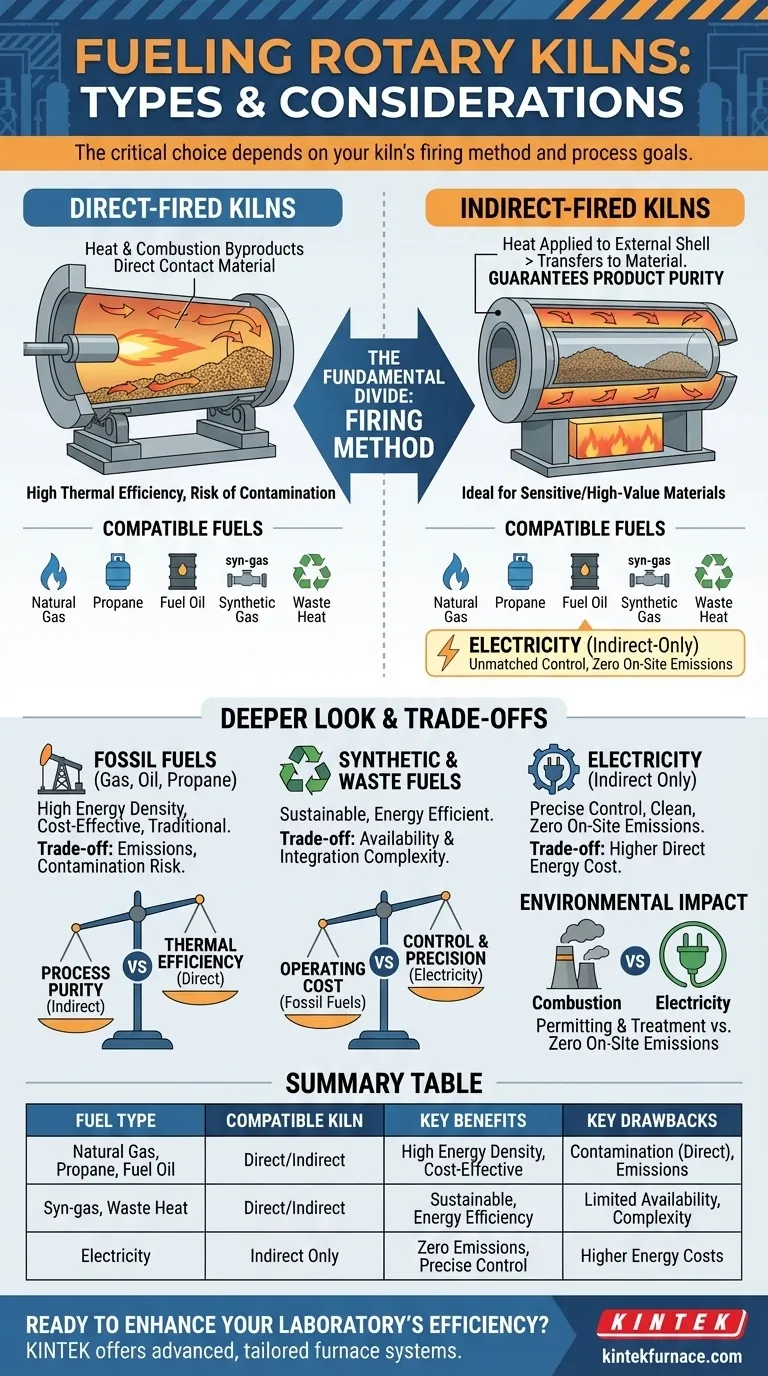
In short, a rotary kiln can use a wide range of fuels, including natural gas, propane, fuel oil, synthetic gas (syn-gas), and even reclaimed waste heat. The specific fuel options available are determined by the fundamental design of the kiln—specifically, whether it is a direct-fired or indirect-fired system. Only indirect-fired kilns have the additional option of using electricity.
The most critical factor in fuel selection is not the fuel itself, but the kiln's firing method. The choice between direct and indirect firing dictates which fuels are possible and directly impacts material purity, thermal efficiency, and operating cost.

The Fundamental Divide: Direct vs. Indirect Firing
To understand your fuel options, you must first understand how your kiln introduces heat to the material being processed. This is the single most important distinction.
How Direct-Fired Kilns Work
In a direct-fired kiln, the burner flame and hot combustion gases are introduced directly into the kiln cylinder. This means the material being processed comes into direct contact with the byproducts of combustion.
This design is highly thermally efficient because heat transfer is immediate. However, it introduces the risk of product contamination from the flame and exhaust gases.
Direct-fired kilns are compatible with most combustion-based fuels, including natural gas, fuel oil, propane, and syn-gas. They can also be designed to utilize waste heat from other industrial processes.
How Indirect-Fired Kilns Work
In an indirect-fired kiln, the material is sealed within the rotating cylinder. Heat is applied to the outside of the kiln shell, which then transfers heat through the cylinder wall to the material inside.
This design guarantees product purity, as the material never contacts the flame or combustion gases. This makes it essential for processing sensitive, high-value, or reactive materials.
Indirect kilns can use the same combustion fuels as direct-fired units (gas, oil, etc.). Critically, they are also the only type that can be heated with electricity via external heating elements.
A Deeper Look at Fuel Options
Each fuel source carries its own profile of benefits, costs, and operational considerations.
Fossil Fuels (Natural Gas, Propane, Fuel Oil)
These are the traditional workhorses for industrial heating. They offer high energy density, are widely available, and are often the most cost-effective option for generating large amounts of thermal energy. Natural gas is typically favored for its clean-burning properties compared to fuel oil.
Synthetic & Waste-Derived Fuels (Syn-gas, Waste Heat)
These options focus on efficiency and sustainability. Syn-gas, produced from various feedstocks, can be a valuable fuel in integrated facilities. Using waste heat from another process (like an incinerator) to power a kiln is an excellent way to improve the overall energy efficiency of a plant.
Electricity (The Indirect-Only Option)
Electricity is unique because it doesn't involve combustion. It is used exclusively in indirect-fired kilns where resistive heating elements surround the rotating shell.
Its primary advantages are unmatched temperature control and zero on-site emissions, making it ideal for processes requiring extreme precision or operating in environmentally sensitive locations. The main drawback is often a higher direct energy cost compared to fossil fuels.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a fuel is a balancing act between your processing goals and operational realities.
Process Purity vs. Thermal Efficiency
This is the central conflict. If your material absolutely cannot be contaminated, you must use an indirect-fired kiln, even though it is inherently less efficient at transferring heat. If slight exposure to combustion gases is acceptable, a direct-fired kiln will offer better thermal efficiency and potentially lower fuel costs.
Operating Cost vs. Control
While natural gas is often the cheapest fuel per unit of energy, electricity offers superior control and repeatability, which can reduce product spoilage and improve overall quality. You must weigh the direct cost of energy against the indirect value of process precision.
Environmental Impact & Permitting
All combustion fuels produce emissions (like CO₂, NOx, and SOx) that are subject to environmental regulations and may require expensive exhaust gas treatment systems. An electrically heated kiln eliminates on-site emissions, simplifying the permitting process significantly, though the emissions are displaced to the power generation source.
Selecting the Right Fuel for Your Process
Your choice should be guided by the non-negotiable requirements of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity: You must use an indirect-fired kiln, with electricity being the ultimate choice for control and cleanliness, or natural gas for a balance of cost and performance.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and cost efficiency: A direct-fired kiln using the most economical local fuel, such as natural gas or fuel oil, is your best option, provided minor contamination is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and process integration: Explore using waste heat from an upstream process or investigate the feasibility of generating and using syn-gas within your facility.
Ultimately, the right fuel is the one that allows your kiln to meet its processing objectives reliably, safely, and economically.
Summary Table:
| Fuel Type | Compatible Kiln Type | Key Benefits | Key Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas, Propane, Fuel Oil | Direct-Fired, Indirect-Fired | High energy density, cost-effective | Risk of contamination (direct), emissions |
| Synthetic Gas (Syn-gas), Waste Heat | Direct-Fired, Indirect-Fired | Sustainable, improves energy efficiency | Limited availability, integration complexity |
| Electricity | Indirect-Fired Only | Zero on-site emissions, precise temperature control | Higher energy costs, lower thermal efficiency |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's efficiency with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental requirements precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your process purity, thermal efficiency, and cost-effectiveness!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















