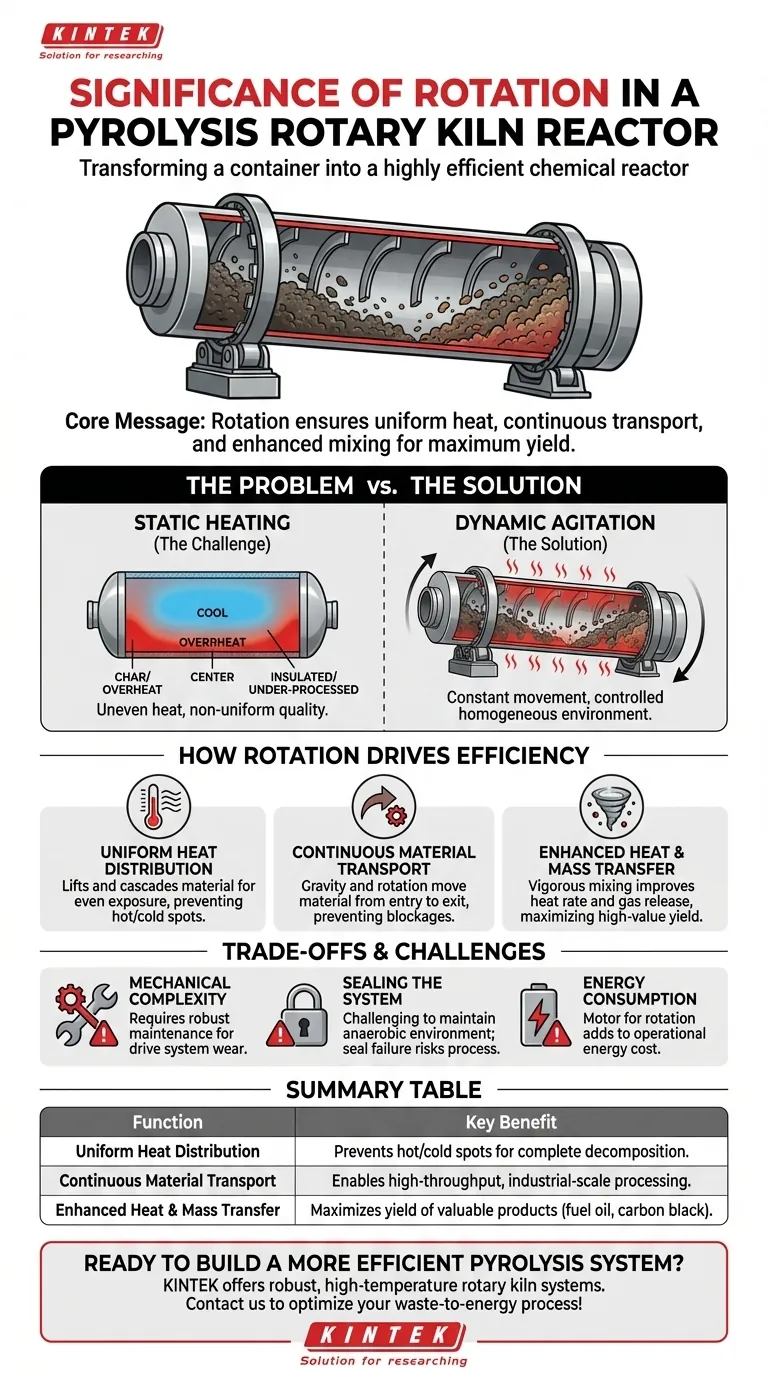
At its core, the rotation of a pyrolysis kiln is what transforms it from a simple heated container into a highly efficient chemical reactor. This movement is fundamental to the process, ensuring uniform heat distribution, facilitating continuous material transport from entry to exit, and enhancing the mixing of solids and gases to maximize the yield of valuable products from waste.
The significance of rotation is not merely about movement; it is the primary mechanism that ensures every particle of material is processed evenly and efficiently, directly impacting product quality, throughput, and operational stability.

The Core Problem: Overcoming Inefficient Heat Transfer
To understand why rotation is so critical, it's helpful to consider the alternative: a static, or non-rotating, heating vessel. This highlights the fundamental challenges that rotation is designed to solve in high-temperature material processing.
The Challenge of Static Heating
In a static reactor, the material at the bottom and sides in direct contact with the hot vessel walls would overheat and char.
Meanwhile, the material in the center of the mass would remain insulated and under-processed, drastically reducing the overall efficiency and creating a non-uniform, low-quality final product.
The Solution: Dynamic Material Agitation
Rotation solves this by constantly tumbling the material. This action, known as agitation, ensures that no single part of the feedstock remains in one place for too long.
This dynamic process is the key to achieving the controlled, homogenous environment necessary for successful pyrolysis.
How Rotation Drives Pyrolysis Efficiency
The benefits of rotation are not singular; they compound to create a highly effective system. The movement directly influences three critical aspects of the pyrolysis process.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Distribution
As the kiln rotates, it continuously lifts the waste material and cascades it through the hotter upper atmosphere of the vessel. This exposes all surfaces of the material to the heat source.
This even heating prevents hot spots and cold spots, promoting a thorough and complete thermal decomposition. This uniformity is directly linked to maximizing the yield of valuable outputs like fuel oil and carbon black.
Facilitating Continuous Material Transport
Most rotary kilns are set at a slight downward angle. The slow, constant rotation works with gravity to gently move material from the loading end to the discharge end.
This mechanism prevents blockages and allows for a continuous, automated process, which is essential for industrial-scale operations that require high throughput and consistent performance.
Enhancing Heat and Mass Transfer
Rotation vigorously mixes the solid waste material with the pyrolysis gases being released. This constant stirring improves the rate of heat transfer into the solids and mass transfer of volatile gases out of them.
Efficiently removing these gases from the hot reaction zone prevents unwanted secondary reactions (cracking), which can degrade the quality of the final fuel oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While essential, the rotating design is not without its complexities. Acknowledging these trade-offs is crucial for a complete understanding of the technology.
Mechanical Complexity
The drive system—consisting of a motor, speed reducer, gears, and support rollers—introduces multiple points of mechanical wear. This requires a robust maintenance schedule to ensure reliability and prevent costly downtime.
Sealing the System
Maintaining an oxygen-free (anaerobic) environment is paramount for pyrolysis. The dynamic seals at the inlet and outlet of a rotating drum are a significant engineering challenge. Any failure in these seals can compromise the process, reduce product quality, and create safety hazards.
Energy Consumption
The electric motor required to turn the large, heavy kiln drum adds to the overall energy consumption of the plant. While pyrolysis is often a net energy producer, the energy cost of the rotation system itself is a key operational factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The rotation system is central to achieving specific operational outcomes. Understanding its function helps align the technology with your primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product yield: The uniform heating provided by rotation is the single most important factor for ensuring complete conversion of feedstock into high-value products.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and scalability: The continuous material transport enabled by rotation is what allows the system to process large volumes of waste efficiently without interruption.
- If your primary focus is process stability and safety: The consistent mixing and movement prevent material blockages and thermal runaways, leading to a more predictable and safer operation.
Ultimately, the rotation of a pyrolysis kiln is the critical design element that enables the consistent, efficient, and scalable conversion of waste into valuable resources.
Summary Table:
| Function of Rotation | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Uniform Heat Distribution | Prevents hot/cold spots for complete material decomposition. |
| Continuous Material Transport | Enables high-throughput, automated industrial-scale processing. |
| Enhanced Heat & Mass Transfer | Maximizes yield of valuable products like fuel oil and carbon black. |
Ready to build a more efficient pyrolysis system?
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers robust, high-temperature rotary kiln systems designed for superior performance and reliability. Our solutions are fully customizable to meet your unique pyrolysis needs, ensuring maximum yield and operational stability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your waste-to-energy process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is an industrial-grade rotary reactor necessary in the oil sludge pyrolysis process? Maximize Yield & Efficiency
- What is the working principle of a pyrolysis rotary kiln reactor? Efficient Waste-to-Energy Conversion
- What are the advantages of a rotary kiln for bio-reductants? Achieve Industrial-Scale Uniformity and Scalability
- How does a rotary furnace compare to a fixed-bed furnace for powder? Optimize Uniformity in Large-Scale Production
- What are the key components and parameters of a rotary kiln? Optimize Your High-Temperature Processing



















