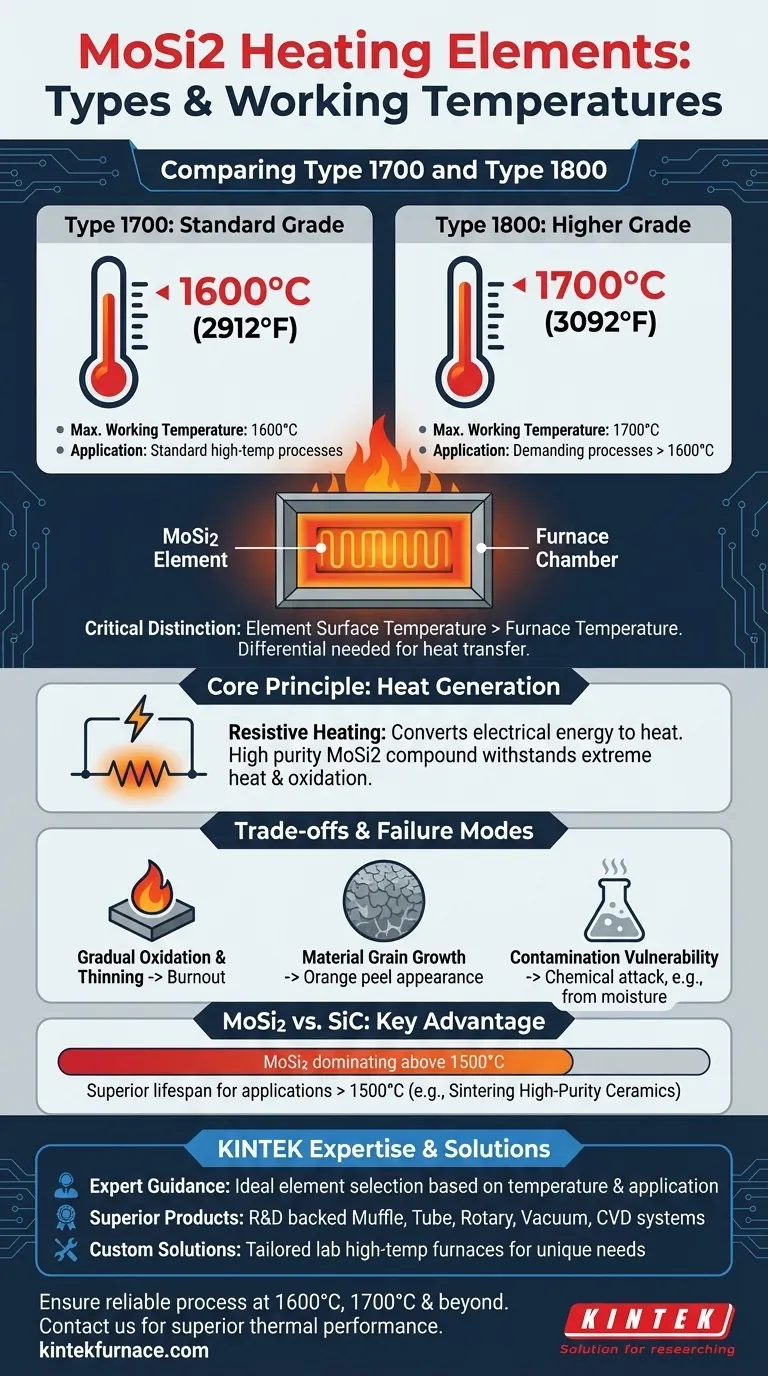
In short, the two most common types of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements are distinguished by their maximum recommended operating temperatures. The Type 1700 element is designed for a working temperature of 1600°C (2912°F), while the Type 1800 element is engineered for a higher working temperature of 1700°C (3092°F).
The key to effectively using MoSi2 heating elements is not just knowing their temperature ratings, but understanding that their long-term performance is dictated by managing oxidation and preventing contamination within their intended operational range.

The Core Principle: How MoSi2 Elements Generate Heat
From Electricity to Extreme Temperatures
Molybdenum Disilicide heating elements are a form of resistive heater. They function by converting electrical energy directly into heat energy.
As a higher electrical current is applied, the element's resistance causes it to heat up, allowing for precise control of extreme temperatures inside a furnace or kiln.
The Role of Molybdenum Disilicide
These elements are fabricated from high-purity Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), a ceramic-metallic compound.
This material is exceptionally well-suited for high-temperature, aggressive environments due to its ability to withstand extreme heat and oxidation.
Decoding the Element Types and Temperature Ratings
Type 1700 Elements
This is the standard grade of MoSi2 element. It is specified for furnaces where the maximum required chamber temperature, or working temperature, is 1600°C.
Type 1800 Elements
This is a higher-grade element designed for more demanding applications. It is specified for furnaces requiring a maximum working temperature of 1700°C.
A Critical Distinction: Element vs. Furnace Temperature
It is important to understand that the element's surface temperature can be significantly higher than the programmable temperature of the furnace chamber.
An element might reach a maximum surface temperature of 1800°C to 1900°C to maintain a stable, programmable furnace temperature of 1700°C. This differential is necessary to transfer heat effectively into the furnace chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Modes
The Inevitable Process of Oxidation
MoSi2 elements do not typically fail suddenly. Instead, they degrade over time through a process of gradual thinning caused by oxidation at high temperatures.
As an area of the element becomes thinner, its electrical resistance increases, causing it to heat up more intensely than thicker sections. This "hot spot" accelerates the degradation, eventually leading to burnout.
Material Grain Growth
At very high operating temperatures, the grain structure of the MoSi2 material can grow. This process can exacerbate the thinning and sometimes results in a rough, "orange peel" appearance on the element's surface.
Vulnerability to Contamination
MoSi2 elements can be more susceptible to chemical attack and contamination than other element types like Silicon Carbide (SiC).
For example, when sintering colored zirconia, it is critical that technicians properly dry the material before heating. Failing to do so can release contaminants that degrade the element and shorten its lifespan.
MoSi2 vs. SiC: Key Advantages
Despite their vulnerabilities, MoSi2 elements offer a distinct advantage over Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements, particularly for processes running above 1500°C.
In this upper temperature range, MoSi2 elements can last significantly longer, making them the preferred choice for applications like sintering high-purity ceramics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing the correct element is fundamental to achieving reliable and efficient high-temperature processing. Your decision should be based on the specific, sustained temperature your application demands.
- If your primary focus is operating at or below 1600°C: The Type 1700 element is the correct and most economical choice for your furnace.
- If your primary focus is operating between 1600°C and 1700°C: The Type 1800 element is required to handle these more extreme thermal demands safely and effectively.
- If your primary focus is sintering sensitive materials like zirconia: Prioritize proper furnace maintenance and ensure all materials are fully dried before processing to prevent element contamination.
Matching the element's capability to your process requirements is the foundation for operational stability and long service life.
Summary Table:
| Type | Maximum Working Temperature | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1700 | 1600°C (2912°F) | Standard high-temperature processes |
| Type 1800 | 1700°C (3092°F) | Demanding applications above 1600°C |
Need the Right High-Temperature Solution?
Choosing the correct MoSi2 heating element is critical for the efficiency and longevity of your high-temperature processes. The experts at KINTEK understand the nuances of operating at extreme temperatures.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Our team helps you select the ideal element type (Type 1700 or Type 1800) based on your specific temperature requirements and application.
- Superior Products: Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all featuring robust and reliable heating elements.
- Custom Solutions: We customize our lab high-temp furnaces to meet your unique needs, ensuring optimal performance for sintering ceramics, research, and other demanding applications.
Ensure your process runs reliably at 1600°C, 1700°C, and beyond. Contact our experts today for a consultation and let us help you achieve superior thermal performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















