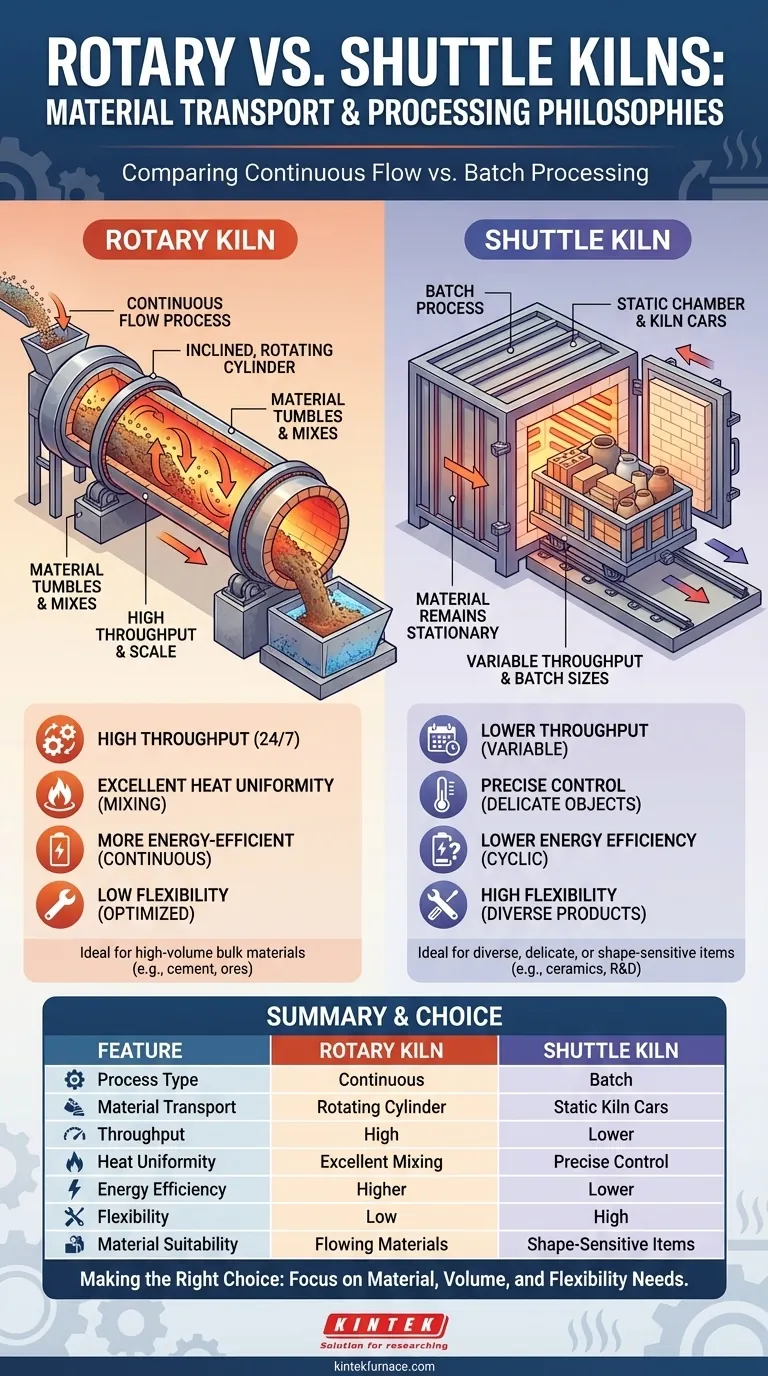
At their core, the material transport methods of rotary and shuttle kilns represent two fundamentally different processing philosophies. A rotary kiln moves material continuously through an inclined, rotating cylinder, while a shuttle kiln processes static material in discrete batches loaded on carts that move in and out of the kiln chamber.
The distinction is not merely mechanical; it is the difference between a continuous flow process (rotary) and a batch process (shuttle). This choice dictates everything from energy efficiency and throughput to the types of materials you can process.

The Mechanics of Material Transport
The way a kiln moves material through its heating zones is central to its design and application. The methods used by rotary and shuttle kilns could not be more different.
Shuttle Kilns: The Batch Process
A shuttle kiln operates on a batch-by-batch basis. Materials are first carefully arranged on a refractory cart, often called a kiln car.
The entire car is moved into the kiln chamber, the doors are sealed, and the programmed heating and cooling cycle begins. Once the cycle is complete, the doors open and the car is removed for unloading.
This method treats the entire load as a single, static unit throughout the firing process.
Rotary Kilns: The Continuous Flow
A rotary kiln is designed for a continuous, uninterrupted flow of material. It consists of a long, cylindrical shell lined with refractory material, which is slightly inclined and rotates slowly.
Material is fed into the elevated end of the cylinder. As the kiln rotates, the material tumbles and mixes, gradually moving down the incline towards the discharge end due to gravity.
There are no doors and no kiln cars; the process is dynamic and designed to run for extended periods without stopping.
Key Operational Differences
Understanding the transport mechanism reveals the deeper operational trade-offs between these two technologies. The choice is less about the kiln itself and more about the nature of your production goals.
Throughput and Scale
A rotary kiln is a high-throughput machine, ideal for large-scale industrial processes like cement manufacturing or mineral calcination where vast quantities of a single product are processed 24/7.
A shuttle kiln is suited for lower volumes, variable production schedules, or products requiring unique firing profiles. Its batch nature allows for frequent changes between different products.
Heat Exposure and Uniformity
In a rotary kiln, the tumbling action provides excellent mixing, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to heat. This is perfect for powders, granules, and slurries where consistent chemical and physical changes are desired throughout the bulk material.
In a shuttle kiln, the material remains stationary. This allows for precise control over the heating and cooling of specific, often delicate or large, objects like sanitaryware, technical ceramics, or art pottery.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither kiln is universally superior; they are specialized tools designed for different tasks. Recognizing their inherent limitations is key to making a sound investment.
Energy Efficiency
Rotary kilns are generally more energy-efficient for large-scale operations. They run continuously at a stable temperature, and energy is not wasted on cyclically heating and cooling the kiln structure or the heavy kiln cars used in shuttle kilns.
Shuttle kilns inherently lose more heat during each cycle when the doors are opened and the entire kiln mass must be reheated for the next batch.
Process Flexibility
Shuttle kilns offer unparalleled process flexibility. Each batch can have a completely different firing curve, temperature, and duration, making them ideal for R&D, pilot production, or manufacturing a diverse product portfolio.
Rotary kilns are highly inflexible. They are optimized for one specific material and process, and changing the setup is a major undertaking, resulting in significant downtime.
Material Suitability
The physical form of your material is a critical constraint. Rotary kilns excel with materials that can flow and tumble without being damaged.
Shuttle kilns are necessary for any item that must maintain its shape, position, or integrity, from large structural bricks to intricate ceramic components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision must be driven by your material, your production volume, and your need for flexibility.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of a bulk material (like cement, lime, or ores): The rotary kiln is the only logical choice due to its throughput and thermal efficiency.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse products, delicate objects, or variable batch sizes (like ceramics, refractories, or specialty chemicals): The shuttle kiln provides the essential control and flexibility for your operation.
Ultimately, choosing the right kiln begins with a clear understanding of whether your process is fundamentally continuous or batch-oriented.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rotary Kiln | Shuttle Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transport | Continuous flow via rotating cylinder | Batch process with static kiln cars |
| Process Type | Continuous | Batch |
| Throughput | High, for large-scale production | Lower, for variable or small batches |
| Heat Uniformity | Excellent mixing for powders/granules | Precise control for delicate/large objects |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher for continuous operations | Lower due to cyclic heating/cooling |
| Flexibility | Low, optimized for specific processes | High, ideal for diverse products and R&D |
| Material Suitability | Flowing materials (e.g., ores, slurries) | Shape-sensitive items (e.g., ceramics, bricks) |
Struggling to choose the right kiln for your lab or production needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to ensure optimal performance for materials like ceramics, ores, and more. Whether you need continuous processing with a rotary kiln or flexible batch handling with a shuttle kiln, we can help enhance your efficiency and outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What are the two main heating methods used in rotary kilns? Choose the Right One for Your Process
- What processes benefit from rotary furnaces in material sintering? Achieve Uniform Sintering for Powders and Ceramics
- What is the role of indirect-fired rotary kilns in energy production? Unlock Sustainable Waste-to-Energy Solutions
- What role does the atmosphere control system play in a rotary tube sintering furnace? Enhance Material Quality and Efficiency
- What industrial applications benefit from indirect-fired rotary kilns? Achieve Purity and Control in High-Temp Processing
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- In which industries is the rotary tube sintering furnace commonly used? Essential for Uniform High-Temp Processing
- What are the main components of a rotary tube sintering furnace? Discover the Key Parts for Uniform Heating



















