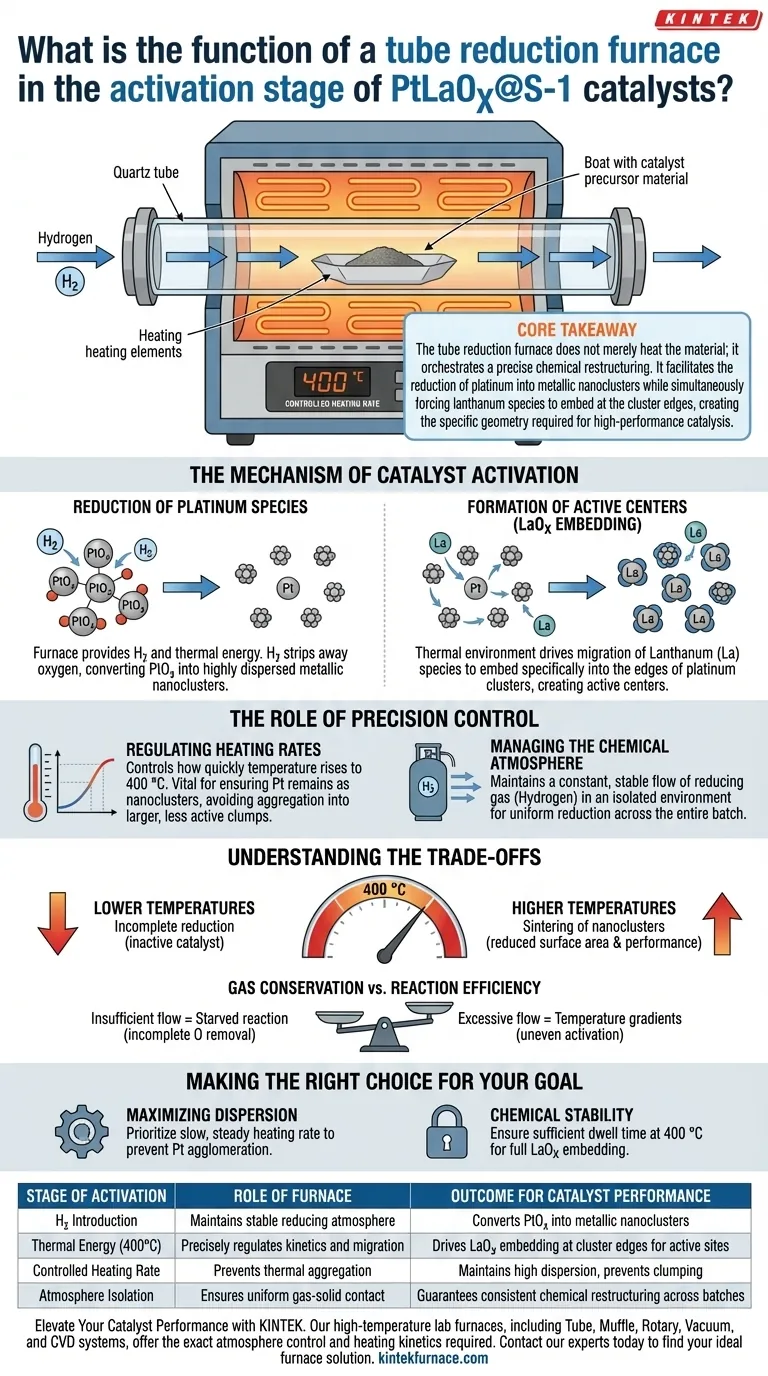
The primary function of a tube reduction furnace in the activation of PtLaOx@S-1 catalysts is to provide a strictly controlled thermal and chemical environment, typically at 400 °C under hydrogen gas. This equipment is essential for transforming precursor materials into active catalytic centers by precisely regulating heating rates and gas flow.
Core Takeaway The tube reduction furnace does not merely heat the material; it orchestrates a precise chemical restructuring. It facilitates the reduction of platinum into metallic nanoclusters while simultaneously forcing lanthanum species to embed at the cluster edges, creating the specific geometry required for high-performance catalysis.

The Mechanism of Catalyst Activation
The tube reduction furnace is the tool that transitions the catalyst from a passive precursor state to an active chemical agent. This transformation occurs through two distinct but simultaneous processes.
Reduction of Platinum Species
The furnace introduces a continuous flow of hydrogen gas (H2).
Under the thermal energy provided by the furnace, the hydrogen reacts with the oxidized platinum species.
This reaction strips away oxygen, converting the platinum from an oxidized state into highly dispersed metallic nanoclusters.
Formation of Active Centers (LaOx Embedding)
While the platinum is being reduced, the thermal environment drives the movement of lanthanum (La) species.
The process encourages these species to migrate and embed themselves specifically into the edges of the platinum clusters.
This results in "single-disperse LaOx" structures, which are critical for constructing the catalyst's high-performance active centers.
The Role of Precision Control
A standard oven cannot achieve the necessary results because it lacks the dynamic control over atmosphere and kinetics that a tube furnace provides.
Regulating Heating Rates
The furnace controls how quickly the temperature rises to the target of 400 °C.
This regulation is vital because the heating rate influences the final size of the metal particles.
A controlled rate ensures the platinum remains as nanoclusters rather than aggregating into larger, less active clumps.
Managing the Chemical Atmosphere
The tube design allows for a isolated environment where the concentration of reducing gas (Hydrogen) is constant.
By maintaining a stable flow, the furnace ensures that the reduction reaction reaches completion uniformly across the entire batch of catalyst material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube reduction furnace is the optimal tool for this process, understanding its operational sensitivities is critical for reproducibility.
Temperature Sensitivity
The specific target of 400 °C is not arbitrary; it is the activation threshold for this specific material system.
Deviating from this temperature involves a trade-off: lower temperatures may result in incomplete reduction (leaving the catalyst inactive), while higher temperatures could cause the nanoclusters to sinter (merge), drastically reducing surface area and performance.
Atmosphere Purity vs. Flow Rate
There is a balance between gas conservation and reaction efficiency.
Insufficient hydrogen flow can lead to a "starved" reaction environment where oxygen is not fully removed from the platinum.
Conversely, excessive flow without proper thermal transfer can lead to temperature gradients within the tube, causing uneven activation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of PtLaOx@S-1 catalysts, you must tailor the furnace operation to your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Dispersion: Prioritize a slow, steady heating rate to prevent the agglomeration of platinum nanoclusters during the transition phase.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Stability: Ensure the dwell time at 400 °C is sufficient to allow the full embedding of LaOx species into the platinum edges, locking in the structure.
The tube reduction furnace is the architect of the catalyst's microstructure, translating raw chemical potential into a defined, high-performance active state.
Summary Table:
| Stage of Activation | Role of Tube Reduction Furnace | Outcome for Catalyst Performance |
|---|---|---|
| H2 Introduction | Maintains stable reducing atmosphere | Converts platinum oxides into metallic nanoclusters |
| Thermal Energy (400°C) | Precisely regulates kinetics and migration | Drives LaOx embedding at cluster edges for active sites |
| Controlled Heating Rate | Prevents thermal aggregation | Maintains high dispersion and prevents particle clumping |
| Atmosphere Isolation | Ensures uniform gas-solid contact | Guarantees consistent chemical restructuring across batches |
Elevate Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a passive precursor and a high-performance catalyst. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions, including Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, specifically engineered to meet the rigorous demands of material activation.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our high-temperature lab furnaces offer the exact atmosphere control and heating kinetics required for complex processes like PtLaOx@S-1 reduction. Whether you need a standard setup or a fully customizable system tailored to your unique research needs, KINTEK is your partner in laboratory excellence.
Ready to optimize your activation process?
Contact our experts today to find your ideal furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Guilin Wei, Xingwen Feng. Embedding Monodisperse LaO <i> <sub>x</sub> </i> Into Pt Nanoclusters for Ultra‐Stable and Efficient Hydrogen Isotope Oxidation. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202504224
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What industrial applications commonly use tube furnaces? Achieve Precise Heating for Advanced Manufacturing
- What core task does a tubular vacuum sintering furnace perform? Optimizing Confined Carbon Chain Synthesis
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in PEO to porous carbon conversion? Mastering Molecular Engineering
- How does the strong process performance of vacuum tube furnaces benefit users? Unlock Superior Quality and Efficiency
- How does a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace work? Achieve Superior Heating Efficiency and Uniformity
- What are the primary functions of a high-precision tube resistance furnace? Optimize Chloride-Doped Composite Synthesis
- Why is uniform heating important in horizontal furnaces? Ensure Material Quality and Process Efficiency
- How does a split tube furnace compare to non-split tube furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab



















