cycled into contact with the hot inner wall of the tube, acting as a highly efficient heat exchanger.
A Multi-Modal Approach to Heating
The tumbling action maximizes heat transfer through multiple physical modes simultaneously:
- Conduction: Occurs when particles of the material physically touch the hot inner wall of the tube.
- Convection: The atmosphere inside the tube is heated, and this hot gas transfers heat as it flows around the particles.
- Radiation: The hot tube wall radiates thermal energy directly to the material within it.
This combination ensures that heat penetrates the entire batch of material quickly and evenly, a feat that is difficult to achieve in a static furnace.
The Direct Benefits of Superior Heat Transfer
This efficient, multi-modal heat transfer mechanism translates directly into tangible process advantages that are critical in both industrial and laboratory settings.
Achieving Unmatched Uniformity
Because every particle is continuously exposed to the heat source (the tube wall), the entire batch reaches the target temperature at nearly the same time.
This eliminates hot and cold spots, ensuring that all the material receives the exact same thermal treatment. This is vital for sensitive chemical reactions, material synthesis, and achieving consistent product characteristics.
Enabling Continuous Batch Processing
The speed of the heat transfer allows material to be processed in a very short time. This makes the furnace ideal for continuous batch processing.
Raw material can be fed into one end of the tilted, rotating tube and the finished product can be discharged from the other. This creates a highly efficient, automated workflow that significantly increases throughput compared to static batch methods.
Minimizing Material Handling in Powder Processing
Rotary tube furnaces are particularly effective for processing powders, granules, and other loose materials. The continuous flow design minimizes the need for manual handling between batches.
This reduces labor, limits the potential for operator error or exposure, and maintains the integrity of the product by reducing its exposure to the ambient environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly effective, the design of a rotary tube furnace presents certain considerations that make it ideal for some applications and less so for others.
Material Suitability
The furnace's primary mechanism relies on the material being able to tumble freely. It is designed for loose materials. Materials that are sticky, prone to clumping at high temperatures, or consist of very large, non-uniform pieces may not be suitable for this process.
Mechanical Complexity
Compared to a simple static box furnace, a rotary tube furnace has more moving parts. The rotation system requires motors, seals, and bearings that necessitate a more involved maintenance schedule to ensure long-term reliability.
Process Scale
The benefits of continuous processing are most pronounced at an industrial or high-throughput lab scale. For very small, infrequent sample testing, the setup and cleaning time might outweigh the benefits over a simpler batch furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a rotary tube furnace should be driven by a clear understanding of your process goals.
- If your primary focus is process throughput and efficiency: A rotary tube furnace is an exceptional choice, as its design is optimized for continuous, automated processing.
- If your primary focus is product uniformity and purity: The combination of indirect heating and constant rotation provides unparalleled temperature consistency and protection from contamination.
- If your primary focus is versatility for loose materials: This furnace can handle a wide range of powders and granules for applications from calcination to material synthesis.
By understanding its unique heat transfer dynamics, you can confidently leverage the rotary tube furnace to achieve superior results in your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect heating prevents contamination and allows precise temperature control. |
| Heat Transfer Modes | Combines conduction, convection, and radiation for rapid, uniform heating. |
| Primary Benefits | Unmatched uniformity, continuous batch processing, minimized material handling. |
| Ideal Applications | Suitable for loose materials like powders and granules in industrial or high-throughput labs. |
| Considerations | Not ideal for sticky or large materials; requires more maintenance due to moving parts. |
Ready to optimize your material processing with advanced rotary tube furnaces?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is designed for efficiency and precision. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring superior heat transfer, purity, and throughput for your powders and granules.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's performance and achieve consistent, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits



















