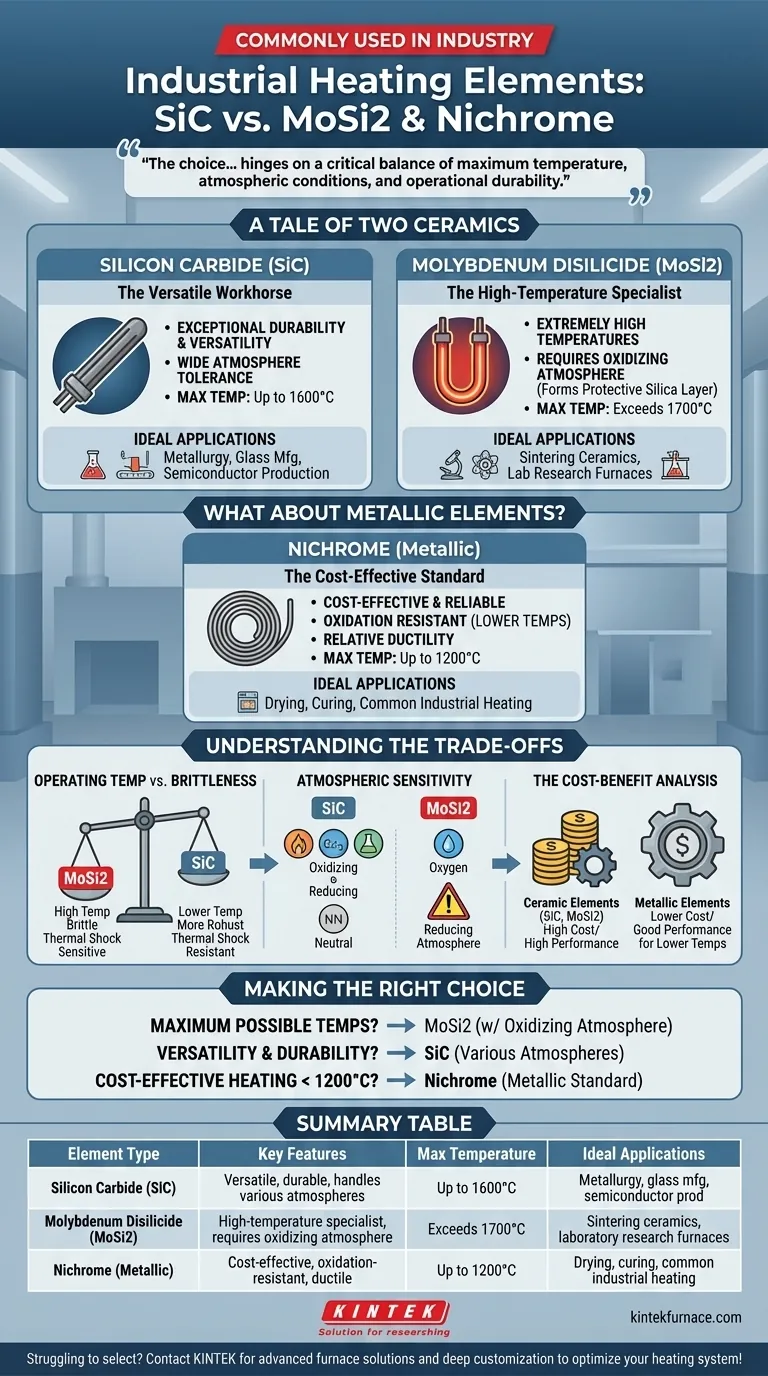
In industrial applications, two of the most common high-temperature heating elements are silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2). These advanced ceramic materials are chosen for their ability to operate reliably at temperatures where traditional metallic elements would fail.
The choice between an industrial heating element is rarely about finding the "best" one, but about matching the material's unique properties to the specific demands of the process. The decision hinges on a critical balance of maximum temperature, atmospheric conditions, and operational durability.
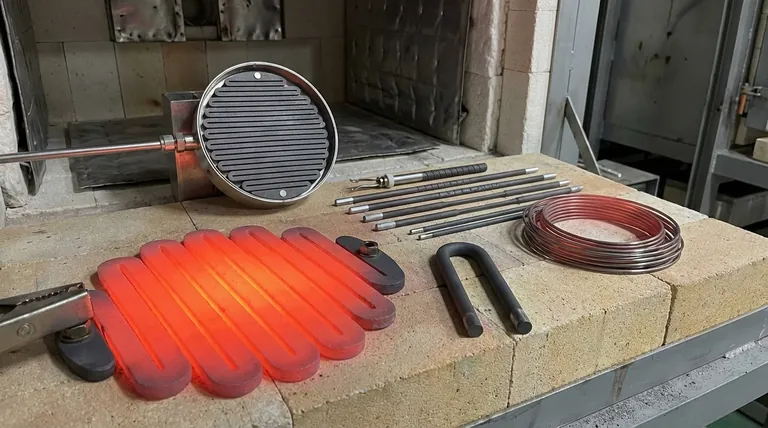

A Tale of Two Ceramics: SiC vs. MoSi2
While both SiC and MoSi2 are ceramic-based, they serve different roles in high-temperature environments. Understanding their core characteristics is the first step to making an informed choice.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The Versatile Workhorse
Silicon carbide elements are known for their exceptional durability and versatility. They are widely used across a range of industries, including metallurgy, glass manufacturing, and semiconductor production.
Their key strength is the ability to operate in a wide variety of furnace atmospheres. This makes them a reliable, all-around choice for many high-temperature applications.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): The High-Temperature Specialist
Molybdenum disilicide elements are engineered for one primary purpose: achieving extremely high operating temperatures, often exceeding those possible with SiC.
At high temperatures in an oxidizing atmosphere, MoSi2 forms a protective layer of silica glass on its surface. This layer "heals" itself, preventing further oxidation of the element and allowing it to function in extreme heat for processes like firing advanced ceramics or in laboratory research furnaces.
What About Metallic Elements?
It is critical to note that ceramic elements are typically reserved for very high-temperature applications. For a vast number of industrial processes, metallic elements are the standard.
The Role of Nichrome
The most common metallic heating element is an alloy called nichrome (typically 80% nickel, 20% chromium). It is favored for applications operating up to approximately 1200°C (2200°F).
Nichrome is valued for its high electrical resistance, strong resistance to oxidation at lower temperatures, and relative ductility compared to ceramics, making it easy to form and less prone to breaking from mechanical shock.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating element involves navigating a series of technical and economic trade-offs. Misunderstanding these can lead to premature failure and costly downtime.
Operating Temperature vs. Brittleness
While MoSi2 elements can reach the highest temperatures, they are also quite brittle, especially at lower temperatures during heat-up and cool-down cycles. SiC is generally more robust and resistant to thermal shock, making it a more forgiving material.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
This is a critical distinction. SiC can tolerate various atmospheres. In contrast, MoSi2 requires an oxidizing atmosphere (one with oxygen present) to maintain its protective silica layer. Using it in a reducing atmosphere can lead to rapid degradation and failure.
The Cost-Benefit Analysis
High-performance ceramic elements like SiC and MoSi2 are significantly more expensive than metallic elements like nichrome. Their use is only justified when the process temperature demands it. For many drying, curing, or heating applications, nichrome provides the necessary performance at a fraction of the cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection should be dictated entirely by the requirements of your specific industrial process.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures: MoSi2 is the superior choice for applications like sintering advanced ceramics or in specialized laboratory furnaces, provided an oxidizing atmosphere is present.
- If your primary focus is versatility and durability at high heat: SiC is a more robust and flexible option, capable of handling various atmospheres in processes like metal forging and glass production.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heating below 1200°C: Metallic elements like nichrome are the industry standard, offering excellent performance and reliability for a vast range of common industrial applications.
Ultimately, aligning the material's properties with your operational reality is the key to an efficient, reliable, and cost-effective heating system.
Summary Table:
| Element Type | Key Features | Max Temperature | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Versatile, durable, handles various atmospheres | Up to 1600°C | Metallurgy, glass manufacturing, semiconductor production |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | High-temperature specialist, requires oxidizing atmosphere | Exceeds 1700°C | Sintering ceramics, laboratory research furnaces |
| Nichrome (Metallic) | Cost-effective, oxidation-resistant, ductile | Up to 1200°C | Drying, curing, common industrial heating |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your industrial furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heating system!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















