In short, tube furnaces are indispensable in advanced manufacturing and research for any process that demands precise, uniform heating within a highly controlled atmosphere. They are commonly used in industries like electronics, materials science, and new energy for synthesizing materials, heat-treating components, and developing next-generation technologies like lithium-ion batteries.
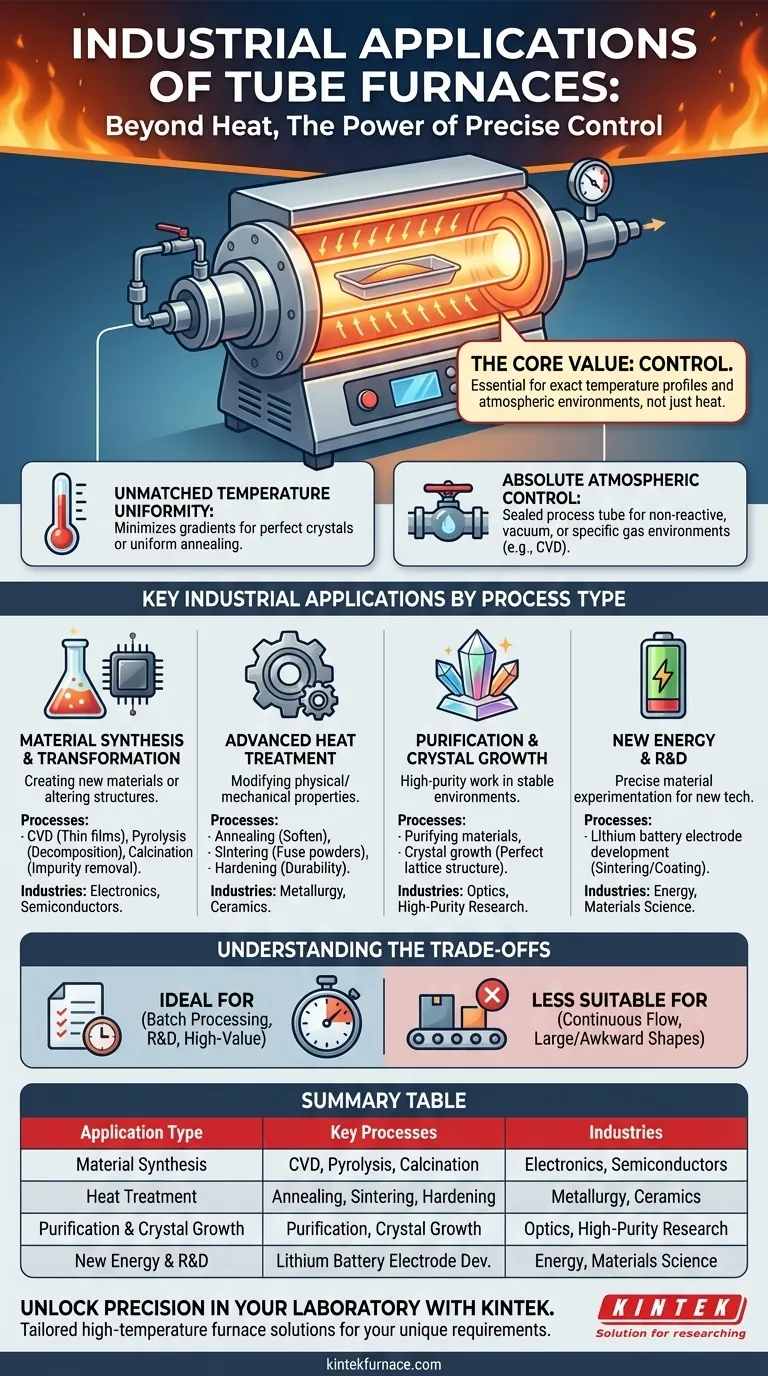
The core value of a tube furnace is not simply heat, but control. These instruments are chosen when the exact temperature profile and atmospheric environment are non-negotiable for achieving a specific material property or chemical reaction.
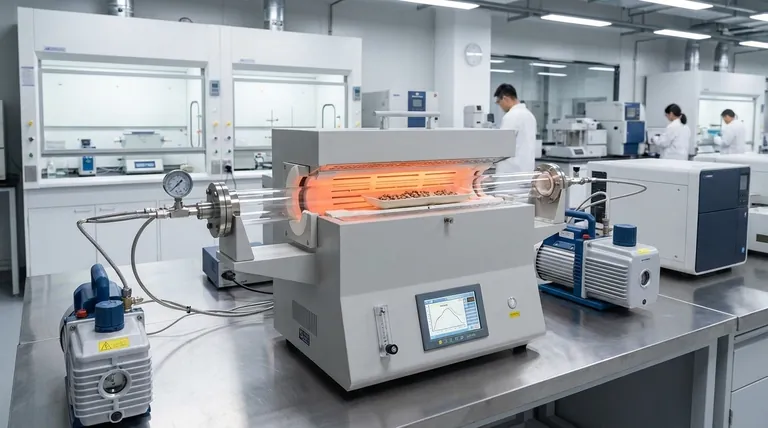

The Core Principle: Why Tube Furnaces?
To understand their applications, you must first understand why tube furnaces are the superior choice for certain tasks. The decision almost always comes down to two key factors: uniformity and atmosphere.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical heating chamber of a tube furnace surrounds the sample, which is held within a process tube. This design ensures that heat radiates evenly from all directions, minimizing temperature gradients across the sample.
This level of uniformity is critical for processes where even minor temperature variations could ruin the outcome, such as growing a perfect crystal or uniformly annealing a metal part.
Absolute Atmospheric Control
The sealed nature of the process tube is the furnace's defining feature. It allows an operator to create a specific, non-reactive environment.
This is achieved by either pulling a vacuum to remove air or by purging the chamber with a specific gas. This control is essential for preventing unwanted oxidation or for introducing reactive gases required for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Key Industrial Applications by Process Type
Instead of just listing industries, it's more useful to group applications by the fundamental process being performed. This clarifies the "why" behind their use.
Material Synthesis and Transformation
This category includes creating new materials or fundamentally altering their chemical structure.
Applications include Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) for creating thin films in semiconductor manufacturing, pyrolysis for decomposing organic materials in a non-oxygen environment, and calcination to drive off impurities and create stable materials like catalysts.
Advanced Heat Treatment
This involves modifying the physical and mechanical properties of a material through controlled heating and cooling cycles.
Tube furnaces are ideal for annealing to soften metals and relieve internal stresses, sintering to fuse powders into a solid mass for ceramics and metallurgy, and hardening to increase the durability of components.
Purification and Crystal Growth
The ability to maintain a pristine, controlled environment makes tube furnaces essential for high-purity work.
They are used for purifying materials by heating them until contaminants vaporize and for crystal growth, where slow, uniform cooling in a stable atmosphere is required to form a perfect lattice structure for electronics or optics.
New Energy and R&D
The development of new technologies relies heavily on precise material experimentation.
Tube furnaces are a cornerstone in materials science labs and are critical for developing lithium battery electrodes, which require precise sintering and coating of materials under controlled atmospheres to achieve optimal performance and longevity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Batch Processing, Not Continuous Flow
A tube furnace processes a finite amount of material in a discrete batch. It cannot handle the continuous, high-volume throughput that a conveyor furnace can.
This makes them ideal for R&D, pilot production, and high-value components, but less suitable for mass-producing low-cost bulk materials.
Sample Size and Geometry Constraints
The workpiece must fit within the process tube. This inherently limits the size and shape of the objects that can be processed.
Large or awkwardly shaped components are not a good fit for a standard tube furnace and may require a different solution, like a box or bell furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a tube furnace should be driven by the technical requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials or thin-film coatings: A tube furnace is essential for processes like CVD and synthesis, where atmospheric purity dictates the outcome.
- If your primary focus is modifying the properties of an existing material: A tube furnace provides the unparalleled temperature uniformity needed for reliable annealing, sintering, or hardening.
- If your primary focus is high-purity research and development: A tube furnace offers the controlled, isolated environment required for repeatable and accurate experimentation.
Ultimately, choosing a tube furnace is a decision to prioritize precision and control over sheer volume or speed.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Key Processes | Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | CVD, Pyrolysis, Calcination | Electronics, Semiconductors |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Sintering, Hardening | Metallurgy, Ceramics |
| Purification & Crystal Growth | Purification, Crystal Growth | Optics, High-Purity Research |
| New Energy & R&D | Lithium Battery Electrode Development | Energy, Materials Science |
Unlock Precision in Your Laboratory with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in electronics, materials science, or new energy, we can help you achieve superior temperature control and atmospheric precision for processes like synthesis, heat treatment, and more. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your research and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















