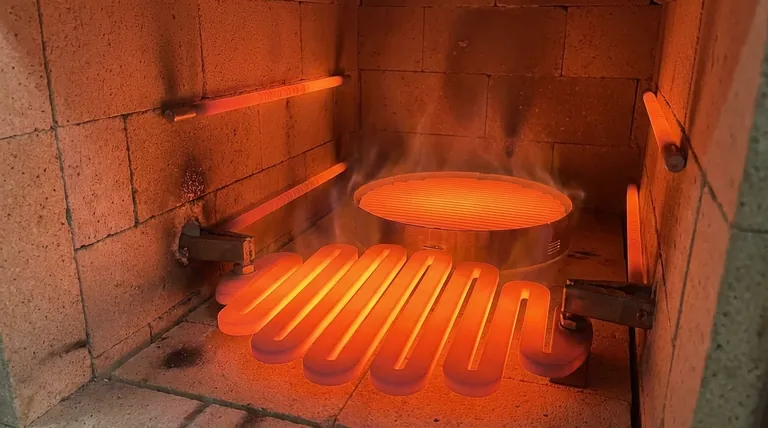
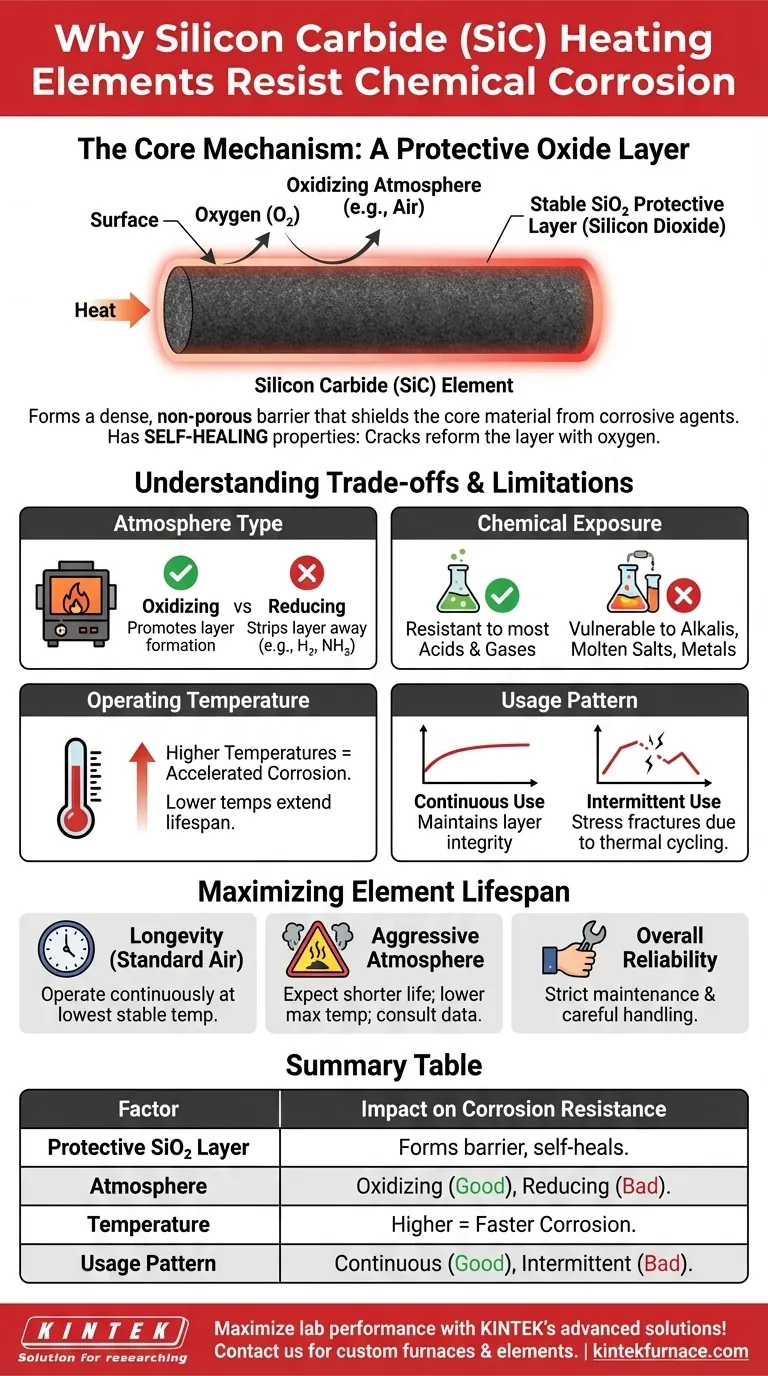
At its core, silicon carbide's exceptional resistance to chemical corrosion stems from its ability to form a stable, non-porous protective layer on its surface when heated. This layer, composed of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), acts as a durable shield, isolating the underlying material from attack by many corrosive gases and chemicals found in aggressive industrial environments.
The key to understanding silicon carbide's durability is recognizing that it isn't the material itself that resists corrosion, but rather the thin, glass-like film of silicon dioxide that naturally forms on its surface during operation. This protective barrier is the primary defense against chemical degradation.

The Core Mechanism: A Protective Oxide Layer
The chemical inertness of a silicon carbide (SiC) heating element is not an abstract property but a tangible, physical phenomenon that occurs at its surface.
The Formation of Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂)
When a SiC element is heated in an oxygen-containing atmosphere (like air), the silicon in the compound reacts with oxygen. This reaction forms a very thin, yet highly dense, layer of pure silicon dioxide (SiO₂) – essentially a type of quartz or glass.
This SiO₂ layer is strongly bonded to the parent SiC material, creating a seamless and robust surface shield.
Why This Layer is Effective
The silicon dioxide layer is chemically stable and largely non-reactive with most acids, salts, and corrosive gases. It functions as an impermeable physical barrier, preventing these aggressive substances from ever reaching and reacting with the silicon carbide element itself.
This is why SiC elements perform exceptionally well in environments for chemical processing and semiconductor manufacturing, where such substances are common.
Self-Healing Properties
In an oxidizing atmosphere, this protective layer has a remarkable self-healing capability. If a minor crack or imperfection occurs on the surface, the exposed SiC underneath will immediately react with available oxygen to reform the SiO₂ layer, effectively patching the breach.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly resistant, silicon carbide's performance is not absolute. Its lifespan is directly influenced by the operating environment and conditions, which can either support or degrade its protective layer.
The Role of Furnace Atmosphere
The composition of the furnace atmosphere is the single most critical factor. While oxidizing atmospheres (like air) promote the formation of the protective SiO₂ layer, certain reducing atmospheres (like hydrogen or cracked ammonia) can actively strip it away, leaving the SiC vulnerable to rapid attack.
Vulnerability to Specific Chemicals
The protective layer is susceptible to attack by specific substances. Molten salts, alkalis, and certain molten metals can dissolve the silicon dioxide film, leading to accelerated corrosion and element failure.
Impact of Operating Temperature
Higher operating temperatures generally accelerate all chemical reactions, including corrosive ones. Operating an element near its maximum temperature limit in a mildly corrosive atmosphere can significantly shorten its service life compared to running it at a more moderate temperature.
Influence of Continuous vs. Intermittent Use
Continuous operation at a stable temperature is ideal for maintaining the integrity of the protective layer. Intermittent use, which involves frequent heating and cooling cycles, can cause stress fractures in the SiO₂ film due to differences in thermal expansion, creating pathways for corrosive agents to penetrate.
Maximizing Element Lifespan
Understanding these principles allows you to align your operating procedures with the material's properties to ensure maximum reliability and longevity.
- If your primary focus is longevity in standard air: Operate the element continuously at the lowest stable temperature that meets your process needs to preserve the protective SiO₂ layer.
- If your primary focus is use in an aggressive atmosphere: Acknowledge that element life will be shorter. Consult manufacturer data for the specific chemical interactions and consider lowering the maximum operating temperature to slow degradation.
- If your primary focus is overall reliability: Implement a strict maintenance schedule and handle elements with care. Mechanical damage creates weak points for chemical attack, bypassing the element's natural resistance.
By understanding how silicon carbide protects itself, you can make informed decisions that maximize its performance and value in your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|
| Protective SiO₂ Layer | Forms a dense, non-reactive barrier that shields SiC from corrosive agents |
| Atmosphere Type | Oxidizing atmospheres (e.g., air) promote layer formation; reducing atmospheres degrade it |
| Operating Temperature | Higher temperatures accelerate corrosion; moderate temps extend lifespan |
| Chemical Exposure | Resistant to most acids and gases; vulnerable to alkalis, molten salts, and metals |
| Usage Pattern | Continuous use maintains layer integrity; intermittent use can cause stress fractures |
Maximize your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable silicon carbide heating elements and custom furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing durability and efficiency in corrosive environments. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















