The primary advantage of using a quartz tube for high-temperature dielectric measurements is its ability to remain electromagnetically "invisible" while withstanding extreme heat. Because quartz exhibits exceptionally low dielectric loss and high thermal resistance, it allows researchers to isolate and measure the true scattering parameters of a sample without interference from the container itself.
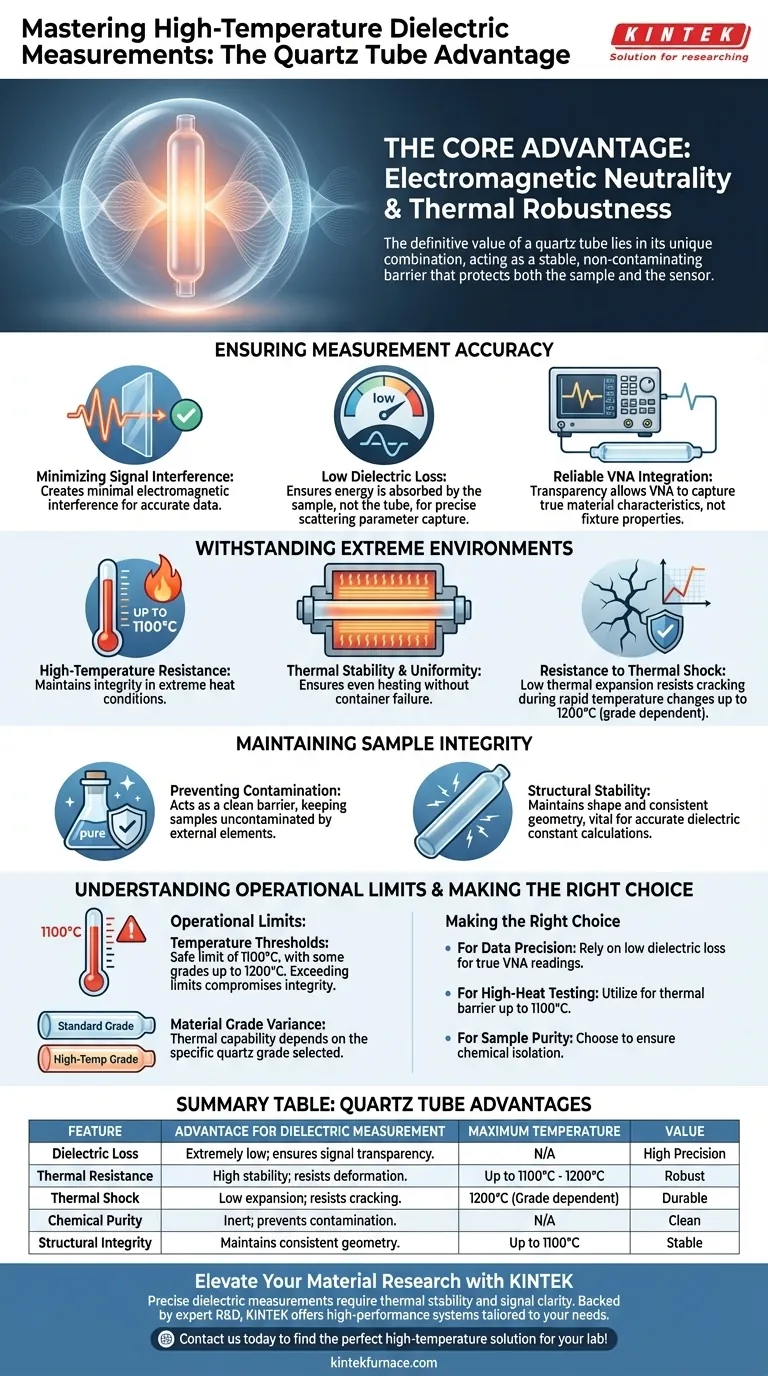
Core Takeaway The definitive value of a quartz tube lies in its unique combination of electromagnetic neutrality and thermal robustness. It acts as a stable, non-contaminating barrier that protects both the sample and the sensor, ensuring that data collected by sensitive instruments like Vector Network Analyzers reflects only the material properties, not the test fixture.

Ensuring Measurement Accuracy
Minimizing Signal Interference
To obtain accurate dielectric data, the sample container must not distort the measurement. Quartz is ideal because it creates minimal electromagnetic interference.
Low Dielectric Loss
Quartz possesses extremely low dielectric loss characteristics. This ensures that the energy transmitted by measurement devices is absorbed by the sample, not the tube, allowing for precise capture of scattering parameters.
Reliable VNA Integration
When using a Vector Network Analyzer (VNA), the container’s transparency to signals is critical. Quartz allows the VNA to capture data that truly reflects the material characteristics of the sample inside, rather than the container holding it.
Withstanding Extreme Environments
High-Temperature Resistance
High-temperature dielectric measurements often push materials to their limits. Quartz tubes offer excellent resistance in these environments, maintaining integrity up to 1100 degrees Celsius.
Thermal Stability and Uniformity
In experimental setups like tube furnaces, uniform heating is essential for valid results. Quartz maintains its structural stability under these conditions, ensuring the sample is heated evenly without container failure.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Supplementary data indicates that quartz has a low thermal expansion coefficient. This allows the tube to resist deformation or cracking, even when subjected to rapid temperature changes or thermal cycling up to 1200°C (depending on the quartz grade).
Maintaining Sample Integrity
Preventing Contamination
When measuring mineral powders or liquids, purity is paramount. The quartz tube serves as a clean barrier, ensuring the sample remains uncontaminated by external elements or reaction with the container walls during the heating process.
Structural Stability
Unlike weaker materials that might soften or warp, quartz maintains its shape and structural stability throughout the experiment. This ensures consistent sample geometry, which is vital for calculating accurate dielectric constants.
Understanding the Operational Limits
Temperature Thresholds
While quartz is highly robust, it is not invincible. The primary references note a safe operating limit of 1100°C, with some grades capable of reaching 1200°C. Exceeding these specific thermal limits can compromise the structural integrity of the tube and validity of the measurement.
Material Grade Variance
Not all quartz is created equal. The specific thermal capability often depends on the grade of quartz selected. It is critical to verify that the specific tube chosen is rated for the maximum temperature of your intended experimental protocol.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is Data Precision: Rely on quartz for its low dielectric loss, which ensures your VNA readings capture the sample's true scattering parameters without container interference.
- If your primary focus is High-Heat Testing: Utilize quartz for experiments requiring temperatures up to 1100°C, as it provides the necessary thermal barrier and structural stability.
- If your primary focus is Sample Purity: Choose quartz to ensure that reactive powders or liquids remain uncontaminated and chemically isolated during the heating process.
By leveraging the dual benefits of thermal resilience and electromagnetic transparency, you ensure your measurements are defined by the sample's properties rather than the limitations of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage for Dielectric Measurement | Maximum Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Loss | Extremely low; ensures signal transparency for accurate VNA readings. | N/A |
| Thermal Resistance | High stability; resists deformation under extreme heat. | Up to 1100°C - 1200°C |
| Thermal Shock | Low expansion coefficient; resists cracking during rapid cycling. | 1200°C (Grade dependent) |
| Chemical Purity | Inert material; prevents sample contamination at high temperatures. | N/A |
| Structural Integrity | Maintains consistent geometry for accurate constant calculations. | Up to 1100°C |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise dielectric measurements require a perfect balance of thermal stability and signal clarity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable lab high-temp furnaces tailored to your unique research needs.
Ensure your data reflects the true properties of your materials without container interference. Contact us today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Rui Xiong, Qian Chen. A High-Temperature and Wide-Permittivity Range Measurement System Based on Ridge Waveguide. DOI: 10.3390/s25020541
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What advantages does a vacuum drying oven offer for BiFeO3 electrode sheets? Optimize Your Battery Research
- What are the key properties of alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Discover Their High-Temp and Chemical Resistance
- Why are laboratory vacuum pumps and pressure gauges essential for aluminum foams? Ensure High-Quality Sintering Results
- What is the significance of using ceramic balls of varying diameters? Optimize Reactor Flow and Filtration
- What role does a heated substrate platform play in the spray pyrolysis deposition? Optimize Your Thin Film Quality
- What are the technical functions of condensation units and gas collection bags? Optimize Your Reduction Experiments
- What is the function of a high alumina crucible in chloride salt purification? Protect Purity and Thermal Stability
- Why is a high-precision Mass Flow Controller necessary for E-Ni/m-MgAlOx catalysts? Ensure Precise Gas Dynamics



















