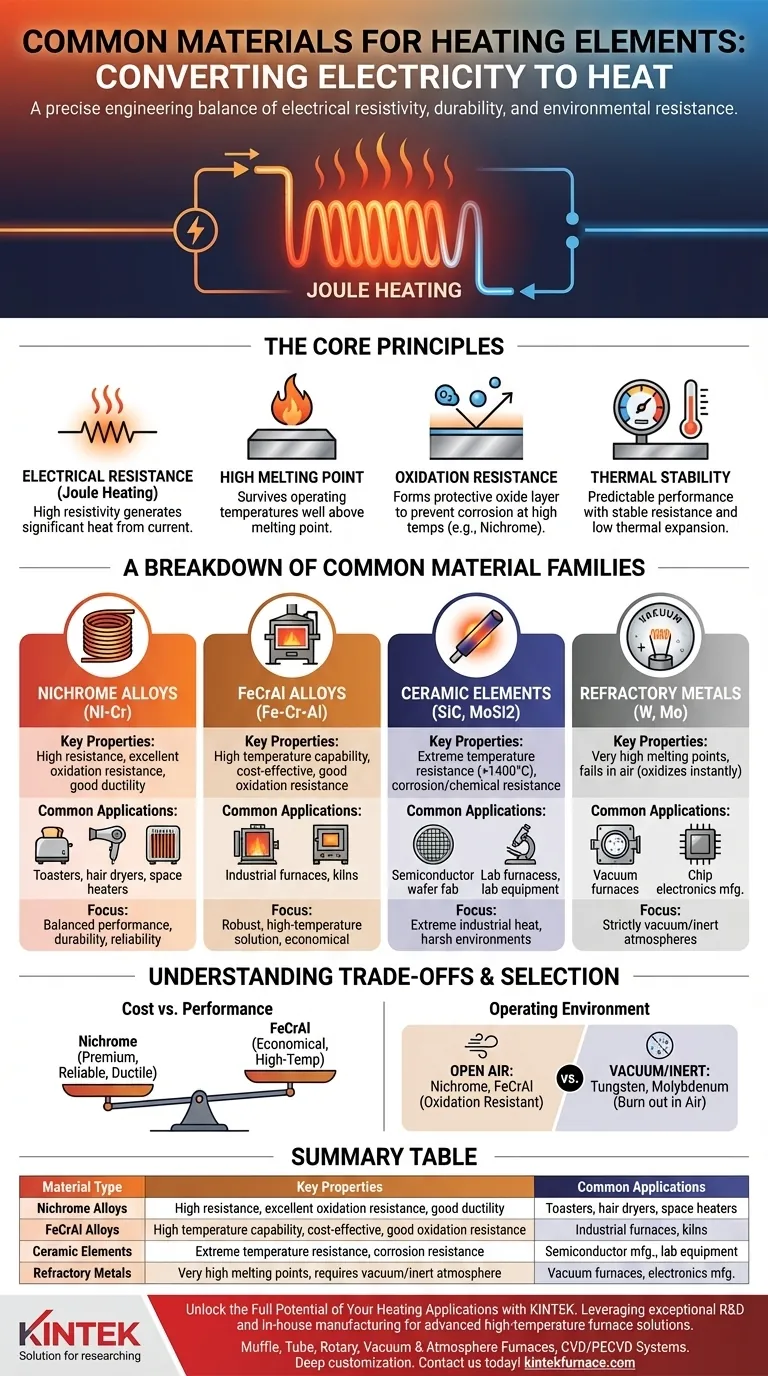
At the core of nearly every electric heating device is a carefully selected material designed to convert electricity into heat. The most common materials are metallic alloys, primarily Nichrome (Nickel-Chromium) and FeCrAl (Iron-Chromium-Aluminum). These are chosen for their high electrical resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures without oxidizing, while more specialized materials like ceramics or refractory metals are reserved for extreme industrial conditions.
The selection of a heating element material is not just about getting hot; it's a precise engineering decision that balances electrical resistivity, high-temperature durability, and resistance to environmental corrosion. Understanding these properties is the key to identifying the right material for any application.
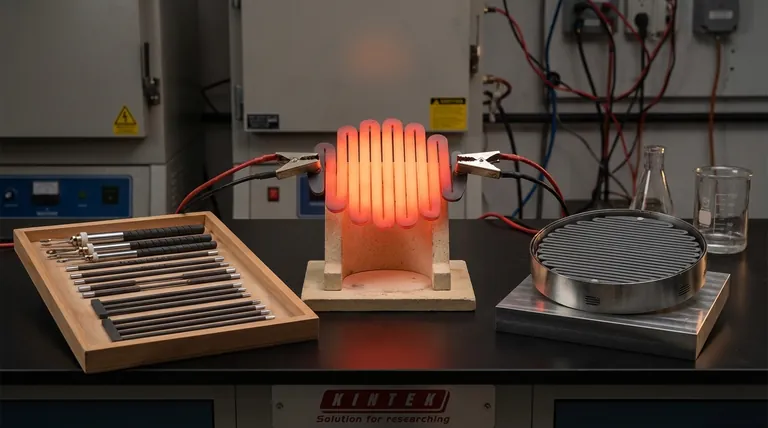

The Core Principles of a Heating Element Material
To understand why certain materials are used, you must first understand the fundamental requirements of the job. A heating element's success depends on a few key physical properties.
The Foundation: Electrical Resistance
The primary function of a heating element is to generate heat through a principle known as Joule heating. When an electric current passes through a material with high electrical resistance, electrical energy is converted directly into thermal energy, or heat.
A material with high resistivity is therefore essential, as it can generate significant heat without requiring excessively high currents or long wires.
The First Hurdle: Surviving High Temperatures
A heating element is useless if it melts under its own operating conditions. An effective material must possess a very high melting point, well above its intended operating temperature, to ensure structural integrity and a long service life.
The Key to Longevity: Oxidation Resistance
Perhaps the most critical property for elements operating in open air is resistance to oxidation. At high temperatures, most metals react with oxygen and corrode or burn away.
The best heating element alloys, like Nichrome, form a thin, durable, and adherent outer layer of oxide (e.g., chromium oxide). This layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing oxygen from reaching the underlying metal and ensuring the element lasts for thousands of hours.
Ensuring Predictable Performance: Thermal Stability
An ideal heating element should behave predictably across its temperature range. This requires two forms of stability: stable electrical resistance and low thermal expansion.
If a material's resistance changes dramatically as it heats up, the power output will be inconsistent. Likewise, minimal expansion and contraction during heating cycles prevent mechanical stress that can lead to fatigue and failure.
A Breakdown of Common Material Families
Heating element materials can be broadly grouped by their composition and ideal operating conditions.
The Workhorse: Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) Alloys
Nichrome, typically an alloy of 80% nickel and 20% chromium, is the most widely used heating element material. It provides an exceptional balance of high resistance, excellent oxidation resistance, and good ductility, making it easy to form into wires and coils.
It is the default choice for a vast range of consumer appliances, including toasters, hair dryers, and space heaters, due to its reliability and proven performance.
The Cost-Effective Alternative: Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) Alloys
FeCrAl alloys (often sold under the brand name Kanthal) serve a similar purpose to Nichrome but at a generally lower cost. They can often operate at even higher temperatures than Nichrome and have excellent oxidation resistance.
These alloys are a popular choice in industrial heating and high-temperature equipment like kilns and furnaces where cost is a significant factor.
For Specialized High Temperatures: Ceramic Elements
For applications that exceed the limits of metallic alloys, ceramic materials are used. Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) are two common examples.
These materials can operate at extremely high temperatures (often above 1400°C / 2550°F) and are highly resistant to corrosion and chemical wear, making them ideal for industrial furnaces, semiconductor manufacturing, and laboratory equipment.
For Oxygen-Free Environments: Refractory Metals
Refractory metals like Tungsten and Molybdenum have incredibly high melting points but one critical weakness: they oxidize and fail almost instantly in the presence of air at high temperatures.
Because of this, their use is strictly limited to vacuum environments or inert gas atmospheres. You will find them in vacuum furnaces, specific types of lighting, and certain electronics manufacturing processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single material is perfect for every situation. The choice always involves balancing competing factors.
Cost vs. Performance
The most common trade-off is between Nichrome and FeCrAl alloys. Nichrome generally offers better ductility and proven long-term stability, making it a premium, reliable choice. FeCrAl provides higher temperature capabilities at a lower price point, making it economically attractive for industrial applications.
Operating Environment: The Air vs. Vacuum Divide
This is a non-negotiable trade-off. If the element will operate in open air, you must use an oxidation-resistant alloy like Nichrome or FeCrAl. If you attempt to use a refractory metal like Tungsten in air, it will burn out immediately. Tungsten is exclusively for oxygen-free environments.
Temperature Range vs. Material Type
Each material family has a distinct temperature range. Copper-nickel alloys are used for low-temperature needs, Nichrome and FeCrAl cover the mid-to-high range typical of most appliances and furnaces, and ceramics like SiC and MoSi2 are reserved for the most extreme industrial heat.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated entirely by the demands of the task.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose appliances or reliable heat: Choose Nichrome alloys for their balanced performance, durability, and excellent oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive industrial furnaces or high-temperature applications: FeCrAl alloys offer a robust, high-temperature solution at a more economical price point.
- If your primary focus is extreme-temperature industrial processes (above 1400°C): Ceramic elements like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) are the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is heating within a vacuum or inert atmosphere: Refractory metals like Tungsten or Molybdenum are the only option due to their high melting points.
Ultimately, choosing the right material is about matching its unique properties to the specific thermal, environmental, and economic constraints of your project.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nichrome Alloys | High resistance, excellent oxidation resistance, good ductility | Toasters, hair dryers, space heaters |
| FeCrAl Alloys | High temperature capability, cost-effective, good oxidation resistance | Industrial furnaces, kilns |
| Ceramic Elements | Extreme temperature resistance, corrosion resistance | Semiconductor manufacturing, lab equipment |
| Refractory Metals | Very high melting points, requires vacuum/inert atmosphere | Vacuum furnaces, electronics manufacturing |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Heating Applications with KINTEK
Struggling to select the right heating element material for your specific needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories and industrial settings. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're working with Nichrome, FeCrAl, ceramics, or refractory metals, our expertise ensures optimal performance, durability, and efficiency for your projects. Don't let material selection hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes and deliver reliable, customized solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















