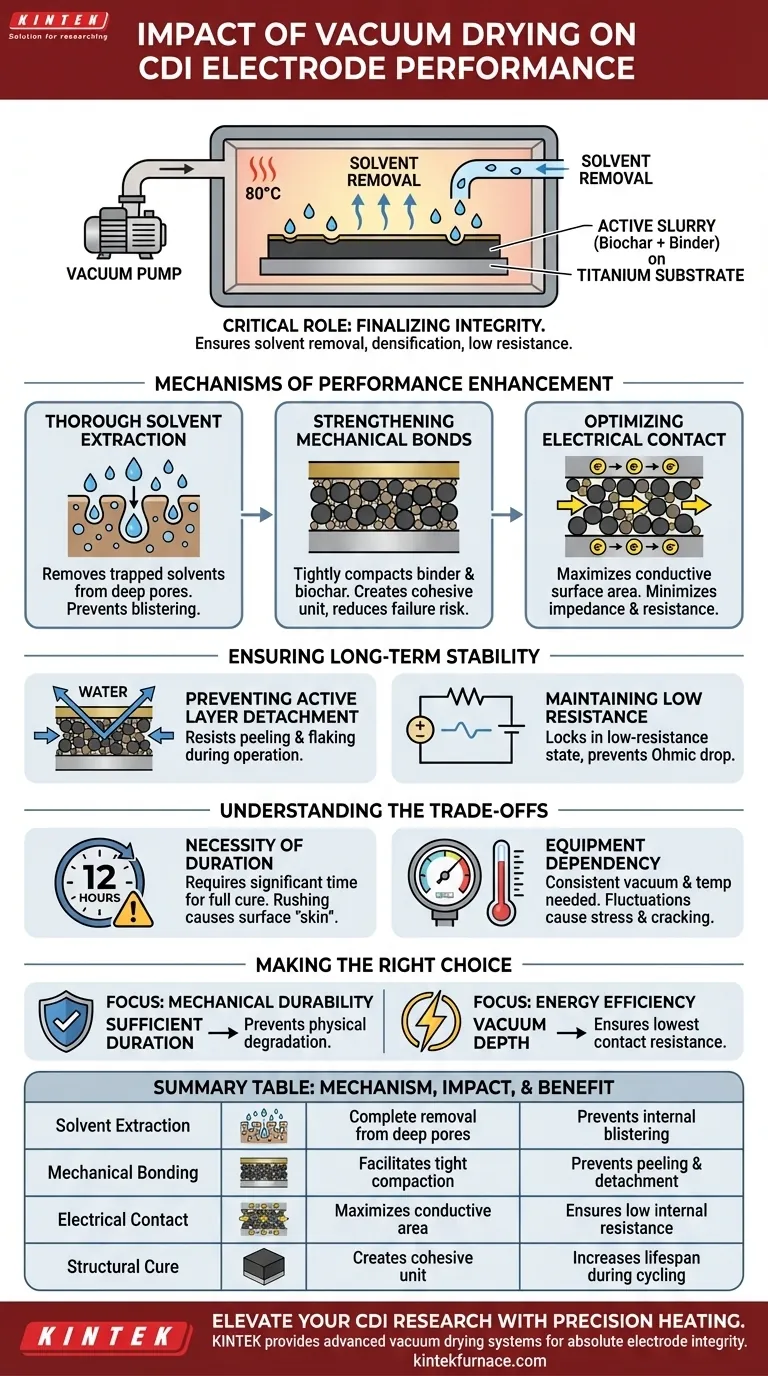
The critical role of a vacuum drying oven lies in its ability to finalize the structural and electrical integrity of CDI electrodes. By subjecting coated plates to controlled heat (typically 80°C) within a low-pressure environment for extended periods, the process ensures the absolute removal of solvents from the active slurry. This creates the robust foundation necessary for the electrode to withstand the rigors of electrochemical cycling.
The primary value of vacuum drying is not just moisture removal, but the densification of the electrode matrix. It prevents the active layer from delaminating and ensures low electrical resistance, directly influencing the lifespan and efficiency of the CDI system.

Mechanisms of Performance Enhancement
Thorough Solvent Extraction
The fundamental function of the vacuum oven is to eliminate liquid components from the electrode slurry.
Standard air drying often leaves microscopic pockets of solvent trapped deep within the porous structure. The low-pressure environment of a vacuum oven lowers the boiling point of these solvents, ensuring they are completely evacuated even from deep pores.
Strengthening Mechanical Bonds
For a CDI electrode to function, the active material (such as biochar) must adhere firmly to the current collector (titanium substrate).
Vacuum drying facilitates a tight compaction of the binder, biochar particles, and the substrate. This creates a cohesive unit rather than a loose coating, significantly reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
Optimizing Electrical Contact
Electrical performance relies on the quality of the contact points between the biochar particles and the titanium current collector.
Residual solvents act as insulators, impeding electron flow. By removing these solvents entirely, vacuum drying maximizes the conductive surface area contact, ensuring the electrode operates with minimal impedance.
Ensuring Long-Term Stability
Preventing Active Layer Detachment
One of the most common failure modes in CDI electrodes is "peeling," where the active material separates from the substrate.
The rigorous drying process creates a robust bond that resists the mechanical stresses of water flow and ion adsorption. This prevents the active layer from flaking off during operation, preserving the electrode's physical structure over time.
Maintaining Low Resistance
An electrode that retains solvent or lacks proper particle-to-substrate contact will exhibit higher internal resistance.
Vacuum drying locks in a low-resistance state before the electrode ever touches water. This prevents the gradual increase in resistance (ohmic drop) that typically degrades system performance during repetitive charging and discharging cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Duration
The process described requires a significant time investment, such as 12 hours at constant temperature.
Rushing this step to save manufacturing time is a false economy. Insufficient drying time results in a "skin" forming on the surface while solvents remain trapped inside, leading to eventual blistering or cracking when voltage is applied.
Equipment Dependency
This method relies on maintaining a consistent vacuum and temperature (80°C).
Fluctuations in pressure or temperature can lead to uneven drying gradients. This can cause internal stresses in the electrode coating, potentially leading to warping or micro-cracking even before the electrode is put into service.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of your CDI electrodes, consider these priorities when setting your drying parameters:
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability: Ensure the drying duration is sufficient (e.g., 12 hours) to fully cure the binder, preventing physical degradation like peeling.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Prioritize the vacuum depth to remove all insulating solvents, which ensures the lowest possible contact resistance between the biochar and titanium.
By treating the vacuum drying phase as a critical manufacturing gate rather than a simple drying step, you ensure the foundational stability required for a high-performance CDI system.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Impact on Electrode Performance | Long-term Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Solvent Extraction | Complete removal of solvents from deep pores | Prevents internal blistering and cracking |
| Mechanical Bonding | Facilitates tight compaction of binder and biochar | Prevents active layer peeling and detachment |
| Electrical Contact | Maximizes conductive surface area contact | Ensures low internal resistance and high efficiency |
| Structural Cure | Creates a cohesive unit on titanium substrate | Increases lifespan during electrochemical cycling |
Elevate Your CDI Research with Precision Heating
High-performance Capacitive Deionization (CDI) starts with meticulous electrode preparation. KINTEK provides the advanced vacuum drying systems necessary to ensure the absolute structural integrity and electrical conductivity of your materials.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable for your unique lab requirements. Our vacuum ovens deliver the consistent temperature control and low-pressure stability needed to prevent delamination and minimize impedance in your electrode matrices.
Ready to optimize your electrochemical systems? Contact us today to find the perfect drying solution and see how our expertise can accelerate your research results.
Visual Guide
References
- Geming Wang, Qirui Wu. Exploring a Porous Biochar-Based Capacitive Deionization Device for Phosphogypsum Wastewater Treatment in Undergraduate Experimental Teaching: Understanding, Development, and Practice. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c05966
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a final drying step necessary when restructuring adsorbents? Ensure Chemical Bonding & Industrial Safety
- What is the function of a flash furnace in sludge treatment? Essential Thermal Preparation for Phosphorus Recovery
- How do stirring equipment and temperature-controlled heating stages influence magnetic nanoparticle quality?
- Why must Ru/GNK catalysts undergo vacuum drying? Ensure Peak Performance with Safe Desorption
- What is the function of a laboratory vacuum drying oven when loading metal nanoparticles onto porous carbon particles?
- What is the firing temperature for sintering? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges
- How is a constant temperature drying oven utilized to establish moisture content gradients in wood? Master the Baseline
- How do thermal systems reveal anti-spalling mechanisms in CDE concrete? Explore Advanced Material Resilience



















