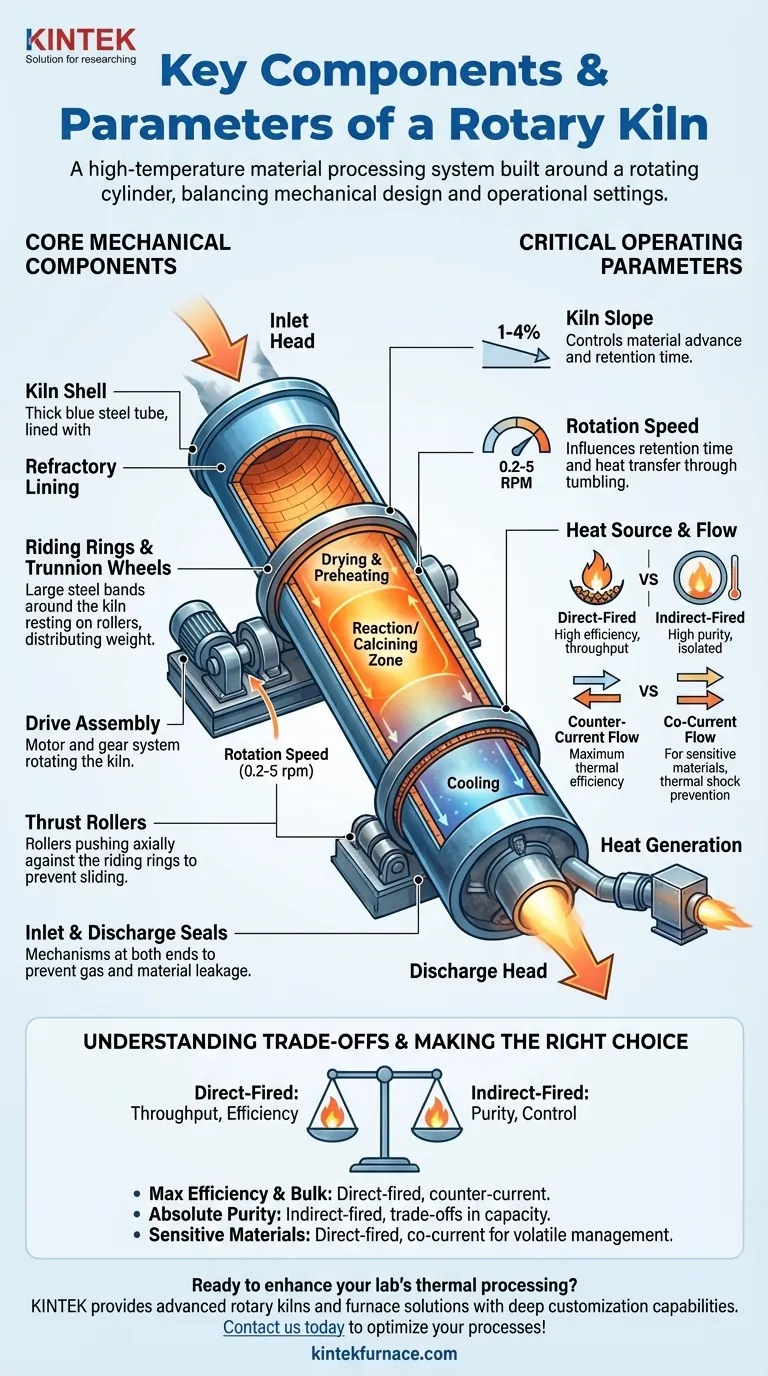
At its core, a rotary kiln is a system designed for high-temperature material processing, built around a large, rotating steel cylinder lined with heat-resistant material. Its key components include the kiln shell, a drive assembly for rotation, and support structures, while its primary operating parameters are the slope of the cylinder, its rotation speed, and the method of applying heat. These elements work in concert to control the material's retention time and temperature exposure.
The individual components and parameters of a rotary kiln are not independent variables. They form an interconnected system where mechanical design (slope, length) and operational settings (speed, heat flow) must be precisely balanced to achieve the desired chemical reaction or physical transformation in the material being processed.

The Core Mechanical Components
The physical structure of a rotary kiln is engineered for continuous operation under extreme thermal and mechanical stress. Each component serves a distinct purpose in containing the process and moving the material.
The Kiln Shell and Refractory Lining
The kiln shell is the main cylindrical body, typically made of heavy-duty steel plate. It provides the structural integrity of the entire rotating assembly.
Inside the shell, a refractory lining (made of specialized brick or castable material) serves two critical functions. It protects the steel shell from the extreme internal process temperatures and prevents chemical corrosion from the material being processed.
The Rotation and Support System
The entire kiln assembly is mounted on two or more riding rings, which are massive steel bands that encircle the shell. These rings distribute the kiln's immense weight onto a series of support rollers called trunnion wheels.
A drive assembly, consisting of a large gear and an electric motor, rotates the kiln at a controlled speed. To prevent the kiln from slowly sliding downhill due to its inclination, thrust rollers push against the riding rings to manage this axial drift.
Material Handling and Containment
Material enters the kiln through the inlet head (or feed end) and exits through the discharge head.
Crucially, seals are installed at both ends of the kiln. These mechanical systems (often spring or leaf seals) prevent cold air from entering the kiln and hot process gases from escaping, which is vital for maintaining thermal efficiency and environmental control.
Critical Operating Parameters
While the mechanical components form the structure, the operating parameters are the levers used to control the process itself. Adjusting these parameters directly impacts the final product quality.
Kiln Slope
Rotary kilns are always installed on a slight slope, typically between 1% and 4% (1-4 cm of drop per meter of length). This inclination is the primary force that causes material to advance from the feed end to the discharge end as the kiln rotates. A steeper slope results in a shorter retention time.
Rotation Speed
The rotation speed, generally between 0.2 and 5 revolutions per minute (rpm), is a critical control parameter. Slower rotation increases the retention time—how long the material spends inside the kiln. It also affects how the material tumbles, which influences heat transfer.
Heat Source and Flow
Heat is generated by a burner located at the discharge end of the kiln. The choice of heating method is a fundamental design decision.
- Direct-Fired: Hot combustion gases flow through the kiln in direct contact with the material. This is highly efficient but can introduce contaminants.
- Indirect-Fired: The kiln shell is heated from the outside. This ensures material purity but is less thermally efficient and limited to smaller-scale applications.
Heat flow can also be either counter-current (gas flows opposite the material) for maximum thermal efficiency or co-current (gas flows with the material) for processing heat-sensitive materials.
Kiln Zoning
A long kiln effectively creates distinct zones where different processes occur sequentially. A typical profile includes a drying zone, a preheating zone, a central calcining or reaction zone with the highest temperature, and a cooling zone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The design and operation of a kiln involve balancing competing priorities. The most fundamental trade-off is between process purity and thermal efficiency, which is dictated by the heating method.
Direct-Fired Kilns: Throughput over Purity
These kilns are the workhorses of heavy industry (e.g., cement, lime). By allowing hot gas to directly contact the material, they achieve excellent heat transfer and high throughput. However, the byproducts of combustion can contaminate the final product.
Indirect-Fired Kilns: Purity over Throughput
When product purity is non-negotiable (e.g., specialty chemicals, food-grade materials, soil remediation), an indirect-fired kiln is necessary. The material is isolated from combustion gases, but heating the massive steel shell from the outside is less efficient and limits the kiln's maximum diameter and capacity.
Counter-Current vs. Co-Current Flow
Counter-current flow is the most common configuration. As hot gas enters the discharge end and flows uphill, it encounters progressively cooler material, maximizing heat transfer and fuel efficiency.
Co-current flow, where gas and material move in the same direction, is used for materials that are sensitive to thermal shock or contain a high percentage of volatiles that need to be burned off quickly upon entry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting and operating a rotary kiln requires aligning its configuration with your specific process objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency and bulk production: A direct-fired, counter-current kiln is the standard and most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute product purity and avoiding contamination: An indirect-fired kiln is the only viable option, accepting the trade-offs in capacity and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is processing temperature-sensitive or high-moisture materials: A direct-fired, co-current flow configuration may be required to prevent thermal shock and manage volatiles safely.
Understanding how these components and parameters function as an integrated system is the key to optimizing any thermal processing operation.
Summary Table:
| Component/Parameter | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Kiln Shell & Lining | Steel cylinder with refractory lining for heat protection and corrosion resistance |
| Drive Assembly | Electric motor and gear system for controlled rotation (0.2-5 rpm) |
| Slope | Inclination (1-4%) to control material flow and retention time |
| Heat Source | Burner with direct or indirect firing for efficiency or purity |
| Flow Configuration | Counter-current for efficiency, co-current for sensitive materials |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our rotary kilns and other solutions can optimize your processes for efficiency and purity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















