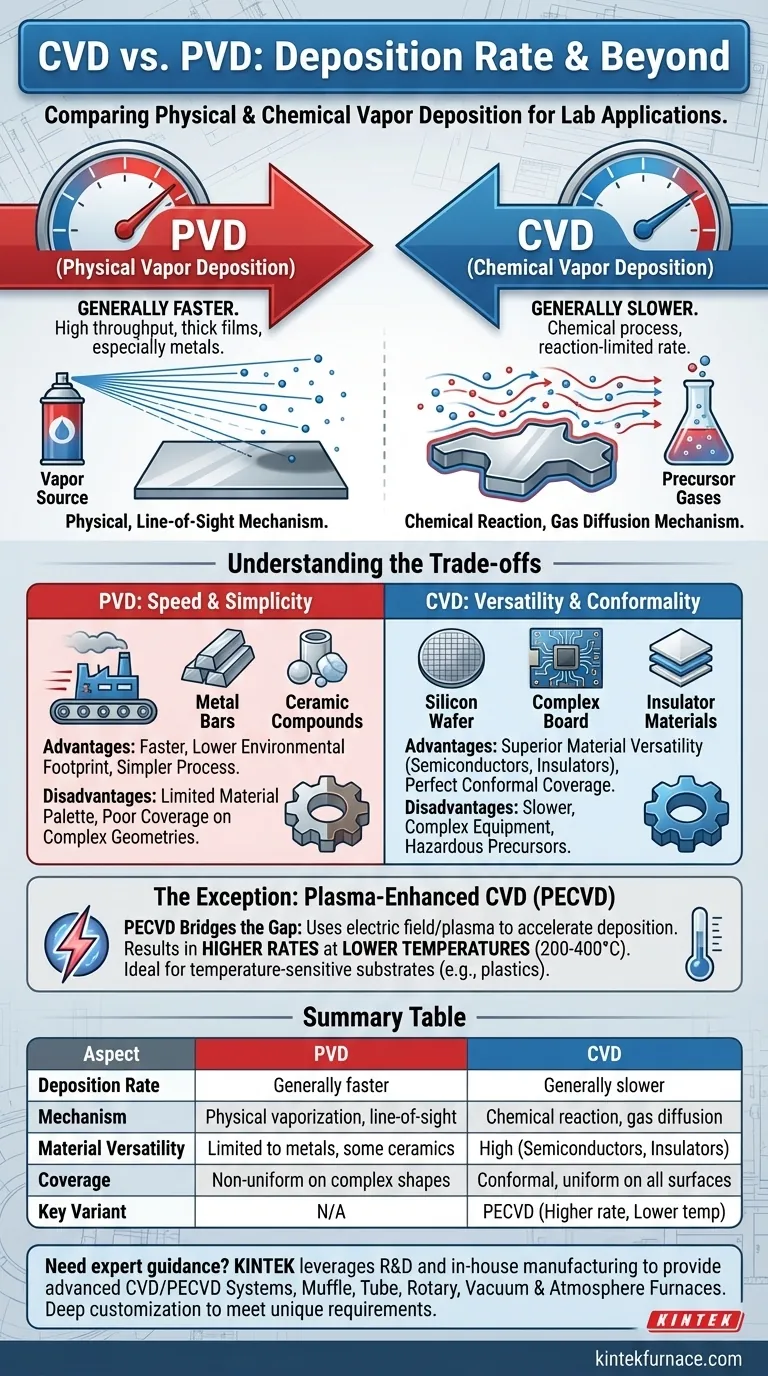
In a direct comparison, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes generally have faster deposition rates than conventional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This makes PVD a preferred method for applications that require high throughput or the rapid buildup of thick films, particularly with metallic materials.
The choice between PVD and CVD is not simply about speed. It's a fundamental trade-off between PVD's rapid, line-of-sight deposition and CVD's slower, more versatile chemical process that excels at material diversity and coating complex surfaces.
The Core Difference in Mechanism
The disparity in deposition rates stems from the fundamentally different ways these two technologies deposit material onto a substrate.
PVD: A Physical, Line-of-Sight Process
In PVD, a solid source material is physically vaporized into a plasma within a vacuum. These vaporized particles then travel in a straight line and condense onto the substrate.
This "line-of-sight" mechanism is direct and efficient, resulting in a rapid accumulation of material. It is analogous to spray painting, where the paint travels directly from the nozzle to the surface.
CVD: A Chemical Reaction Process
CVD, by contrast, relies on a chemical reaction. Precursor gases are introduced into a chamber, where they flow and diffuse around the substrate.
These gases then react on the hot surface of the substrate to form the desired solid film. The rate is often limited by the speed of this chemical reaction and the flow of reactant gases, making it inherently slower than the physical condensation of PVD.
When Deposition Rate Isn't the Only Factor
While PVD wins on raw speed, CVD is chosen for its unique capabilities that PVD cannot match. The "slower" process is often the only viable one for specific, high-value applications.
Material Versatility
PVD is primarily used for depositing metals and some ceramic compounds.
CVD's chemical nature gives it far greater versatility. It is the go-to method for depositing a wide range of materials, including critical semiconductors (like silicon) and insulators, which are fundamental to the electronics industry.
Conformal Coverage
PVD's line-of-sight deposition struggles to coat complex, 3D shapes uniformly. Areas not in the direct path of the vapor source receive little to no coating, creating a "shadowing" effect.
CVD's use of a diffuse, flowing gas allows it to deposit a highly uniform, or "conformal," layer over intricate topographies, ensuring complete and even coverage on all surfaces.
The Exception: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
A key variant, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), alters the traditional CVD trade-off by offering higher deposition rates at much lower temperatures.
How PECVD Accelerates Deposition
Instead of relying solely on high heat to drive the chemical reaction, PECVD uses an electric field to generate a plasma. This plasma excites the precursor gases, allowing the deposition reaction to occur more readily.
This activation método can result in higher deposition rates than conventional thermal CVD, bridging ઉત્પાદકતા the gap with PVD in some cases.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
Traditional CVD often requires very high temperatures, which can damage a substrate. PECVD operates at significantly lower temperatures, typically 200-400°C.
This makes PECVD ideal for depositing high-quality films onto temperature-sensitive substrates, such as plastics or pre-processed semiconductor wafers, without causing damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition technology requires a clear-eyed assessment of its advantages and disadvantages relative to your specific goal.
PVD: Speed vs. Simplicity
PVD is faster and often has a lower environmental footprint, as it does not typically involve the toxic byproduct gases common in CVD. However, it is limited in its material palette and cannot effectively coat complex geometries.
CVD: Versatility vs. Complexity
CVD offers superior material versatility and perfect conformal coverage. This comes at the cost of a slower deposition rate, more complex equipment, and the need to handle potentially hazardous precursor and byproduct gases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best technology is the one that meets your specific engineering requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput deposition of thick metal films on flat surfaces: PVD is the superior choice due to its unmatched speed.
- If your primary focus is depositing a perfectly uniform, conformal layer on a complex 3D structure: CVD is the necessary technology, and you must accept the slower deposition rate.
- If your primary focus is depositing semiconductor or insulator films, especially on temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD provides a critical balance of a reasonable deposition rate and a low-temperature process.
Ultimately, your decision should be guided by the material properties and geometric coverage you need, not by deposition rate alone.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD | CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Deposition Rate | Generally faster | Generally slower |
| Mechanism | Physical vaporization, line-of-sight | Chemical reaction, gas diffusion |
| Material Versatility | Limited to metals and some ceramics | High, including semiconductors and insulators |
| Coverage | Non-uniform on complex shapes | Conformal, uniform on all surfaces |
| Key Variant | N/A | PECVD (higher rate, lower temperature) |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right deposition technology for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working with metals, semiconductors, or complex geometries. Contact us today to optimize your process and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What is plasma-deposited silicon nitride, and what are its properties? Discover Its Role in Solar Cell Efficiency
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties



















