In choosing a deposition technology, the primary advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) over Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are its superior ability to create uniform coatings on complex, three-dimensional surfaces and its versatility in synthesizing a wide range of materials. While PVD excels in depositing very pure films on flat surfaces, CVD's unique mechanism allows it to "grow" a film that perfectly conforms to any geometry.
While PVD physically "paints" a surface from a direct line of sight, CVD chemically "grows" a film from a reactive gas that envelops the entire object. This fundamental difference makes CVD the superior choice for coating intricate geometries, even though it introduces greater process complexity.
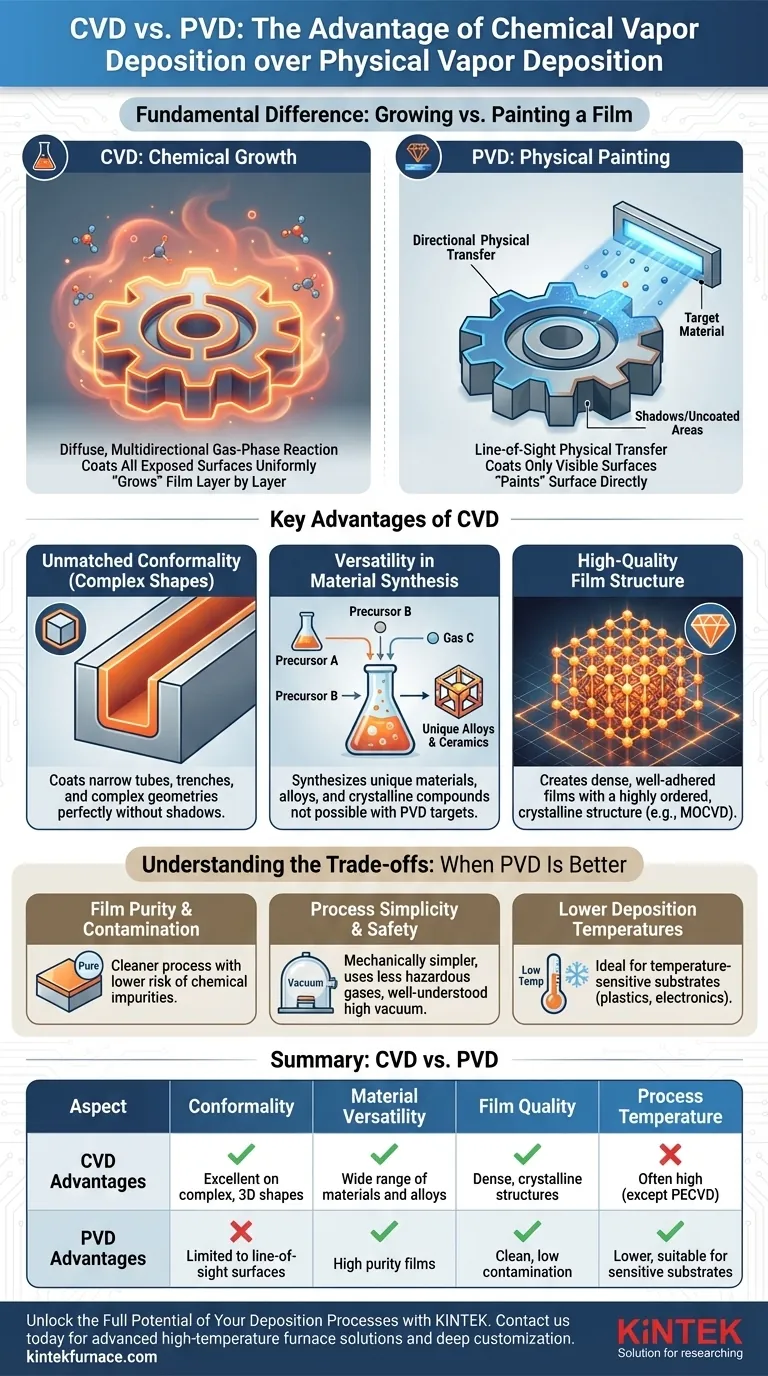
The Fundamental Difference: Growing vs. Painting a Film
To understand the advantages of each method, you must first understand their core mechanisms. They are not interchangeable processes; they represent two distinct philosophies for building a thin film.
How CVD Works: A Chemical Reaction
Chemical Vapor Deposition uses volatile chemical precursors, which are introduced as gases into a reaction chamber containing the substrate.
Heat or pressure is then applied, initiating a chemical reaction directly on the substrate's surface. This reaction breaks down the precursor gases, and the desired material is deposited, "growing" a solid film layer by layer.
Because this process occurs in a gaseous state, the deposition is diffuse and multidirectional. The reactive gas envelops the substrate, reaching every exposed surface equally.
How PVD Works: A Physical Transfer
Physical Vapor Deposition involves the physical transfer of material in a high-vacuum environment. A solid source material, known as a "target," is vaporized into a plasma through methods like sputtering or evaporation.
These vaporized particles then travel in a straight, line-of-sight path until they strike the substrate and condense, forming the coating.
This process is analogous to spray painting. Only the surfaces directly visible to the source are coated effectively.
Key Advantages of CVD
The chemical, gas-phase nature of CVD gives it distinct advantages in specific applications where PVD would fail.
Unmatched Conformality for Complex Shapes
This is the single most important advantage of CVD. Because the reactive gas surrounds the object, CVD coats all surfaces with exceptional uniformity.
This includes the inside of narrow tubes, deep trenches, and around sharp corners on complex mechanical parts. PVD, being line-of-sight, cannot achieve this and would leave "shadows" or uncoated areas on such geometries.
Versatility in Material Synthesis
CVD allows for the creation of materials that may not exist in a stable, solid form suitable for a PVD target.
By precisely mixing different precursor gases, engineers can synthesize a vast range of materials, including unique alloys, ceramics, and crystalline compounds. This provides a level of material engineering flexibility that is difficult to achieve with PVD.
High-Quality Film Structure
The conditions of a CVD process, often involving high temperatures, are ideal for growing dense, well-adhered films with a highly ordered or crystalline structure.
Processes like Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD) are critical in manufacturing high-performance semiconductors because they allow for the growth of perfect crystal layers, which is essential for device performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When PVD Is Better
CVD's advantages do not make it universally superior. The complexity and chemistry of the process create trade-offs where PVD is the clear winner.
Film Purity and Contamination
PVD is often considered a "cleaner" process. Since it physically transfers an already pure source material, there is a lower risk of incorporating unwanted elements into the film.
CVD relies on chemical reactions, which can sometimes be incomplete. This can leave behind residual elements from the precursor molecules (like carbon or hydrogen) as impurities in the final film.
Process Simplicity and Safety
The PVD process is mechanically simpler and operates in a high vacuum, which is a well-understood and controlled environment.
CVD equipment is more complex, requiring precise control of gas flow rates, pressure, and temperature. Furthermore, it often involves the use of toxic, corrosive, or flammable precursor gases and produces hazardous byproducts that must be carefully managed.
Lower Deposition Temperatures
While some forms of CVD exist that operate at lower temperatures (like PECVD), many traditional CVD processes require very high heat to initiate the chemical reaction.
PVD processes can typically be run at much lower temperatures. This makes PVD the ideal choice for coating temperature-sensitive substrates, such as plastics or certain electronic components, that would be damaged or destroyed by high-temperature CVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct technology requires a clear understanding of your primary goal and the geometry of the part you need to coat.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D geometries: CVD is the superior choice due to its excellent, uniform coverage on all surfaces.
- If your primary focus is depositing the purest possible film on a simple surface: PVD is often preferred for its clean, physical transfer mechanism and lower risk of chemical contamination.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials: PVD is generally the safer option as many of its processes run at significantly lower temperatures than traditional CVD.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing unique compounds or highly crystalline films: CVD offers greater flexibility through the combination of precursor gases and precise control over the growth process.
Understanding the core mechanism—chemical growth versus physical painting—is the key to selecting the right deposition technology for your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD Advantages | PVD Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Conformality | Excellent on complex, 3D shapes | Limited to line-of-sight surfaces |
| Material Versatility | Wide range of materials and alloys | High purity films |
| Film Quality | Dense, crystalline structures | Clean, low contamination |
| Process Temperature | Often high (except PECVD) | Lower, suitable for sensitive substrates |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Deposition Processes with KINTEK
Struggling to choose between CVD and PVD for your unique application? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including our specialized CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, whether you need uniform coatings on complex geometries or tailored material synthesis.
Don't let process complexity hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What methods are used to analyze and characterize graphene samples? Unlock Key Techniques for Accurate Material Analysis
- How does a PECVD system contribute to (n)poly-Si layers? High-Throughput In-Situ Doping Explained
- What are the technical advantages of using a CVD system? Optimize Carbon Nanotube Growth for Thermal Conductivity
- What environments does a PECVD system provide for silicon nanowires? Optimize Growth with Precise Thermal Control
- What is the necessity of high-bias gas ion cleaning? Achieve Atomic-Level Coating Adhesion



















