High-purity Argon functions as the critical stabilizer and transport medium in the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process. It serves two distinct but essential roles: it acts as an inert protective gas to prevent contamination and as a carrier gas to deliver chemical reactants to the substrate.
Core Takeaway: Argon’s chemically inert nature allows it to create a pristine reaction environment by displacing oxygen and moisture, while its steady flow ensures the uniform delivery of volatile precursors without participating in the reaction itself.
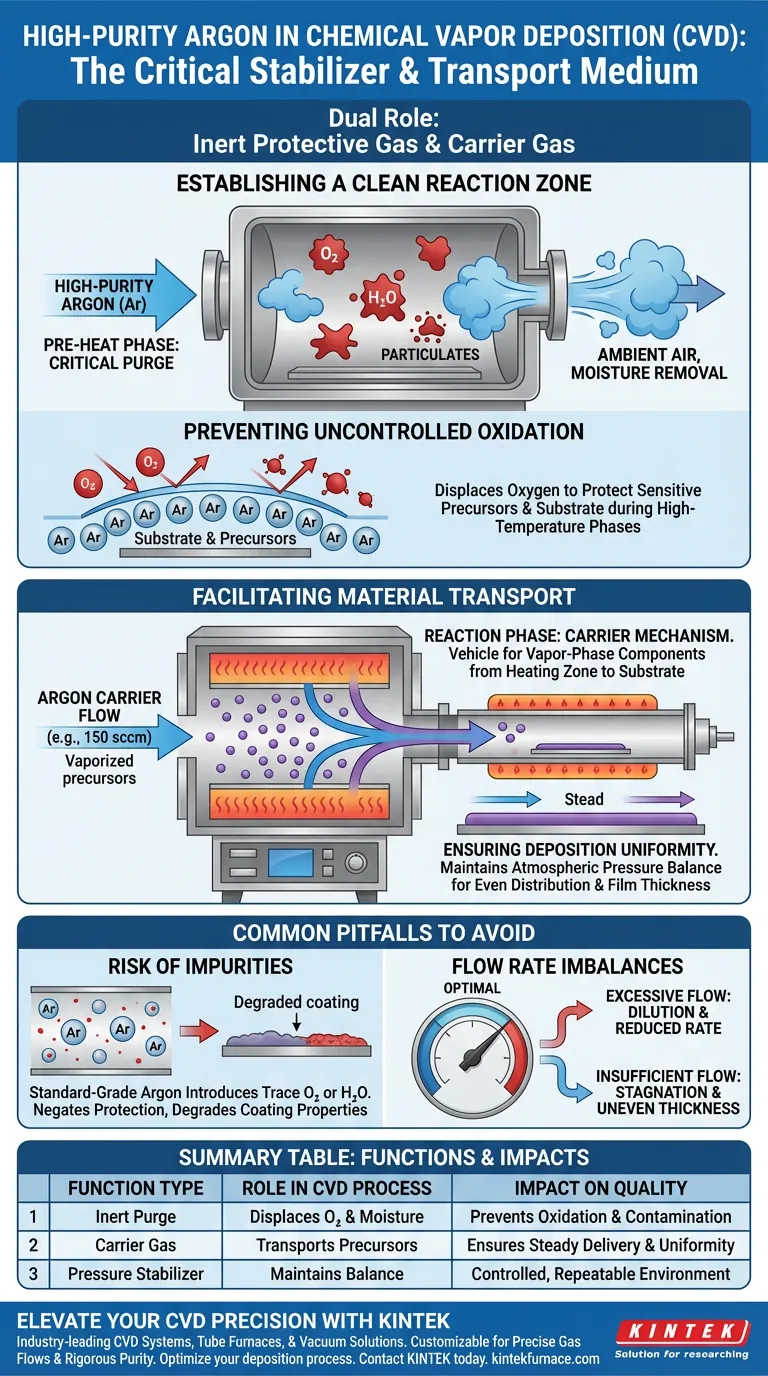
Establishing a Clean Reaction Zone
The first function of high-purity Argon is to condition the environment before the actual deposition begins.
The Critical Purge Phase
Prior to increasing the temperature, Argon is flushed through the furnace tube. This physical purging removes ambient air, moisture, and particulate matter from the chamber.
Preventing Uncontrolled Oxidation
By displacing oxygen, Argon prevents the uncontrolled oxidation of both the sensitive precursors and the substrate materials. This protection is vital during high-temperature phases where materials are most reactive and vulnerable to atmospheric contaminants.
Facilitating Material Transport
Once the reaction phase begins, Argon shifts roles to become an active component of the transport mechanics.
The Carrier Mechanism
During the reaction, a constant flow of Argon (e.g., 150 sccm) serves as a vehicle for vapor-phase components. It stabilizes the transport of these volatile materials from the primary heating zone directly to the reaction site on the substrate.
Ensuring Deposition Uniformity
The steady, controlled flow of Argon maintains atmospheric pressure balance within the furnace. This stability ensures that the precursors are distributed evenly, resulting in the uniformity of the deposited layer across the substrate surface.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While Argon is chemically inert, its physical management significantly impacts process outcomes.
The Risk of Impurities
The specification of "high-purity" is not optional. Using standard-grade Argon introduces trace amounts of oxygen or moisture, which negates the gas's protective function and can degrade the electrical or mechanical properties of the final coating.
Flow Rate Imbalances
While Argon assists in transport, the flow rate must be precisely calculated. Excessive flow can overly dilute the precursor concentration, reducing the deposition rate, while insufficient flow leads to stagnation and uneven film thickness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of Argon in your CVD process, align your control parameters with your specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is Film Purity: Prioritize the sourcing of certified high-purity Argon to strictly eliminate all potential sources of oxidation during the pre-heat and cooling stages.
- If your primary focus is Layer Uniformity: Focus on calibrating the Argon flow rate to ensure it stabilizes precursor transport without creating turbulence or dilution.
Ultimately, high-purity Argon provides the invisible, inert foundation that allows complex chemical deposition to occur with precision and repeatability.
Summary Table:
| Function Type | Role in CVD Process | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Purge | Displaces oxygen and moisture before heating | Prevents uncontrolled oxidation & contamination |
| Carrier Gas | Transports volatile precursors to the substrate | Ensures steady delivery & film thickness uniformity |
| Pressure Stabilizer | Maintains constant atmospheric balance | Provides a controlled, repeatable reaction environment |
Elevate Your CVD Precision with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect thin film requires more than just high-purity gas; it demands a high-performance environment. KINTEK provides industry-leading CVD systems, Tube furnaces, and Vacuum solutions designed to handle precise gas flows and rigorous purity standards.
Backed by our expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique research or production needs. Don't let atmospheric contaminants compromise your results—leverage our expertise in high-temperature lab equipment to secure superior material outcomes.
Ready to optimize your deposition process? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Aruna Vijayan, N. Sandhyarani. Efficient and sustainable hydrogen evolution reaction: enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of ReO<sub>3</sub>-incorporated Cu<sub>2</sub>Te catalysts. DOI: 10.1039/d4ya00023d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What assurances are provided regarding the quality and reliability of CVD furnaces? Ensure Precision and Durability for Your Lab
- When is CVD the preferred choice? Achieve Superior Thin Films for Complex Applications
- How is CVD used in the aerospace industry? Enhance Engine Performance with Protective Coatings
- What are the typical process temperature ranges for HT CVD and MT CVD processes? Optimize Your Coating Performance
- What are the characteristics and uses of diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings? Enhance Durability and Efficiency in Your Applications
- What are the main components of a CVD system? Key Parts for Precise Thin Film Deposition
- How does CVD compare to PVD in deposition rates? PVD is faster, but CVD offers versatility.
- What are the applications of CVD coating? Creating Durable, Functional Surfaces for Industry



















