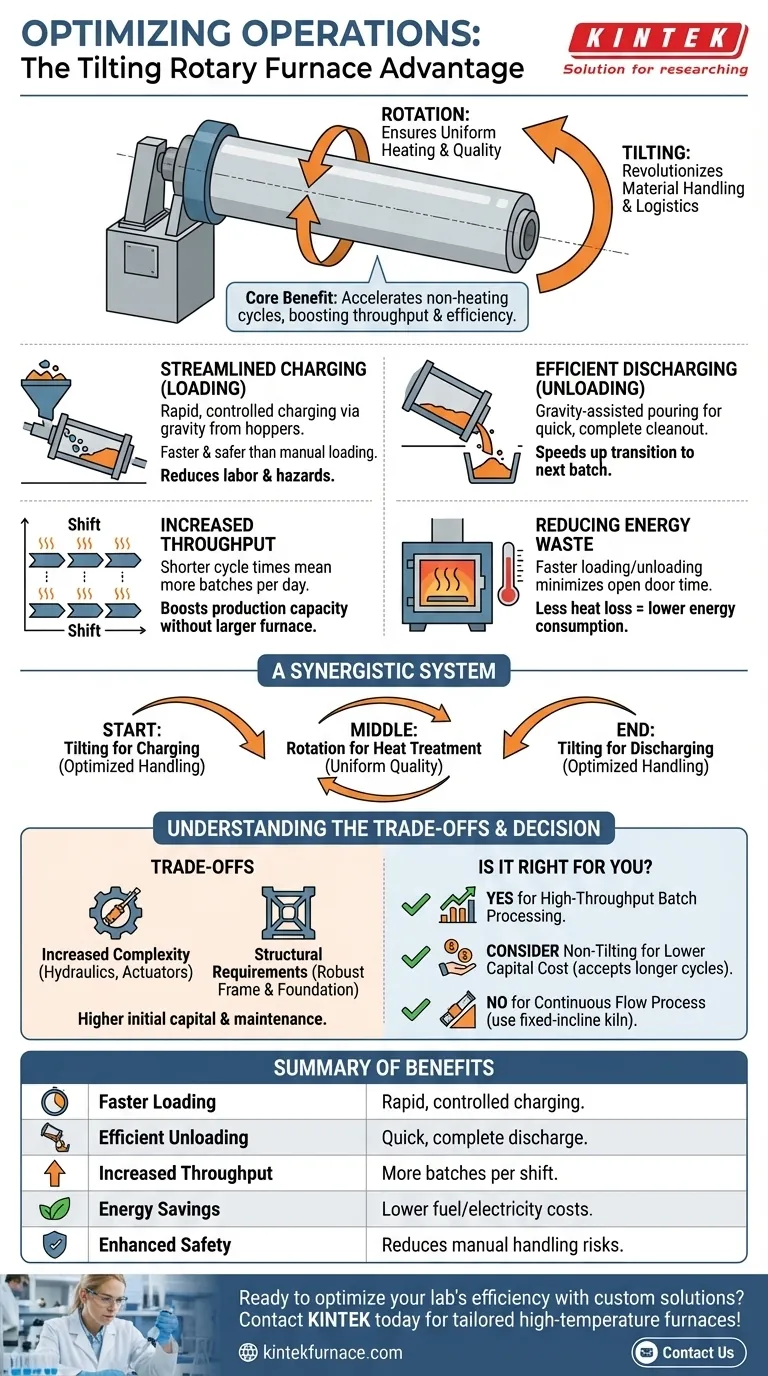
At its core, the tilting mechanism in a rotary furnace is a solution to a fundamental logistical challenge: efficiently moving materials into and out of the heating chamber. This design directly accelerates the non-heating portions of the work cycle, resulting in significantly shorter overall cycle times, increased throughput, and lower energy consumption per batch.
While the rotation of the furnace ensures product quality through even heating, it is the tilting function that revolutionizes material handling. This optimization of loading and unloading is the key driver of the furnace's operational and economic efficiency.

The Strategic Advantage of Tilting: Optimizing the Process Cycle
The primary benefits of the tilting feature are not related to the heating process itself, but to everything that happens before and after. By simplifying material handling, the design unlocks significant gains in speed and efficiency.
Streamlined Charging (Loading)
A tilting furnace can be angled downward toward the loading side. This allows for rapid and controlled charging of raw materials directly from hoppers, bins, or conveyors with minimal spillage or manual intervention.
This controlled process is faster and safer than manually loading a fixed furnace, reducing labor costs and potential workplace hazards.
Efficient Discharging (Unloading)
Once the process is complete, the furnace tilts in the opposite direction. This uses gravity to pour the finished product out cleanly and completely into a receptacle or onto a cooling conveyor.
This method is far quicker than using rakes or other mechanical means to empty a static furnace, ensuring a rapid transition to the next batch.
The Direct Impact on Throughput
The time saved during charging and discharging directly shortens the total cycle time for each batch.
A shorter cycle time means more batches can be processed within a given shift or day. This directly translates to higher plant throughput and increased production capacity without needing a larger furnace.
Reducing Energy Waste
Furnace doors or openings are a major source of heat loss. The speed of tilt-based loading and unloading minimizes the time the furnace is open to the ambient environment.
This reduction in heat loss means less energy is required to bring the furnace back up to operating temperature for the next cycle, leading to tangible savings in fuel or electricity costs.
How Tilting Complements the Rotary Action
It is critical to distinguish between the furnace's two key movements: tilting and rotating. They serve different purposes but work together to create a highly effective system.
The Role of Rotation: Ensuring Uniform Quality
The slow rotation of the furnace tube is what ensures process quality. It gently tumbles the material, constantly exposing new surfaces to the heat source.
This action prevents local overheating, eliminates hot spots, and guarantees uniform heating, drying, or sintering throughout the entire batch.
A Synergistic System
Tilting optimizes the beginning and end of the batch process (material handling). Rotation optimizes the middle of the process (heat treatment).
Together, they create a system where both material logistics and thermal performance are maximized, delivering a high-quality product with exceptional operational efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, the tilting mechanism is not without its considerations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Increased Mechanical Complexity
A tilting system relies on powerful hydraulic or electromechanical actuators. This adds complexity to the furnace's design, increasing the initial capital cost.
These components also introduce additional maintenance requirements and potential points of failure compared to a simpler, static furnace design.
Structural and Foundation Requirements
The dynamic forces generated by tilting a massive, heated furnace require a more robust and heavily engineered support frame and foundation.
This can increase installation costs and may have implications for the layout and construction of the facility itself.
Is a Tilting Furnace Right for Your Operation?
Choosing the correct furnace design requires aligning the equipment's capabilities with your specific production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput batch processing: The tilting design is essential for minimizing cycle times and maximizing output.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital cost: A non-tilting furnace may be a more economical choice, but you must account for higher operational labor and longer cycle times.
- If your primary focus is a continuous process with a steady flow of material: A fixed-incline rotary kiln is often the superior design, as the batch-oriented tilting function is unnecessary.
By understanding the distinct roles of tilting and rotation, you can select a furnace design that aligns precisely with your operational and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Faster Loading | Tilting enables rapid, controlled charging from hoppers or conveyors, reducing labor and hazards. |
| Efficient Unloading | Gravity-assisted pouring ensures quick, complete discharge, speeding up batch transitions. |
| Increased Throughput | Shorter cycle times allow more batches per shift, boosting production capacity. |
| Energy Savings | Minimized heat loss during operations lowers fuel or electricity costs per batch. |
| Enhanced Safety | Reduces manual handling risks, improving workplace safety. |
Ready to optimize your lab's efficiency with a custom high-temperature furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering precise temperature control, uniform heating, and enhanced throughput. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace designs can revolutionize your operations and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What makes rotary tube furnaces user-friendly? Achieve Superior Process Uniformity and Efficiency
- What level of process control do rotary tube furnaces provide? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing for Uniform Results
- What is the role of rotary tube furnaces in the energy sector? Boost Efficiency in Biomass and Battery Material Processing
- How is the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace used in the carbon activation process? Achieve Uniform, High-Porosity Activated Carbon
- What are the key components of a rotary tube furnace? Essential Parts for Uniform Heating



















