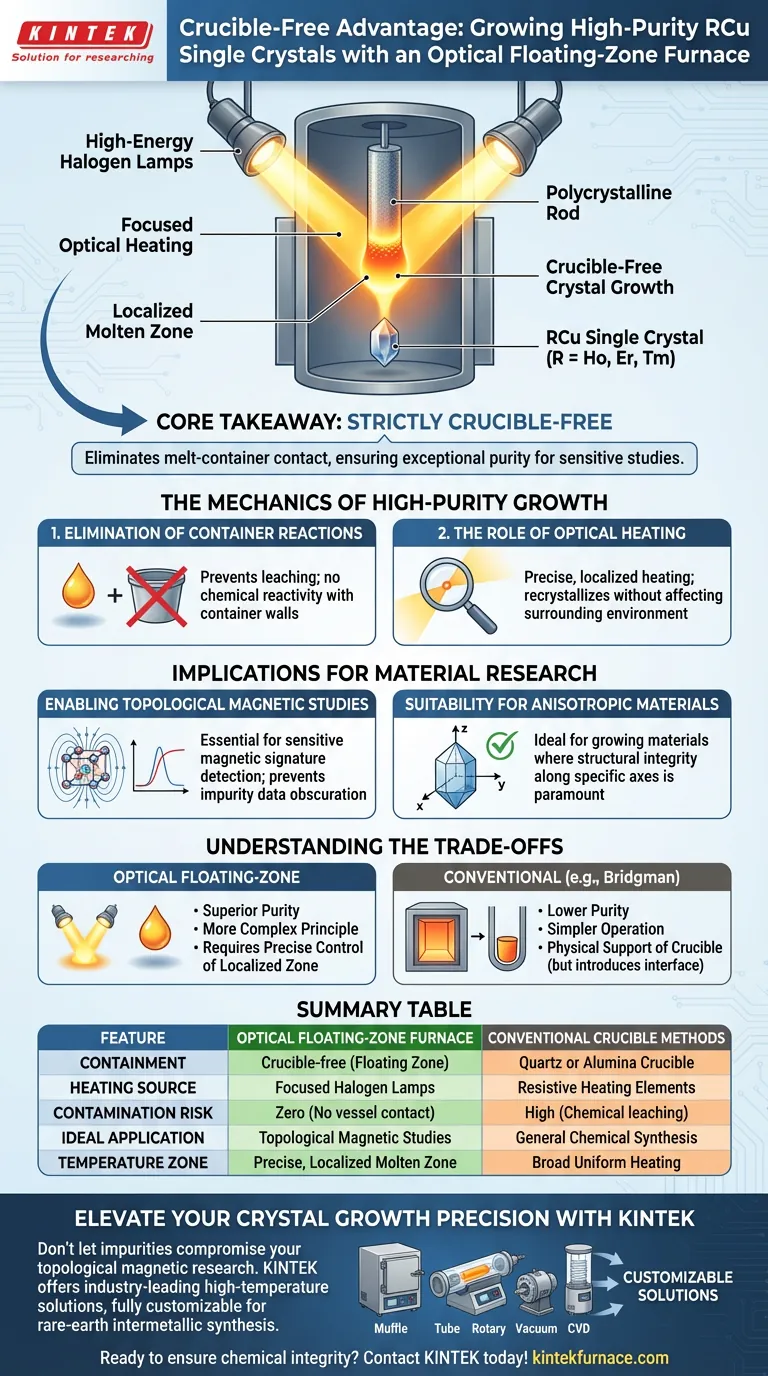
The optical floating-zone furnace provides a critical advantage for growing RCu series single crystals by enabling a strictly crucible-free process. By utilizing high-energy halogen lamps to generate a localized molten zone, this technique circumvents the need for physical containment. This approach directly addresses the primary challenge in growing rare-earth intermetallic compounds: preventing chemical reactivity at high temperatures.
Core Takeaway The optical floating-zone furnace is essential for RCu crystal growth because it completely eliminates contact between the melt and container walls. This "crucible-free" capability ensures the exceptional purity required to prevent impurities from obscuring data in sensitive topological magnetic studies.
The Mechanics of High-Purity Growth
Elimination of Container Reactions
The defining feature of the optical floating-zone furnace is its ability to facilitate crystal growth without a crucible.
In conventional methods, the molten material inevitably touches the walls of a container. For reactive materials like RCu series compounds (where R = Ho, Er, Tm), this contact typically leads to chemical reactions.
By suspending the melt in a floating zone, you completely eliminate the vessel from the equation. This prevents the leaching of elements from the container into the crystal lattice.
The Role of Optical Heating
This system does not rely on standard resistive heating elements that heat an entire chamber.
Instead, it employs high-energy halogen lamps to focus intense light onto a specific point. This creates a precise, localized high-temperature molten zone.
This targeted energy allows the polycrystalline rod to recrystallize into a single crystal while the surrounding environment remains chemically inert.
Implications for Material Research
Enabling Topological Magnetic Studies
The ultimate value of this purity lies in the downstream research applications.
The RCu series compounds are frequently used in topological magnetic studies. These experiments are highly sensitive to material defects and chemical inhomogeneities.
Even trace impurities from a crucible can alter the magnetic signature of the crystal, rendering experimental data useless. The floating-zone method ensures the material retains the intrinsic properties necessary for accurate characterization.
Suitability for Anisotropic Materials
While the primary focus for RCu is purity, this method is broadly validated for high-quality crystal growth.
As noted in comparative contexts for superconductors (like BSCCO), the crucible-free nature of this furnace is the standard for growing materials where anisotropy and structural integrity are paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity vs. Containment
While the optical floating-zone furnace offers superior purity, it operates on a more complex principle than container-based methods.
Systems like the vertical single-temperature zone tube furnace (often used for Bridgman growth) utilize a quartz tube and a slow, mechanical lifting mechanism to control cooling. This provides physical support for the melt but introduces the container interface.
The trade-off with the optical floating-zone method is that you lose the physical support of a crucible. You must rely entirely on the stability of the localized molten zone created by the halogen lamps. This requires precise control over the optical focus and power to maintain the zone without spilling the melt, a challenge not present in contained growth methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if the optical floating-zone furnace is the correct tool for your specific application, consider the following research priorities:
- If your primary focus is Topological Magnetic Studies: You must use the optical floating-zone furnace to ensure the elimination of impurities that would otherwise distort magnetic data.
- If your primary focus is General Chemical Synthesis: A standard crucible-based method (like a vertical tube furnace) may suffice if extreme purity is not the limiting factor for your measurements.
For RCu rare-earth intermetallic compounds, the optical floating-zone furnace is not just an option; it is the definitive method for ensuring the chemical integrity required for high-level physical research.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Optical Floating-Zone Furnace | Conventional Crucible Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Containment | Crucible-free (Floating Zone) | Quartz or Alumina Crucible |
| Heating Source | Focused Halogen Lamps | Resistive Heating Elements |
| Contamination Risk | Zero (No contact with vessel) | High (Chemical leaching from walls) |
| Ideal Application | Topological Magnetic Studies | General Chemical Synthesis |
| Temperature Zone | Precise, Localized Molten Zone | Broad Uniform Heating |
Elevate Your Crystal Growth Precision with KINTEK
Don't let impurities compromise your topological magnetic research. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions, including specialized systems designed for the rigorous demands of rare-earth intermetallic compound synthesis.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab furnaces—from Muffle, Tube, and Rotary systems to Vacuum and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique single-crystal growth needs.
Ready to ensure the chemical integrity of your next project? Contact us today to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Wolfgang Simeth, C. Pfleiderer. Topological aspects of multi-k antiferromagnetism in cubic rare-earth compounds. DOI: 10.1088/1361-648x/ad24bb
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of high vacuum furnaces? Understand Costs, Time, and Material Challenges
- Why is a Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system superior to traditional furnaces? Speed and Density for Ceramics
- Why is a vacuum environment important for high-temperature metal processing? Prevent Oxidation and Boost Metal Purity
- What are the typical components of a vacuum system used in a high-temperature distillation furnace? Ensure Process Precision
- Why is it necessary to use a vacuum drying oven for Silicon Carbide slurry? Enhance Purity and Green Body Density
- What is the specific function of the high vacuum in SiC/Cu-Al2O3 sintering? Achieve 1.5x10^-2 Pa for Peak Density
- What alternative solutions are suggested for heating small parts in a vacuum or inert atmosphere? Explore Efficient, Customizable Options
- What role does an industrial-grade vacuum furnace play in the brazing process of MnCoNiCuGe5 high-entropy alloys?



















