From an environmental standpoint, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are considered friendly primarily because of their exceptional energy efficiency. This high efficiency translates directly into lower energy consumption during operation, significantly reducing the carbon footprint associated with high-temperature industrial processes compared to less advanced heating solutions.
The environmental case for SiC heating elements is built on their operational efficiency in demanding applications. However, this advantage must be carefully weighed against practical lifecycle considerations, such as their lifespan and replacement requirements, to determine their true environmental impact.
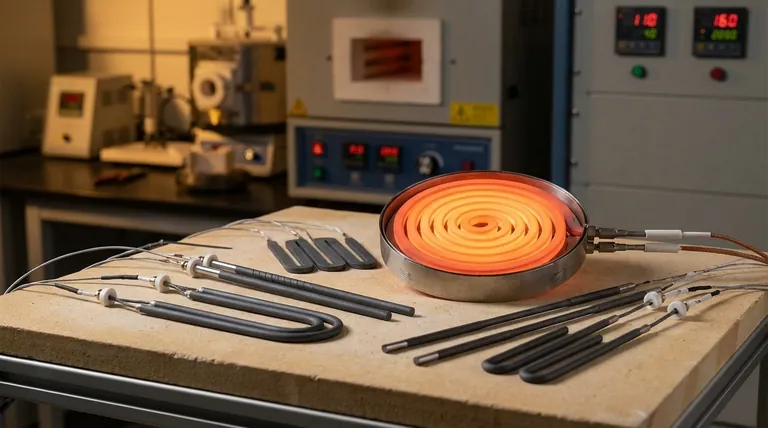

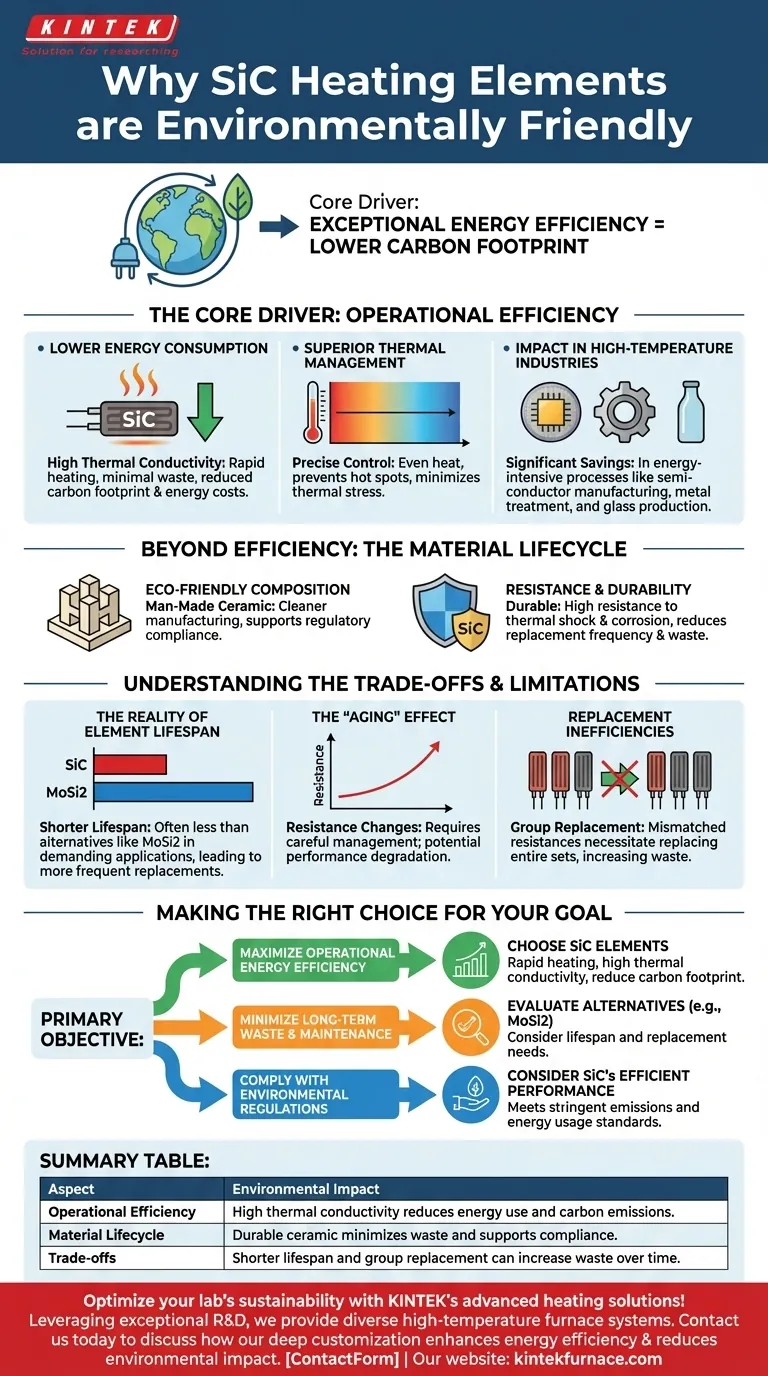
The Core Driver: Operational Efficiency
The primary environmental benefit of SiC elements comes not from what they are, but from how they perform. In energy-intensive industrial settings, small gains in efficiency yield massive environmental savings.
Lowering Energy Consumption
SiC elements possess excellent thermal conductivity, allowing them to heat up quickly and transfer energy to the target application with minimal waste. This means less electricity is required to reach and maintain high temperatures, directly lowering a facility's carbon footprint and energy costs.
Superior Thermal Management
Their ability to distribute heat evenly prevents energy-wasting hot spots and the need to "overshoot" a temperature target to ensure uniformity. This precise control reduces overall energy use and extends the element's operational life by minimizing thermal stress.
Impact in High-Temperature Industries
These efficiency gains are most significant in applications like semiconductor manufacturing, metal treatment, and glass production. In these processes, which run at extreme temperatures, SiC's performance can dramatically reduce the environmental impact of production.
Beyond Efficiency: The Material Lifecycle
While operational efficiency is the main story, the material properties of SiC also contribute to its environmental profile.
Eco-Friendly Composition
As a man-made ceramic, silicon carbide can be manufactured using processes that are more environmentally sound than the mining and refining of some traditional metal heating elements. This helps in complying with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Resistance and Durability
SiC is highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. This inherent durability means elements can last longer than some conventional alternatives, reducing the frequency of replacement and the associated material waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
A trusted evaluation requires looking at the full picture. SiC elements are not without their environmental downsides and operational challenges.
The Reality of Element Lifespan
While durable, SiC elements often have a shorter lifespan than advanced alternatives like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements, especially in the most demanding, highest-temperature applications. A shorter life means more frequent replacements and more material waste over time.
The "Aging" Effect
The electrical resistance of SiC elements changes as they age. This requires careful system management to maintain efficiency and can lead to performance degradation if not properly accounted for.
Replacement Inefficiencies
When a single SiC element in a set fails, it is often necessary to replace the entire group or at least a pair. This is because mismatched resistances between old and new elements can cause system failure. This practice generates more waste than replacing a single failed component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating technology requires aligning its specific characteristics with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing operational energy efficiency: SiC elements are an excellent choice due to their rapid heating and high thermal conductivity, directly reducing your carbon footprint during use.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term waste and maintenance: You must carefully evaluate SiC's lifespan and replacement requirements against alternatives like MoSi2, which may offer a longer service life.
- If your primary focus is complying with environmental regulations: SiC's efficient performance and ceramic composition make it a strong candidate for meeting stringent emissions and energy usage standards.
Ultimately, a truly sustainable choice balances operational efficiency with the total lifecycle impact of the technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|
| Operational Efficiency | High thermal conductivity reduces energy use and carbon emissions in high-temperature processes. |
| Material Lifecycle | Durable, corrosion-resistant ceramic minimizes waste and supports regulatory compliance. |
| Trade-offs | Shorter lifespan and group replacement needs can increase material waste over time. |
Optimize your lab's sustainability with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















