In waste management, an indirect-fired rotary kiln is a specialized thermal processing tool used to transform waste streams into valuable resources or energy. It achieves this through processes like pyrolysis, gasification, and thermal decomposition, handling materials from municipal solid waste and sewage sludge to industrial residues. The core function is to reduce waste volume while enabling resource recovery in a controlled environment.
The fundamental advantage of an indirect-fired rotary kiln is its ability to separate the heating source from the material being processed. This allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere and temperature, making it possible to execute targeted chemical transformations like pyrolysis without interference from combustion gases.
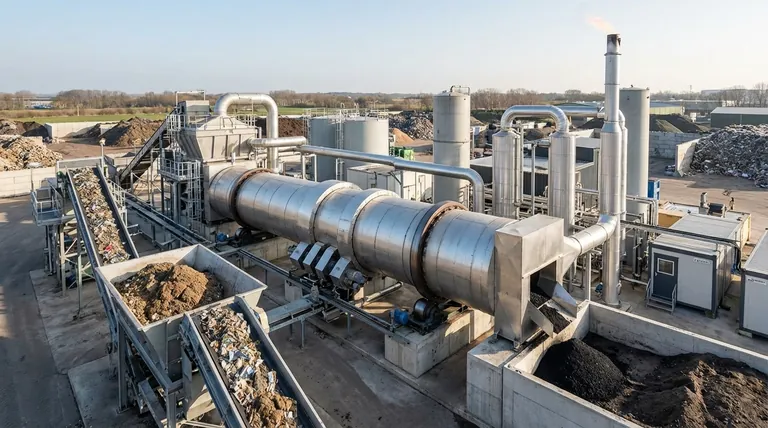

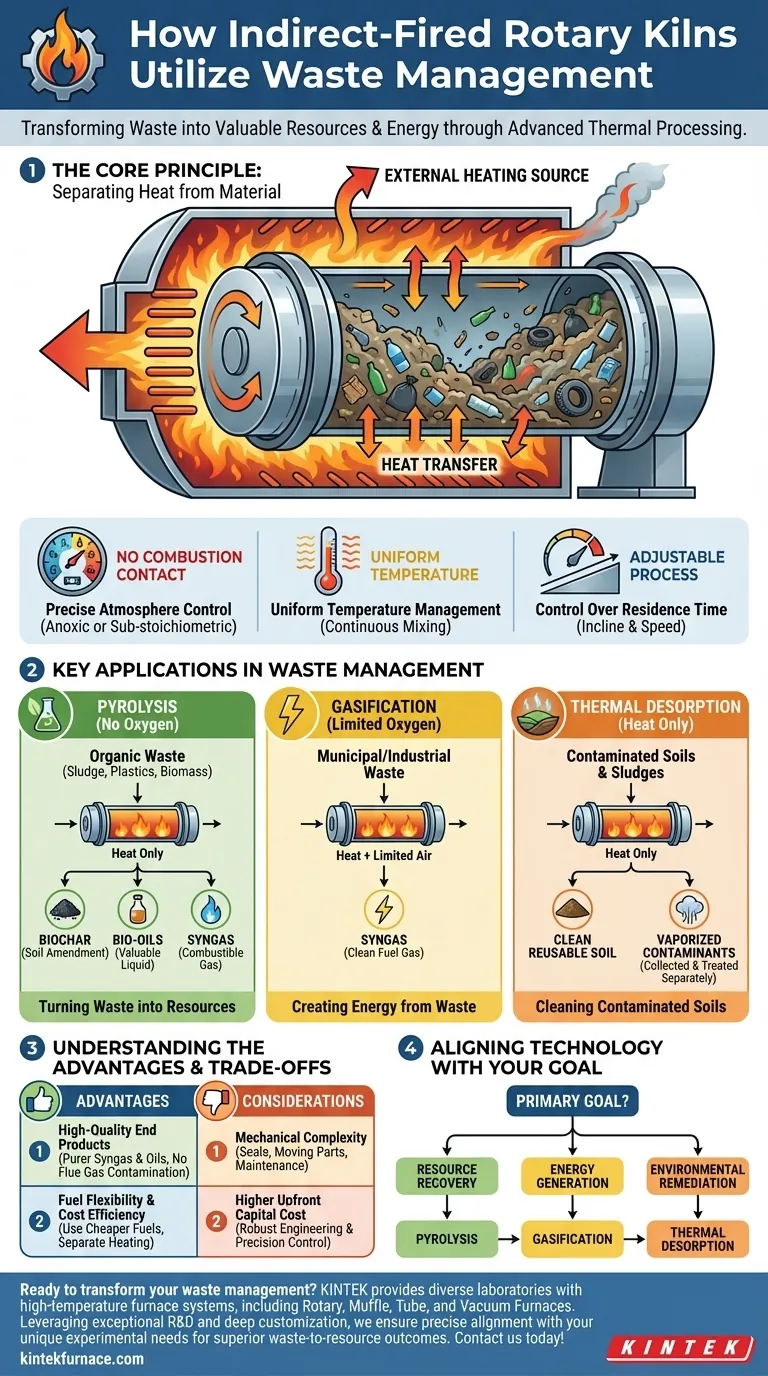
The Core Principle: Separating Heat from Material
An indirect-fired rotary kiln operates like a large, rotating drum that is heated from the outside. Waste material tumbles through the inside of the drum, but the flames or hot gases used for heating never make direct contact with it. This fundamental design separation is what unlocks its key capabilities.
Precise Atmosphere Control
Because combustion does not occur inside the kiln, operators have complete control over the internal atmosphere. This allows for creating an oxygen-free (anoxic) environment, which is essential for pyrolysis, or an oxygen-starved (sub-stoichiometric) environment required for gasification.
Uniform Temperature Management
The slow, continuous rotation of the kiln ensures that the waste material is constantly mixed and lifted. This action exposes all particles to the heated drum wall, guaranteeing uniform heat transfer and preventing hot or cold spots that could lead to an incomplete reaction.
Control Over Residence Time
The angle of the kiln's incline and its rotational speed determine how long the material stays inside. This residence time is a critical parameter that can be adjusted to optimize the specific thermal process for different types of waste, ensuring the desired transformation is complete.
Key Applications in Waste Management
The precise control offered by indirect-fired kilns makes them ideal for several high-value waste treatment processes that go beyond simple incineration.
Pyrolysis: Turning Waste into Resources
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of material in the absence of oxygen. In a kiln, this process breaks down organic wastes like sewage sludge, plastics, or biomass into valuable products.
The outputs typically include syngas (a combustible gas mixture), bio-oils, and a solid carbon-rich residue called biochar, which can be used as a soil amendment.
Gasification: Creating Energy from Waste
Gasification uses a limited amount of oxygen to partially combust waste, converting it primarily into syngas. This syngas can then be cleaned and used as a fuel to generate electricity or heat in a waste-to-energy (WTE) facility.
This process is more efficient for energy conversion than direct combustion because it creates a consistent, usable fuel gas.
Thermal Desorption: Cleaning Contaminated Soils
This application involves heating hazardous materials, such as contaminated soil or industrial sludge, to a temperature high enough to vaporize volatile contaminants like hydrocarbons.
The kiln's indirect heating gently removes the pollutants without destroying the soil matrix itself. The vaporized contaminants are then collected and treated separately, leaving behind clean, reusable soil.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
While powerful, this technology comes with a specific set of benefits and considerations that are important for any project evaluation.
Advantage: High-Quality End Products
Because the process gas is not diluted or contaminated by flue gas from combustion, the resulting products (syngas, oils) are purer and have a higher value. This is a significant advantage over direct-fired systems.
Advantage: Fuel Flexibility and Cost Efficiency
The external heating system is separate from the process, allowing for the use of a wide range of fuels, including lower-cost options like coal or waste heat. This can significantly reduce operational fuel expenses compared to processes that require more expensive fuel sources.
Consideration: Mechanical Complexity
Rotary kilns are large, heavy-duty machines with critical moving parts. The seals at either end of the rotating drum are crucial for maintaining atmospheric control and require regular inspection and maintenance to prevent leaks.
Consideration: Higher Upfront Capital Cost
The robust engineering, large footprint, and precision control systems mean that indirect-fired rotary kilns typically represent a higher initial capital investment compared to simpler static furnace designs.
Aligning the Technology with Your Goal
Choosing the right thermal process depends entirely on your primary objective for the waste stream.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery: Pyrolysis is the ideal path for converting organic waste into marketable products like biochar and bio-oils.
- If your primary focus is energy generation: Gasification offers an efficient method for creating a clean, consistent syngas to fuel a waste-to-energy power plant.
- If your primary focus is environmental remediation: Thermal desorption provides a proven method for cleaning contaminated soils and sludges while preserving the soil itself.
By understanding its core principles of control, you can effectively leverage this technology to meet specific sustainability and economic goals.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Separates heating source from waste for precise atmosphere and temperature control |
| Main Processes | Pyrolysis, Gasification, Thermal Desorption |
| Key Advantages | High-quality end products, fuel flexibility, uniform heating |
| Considerations | Higher capital cost, mechanical complexity |
| Target Applications | Resource recovery, energy generation, environmental remediation |
Ready to transform your waste management with advanced thermal solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior waste-to-resource outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is the role of indirect-fired rotary kilns in energy production? Unlock Sustainable Waste-to-Energy Solutions
- What are the key components and parameters of a rotary kiln? Optimize Your High-Temperature Processing
- How do pyrolysis rotary kiln reactors function? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Value Conversion
- Why is an industrial-grade rotary reactor necessary in the oil sludge pyrolysis process? Maximize Yield & Efficiency
- What technical requirements are placed on heating equipment for fast pyrolysis? Master High-Yield Bio-Oil Production



















