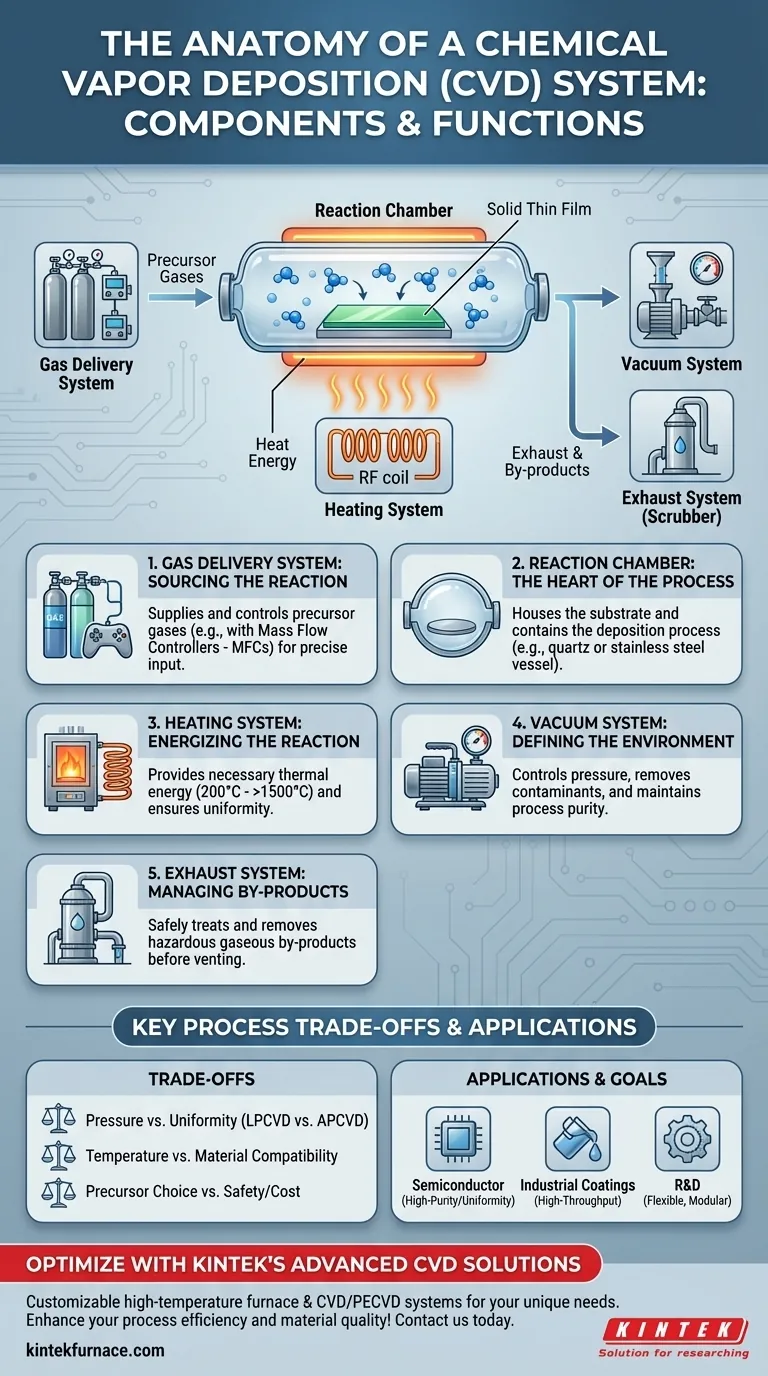
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system is a sophisticated apparatus designed for a single purpose: growing a solid thin film onto a surface from gaseous precursors. The primary components are a gas delivery system to supply the reactive chemicals, a reaction chamber to contain the process, a heating system to provide the necessary energy, a vacuum system to control the pressure and purity of the environment, and an exhaust system to safely remove by-products.
A CVD system is best understood not as a collection of parts, but as a highly controlled environment. Each component works in concert to precisely manage the temperature, pressure, and chemical composition required to trigger a specific gas-phase reaction that results in a solid material depositing onto a substrate.

The Anatomy of a CVD System: A Functional Breakdown
To truly understand a CVD system, we must look at how each component contributes to the overall process of film deposition. The system is designed to execute three key steps: introduce precursor gases, energize them to react, and form a solid film.
The Gas Delivery System: Sourcing the Reaction
The process begins with the precursors—the gaseous chemical building blocks for the final film.
The gas delivery system is responsible for storing these precursors and introducing them into the reaction chamber in precise, repeatable amounts. This is typically achieved using Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs), which regulate the flow rate of each gas with high accuracy.
The Reaction Chamber: The Heart of the Process
This is the sealed vessel, often a quartz tube or a stainless steel chamber, where the deposition takes place. It houses the substrate, which is the material (like a silicon wafer) onto which the thin film will be grown.
The chamber's design is critical for ensuring a clean, contained environment, preventing contamination from the outside atmosphere and ensuring the reactive gases are confined to the process area.
The Heating System: Energizing the Reaction
Most CVD processes are thermally driven, requiring high temperatures (from 200°C to over 1500°C) to break down the precursor gases and drive the chemical reaction.
This is the job of the heating system, which is typically a resistive tube furnace or an RF induction heater. A key requirement is temperature uniformity across the substrate to ensure the deposited film has a consistent thickness and properties.
The Vacuum System: Defining the Environment
The vacuum system serves two critical functions. First, it pumps out the air and any contaminants from the chamber before the process begins, creating a pure environment.
Second, it maintains the desired process pressure, which can range from high vacuum (low pressure) to near-atmospheric pressure. This is managed by a combination of vacuum pumps and a throttle valve, which work together to control how quickly gas is removed from the chamber.
The Exhaust System: Managing By-products
The chemical reactions that form the solid film also produce gaseous by-products, which, along with any unreacted precursors, must be safely removed from the chamber.
The exhaust system, or "scrubber," treats these often hazardous or corrosive gases before they are vented, preventing environmental contamination and ensuring operator safety.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
The configuration and operation of these components involve critical trade-offs that directly impact the quality, speed, and cost of the deposition process.
Pressure vs. Film Uniformity
Operating at low pressure (LPCVD) forces the gas molecules to travel further before colliding, which generally results in a more uniform film that can conformally coat complex, three-dimensional structures.
Conversely, operating at atmospheric pressure (APCVD) allows for much higher deposition rates but can lead to less uniform films due to gas-phase nucleation and less controlled flow dynamics.
Temperature vs. Material Compatibility
Higher temperatures typically increase the deposition rate and can improve film quality. However, the maximum temperature is often limited by the thermal stability of the substrate.
Choosing the right temperature is a balancing act between achieving the desired film properties and preventing damage or unwanted reactions with the underlying material.
Precursor Choice vs. Safety and Cost
The ideal precursor provides a high-quality film with minimal impurities. However, the most effective precursors can also be highly toxic, pyrophoric (igniting on contact with air), or extremely expensive.
Engineers must constantly weigh the desired film characteristics against the significant safety protocols and costs associated with handling hazardous materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal CVD system configuration depends entirely on your end goal. Understanding how the components serve the process allows you to prioritize the right features.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, uniform films (e.g., semiconductor manufacturing): You need a low-pressure (LPCVD) or plasma-enhanced (PECVD) system with high-precision mass flow controllers and excellent temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, industrial coatings (e.g., hardening tools): You may prioritize a simpler, faster atmospheric pressure (APCVD) system designed for rapid deposition on durable substrates.
- If your primary focus is research and development: You need a flexible, modular system with a wide operational window for temperature and pressure, along with programmable controls to easily test new processes.
By understanding these fundamental components and their functions, you can effectively control the conditions within the reaction chamber to engineer materials with specific, desired properties.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Delivery System | Supplies and controls precursor gases | Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs) |
| Reaction Chamber | Houses substrate and contains the deposition process | Quartz tube, stainless steel chamber |
| Heating System | Provides energy for chemical reactions | Resistive tube furnace, RF induction heater |
| Vacuum System | Controls pressure and ensures purity | Vacuum pumps, throttle valve |
| Exhaust System | Removes and treats hazardous by-products | Scrubbers |
Optimize your thin film deposition with KINTEK's advanced CVD solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization capability ensures precise performance for applications in semiconductors, industrial coatings, and R&D. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process efficiency and material quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More



















