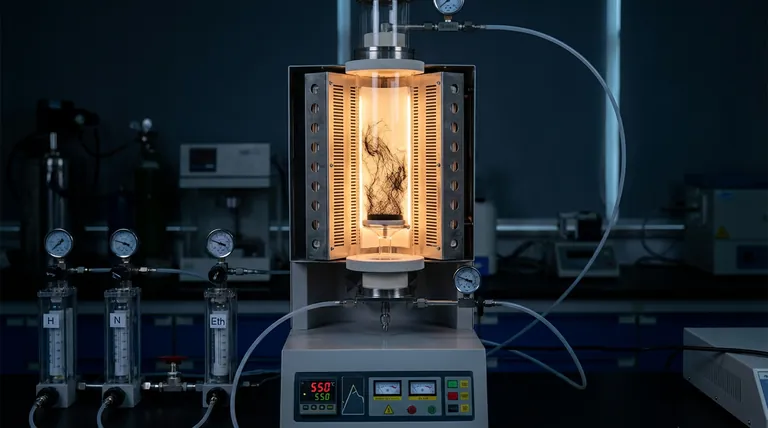
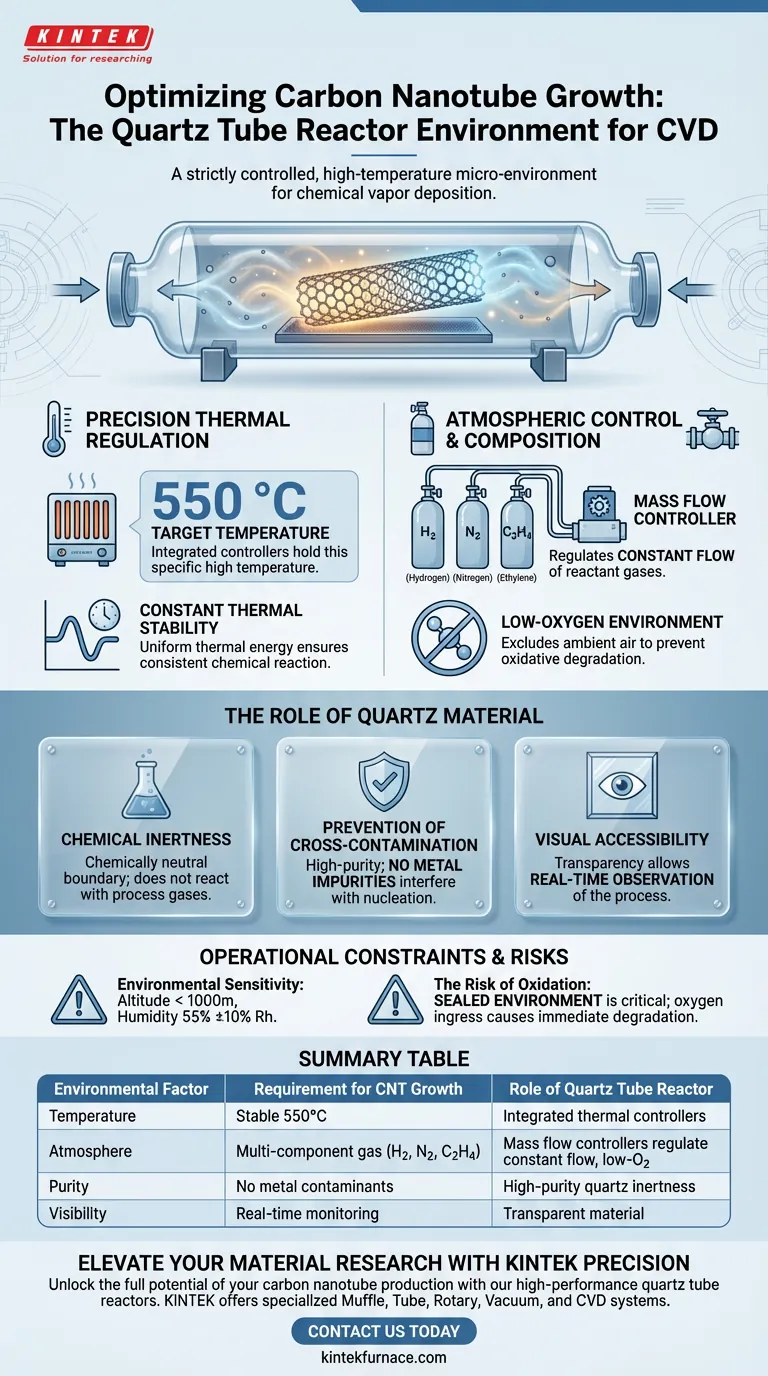
A quartz tube reactor creates a strictly controlled, high-temperature micro-environment essential for the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process. It functions as a sealed chamber that maintains specific thermal conditions (typically 550 °C) while regulating a multi-component gas mixture to facilitate carbon nanotube reduction and growth.
The reactor isolates the growth process to ensure three critical factors: a precise, constant temperature; a low-oxygen, constant-flow gas atmosphere; and a chemically inert boundary that prevents contamination.

Precision Thermal Regulation
Target Temperature Maintenance
The reactor is integrated with thermal controllers designed to reach and hold specific high temperatures. For this specific CVD process, the environment is typically maintained at 550 °C.
Constant Thermal Stability
Consistency is paramount during the growth phase. The system provides a constant-temperature environment, ensuring that the thermal energy required for the chemical reaction remains uniform throughout the deposition process.
Atmospheric Control and Composition
Multi-Component Gas Mixture
The reactor creates a specific chemical atmosphere by introducing a controlled mixture of gases. This typically includes Hydrogen (H2), Nitrogen (N2), and Ethylene (C2H4) to drive the reduction and growth of the nanotubes.
Mass Flow Regulation
To maintain the correct stoichiometry, the reactor utilizes mass flow controllers. These devices ensure a constant flow of the reactant gases, preventing fluctuations that could alter the growth rate or structure of the nanotubes.
Low-Oxygen Environment
A critical function of the sealed quartz environment is the exclusion of ambient air. The reactor maintains a low-oxygen condition to prevent the oxidative degradation of the fibers, which would occur rapidly if exposed to oxygen at these high temperatures.
The Role of Quartz Material
Chemical Inertness
The high-purity quartz material provides a chemically neutral boundary for the reaction. It possesses excellent chemical inertness, ensuring the tube does not react with process gases or introduce impurities into the growth environment.
Prevention of Cross-Contamination
Unlike metal reactors, high-purity quartz contains no metal impurities. This prevents cross-contamination, ensuring that foreign metallic particles do not interfere with the nucleation or growth of the carbon nanotubes.
Visual Accessibility
The transparency of the quartz allows for real-time observation of the process inside the environment. This enables operators to visually monitor the wire-feeding process and the status of the reaction without breaching the sealed environment.
Understanding the Operational Constraints
Environmental Sensitivity
While the internal environment is robust, the external equipment is sensitive to its surroundings. To function correctly, the system typically requires an installation altitude below 1000 meters and specific ambient humidity (55% ±10% Rh) and temperature ranges.
The Risk of Oxidation
The system's reliance on a sealed environment is its primary point of failure. If the seal is compromised, the ingress of oxygen into the 550 °C chamber will lead to immediate oxidative degradation of the carbon structures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a quartz tube reactor for CVD, align your operational protocols with your specific output requirements.
- If your primary focus is Purity: Leverage the inert nature of the quartz tube to prevent metal cross-contamination, which is critical for high-grade electronic applications.
- If your primary focus is Structural Consistency: Prioritize the calibration of mass flow and thermal controllers to ensure the constant-flow and constant-temperature conditions are never violated.
The success of carbon nanotube growth relies not just on the heat, but on the precise isolation and stability of the reaction environment.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Factor | Requirement for CNT Growth | Role of Quartz Tube Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Stable 550 °C | Integrated thermal controllers ensure constant-temperature stability. |
| Atmosphere | Multi-component gas (H2, N2, C2H4) | Mass flow controllers regulate a constant-flow, low-oxygen environment. |
| Purity | No metal contaminants | High-purity quartz provides chemical inertness and prevents cross-contamination. |
| Visibility | Real-time monitoring | Transparent material allows for visual observation of the CVD process. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your carbon nanotube production with our high-performance quartz tube reactors. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your laboratory's exacting needs. Whether you require precise thermal stability or a contamination-free growth environment, our customizable high-temperature furnaces are designed to deliver consistent, high-purity results.
Ready to optimize your CVD process? Contact us today to discuss your unique project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Suma Ayyagari, Marwan Al‐Haik. Mitigating Crack Propagation in Hybrid Composites: An Experimental and Computational Study. DOI: 10.3390/jcs8040122
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is CVD considered a scalable process? Unlock High-Volume, Uniform Coatings for Your Industry
- What are the benefits of CVD coatings in aerospace and automotive industries? Boost Durability and Efficiency
- What forms of energy can be applied in CVD to initiate chemical reactions? Explore Heat, Plasma, and Light for Optimal Thin Films
- What are the key features of CVD tube furnaces for 2D material processing? Unlock Precision Synthesis for Superior Materials
- Why is CVD suitable for dense, uniform films on irregular surfaces? Master Conformal Coating for Complex Shapes
- What are the practical applications of gate media prepared by CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Advanced Electronics and More
- What are the advantages of CVD over PVD? Superior Conformality for Complex Shapes
- What is the role of a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system in the preparation of h-BN films? Precision & Scalability



















