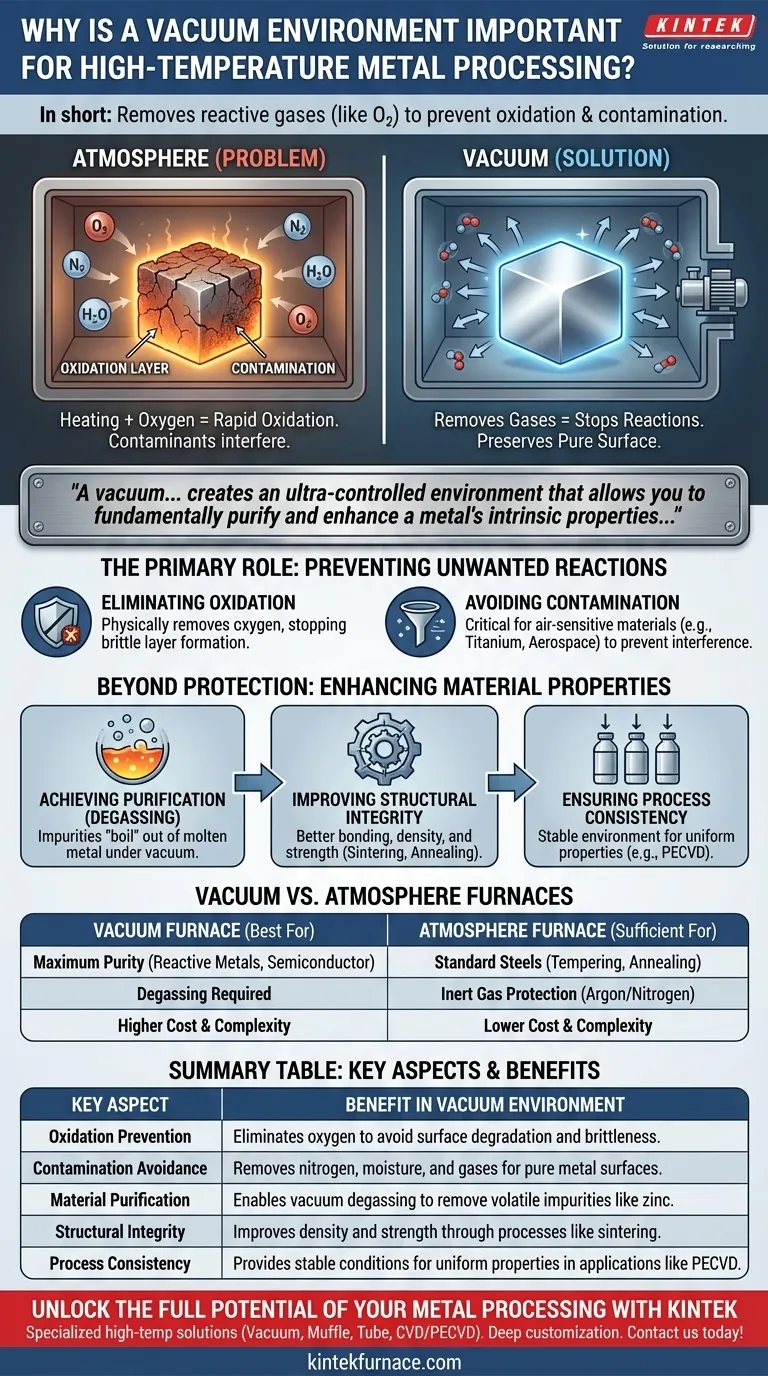
In short, a vacuum environment is essential for high-temperature metal processing because it removes the reactive gases, primarily oxygen, from the chamber. This prevents oxidation, contamination, and other unwanted chemical reactions that would otherwise degrade the metal's quality, strength, and surface finish when heated.
A vacuum does more than just prevent rust; it creates an ultra-controlled environment that allows you to fundamentally purify and enhance a metal's intrinsic properties in ways that are impossible in an open atmosphere.
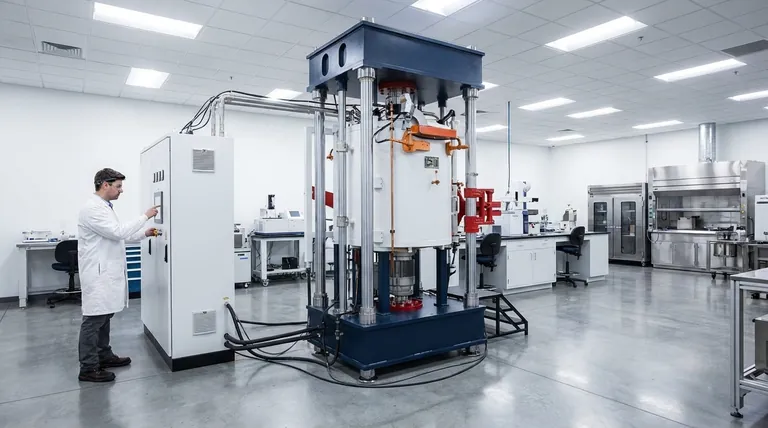

The Primary Role: Preventing Unwanted Reactions
When processing metals at high temperatures, the primary challenge is managing their reactivity. A vacuum provides the most effective solution for controlling the processing environment.
Eliminating Oxidation
Heating metal in the presence of oxygen causes rapid oxidation, forming a brittle, undesirable layer on the surface.
A vacuum furnace physically removes the vast majority of oxygen molecules, stopping this reaction before it can begin and preserving the metal's pure surface.
Avoiding Contamination
Beyond oxygen, our atmosphere contains nitrogen, moisture, and other trace gases that can react with hot metals.
This is especially critical for air-sensitive materials like titanium or specific alloys used in aerospace and medical applications. A vacuum ensures these contaminants do not interfere with the process or become embedded in the final product.
Beyond Protection: Enhancing Material Properties
Using a vacuum goes beyond simple protection. It actively improves the final material by enabling processes that are otherwise unachievable.
Achieving Purification
Many raw metals contain unwanted impurity elements like lead, zinc, or magnesium, which have high vapor pressures.
Under vacuum, these impurities essentially "boil" out of the molten metal and are evacuated by the vacuum pump. This process, known as vacuum degassing, is a powerful method for purification.
Improving Structural Integrity
Processes like vacuum sintering and vacuum annealing create parts with superior density, strength, and wear resistance.
By removing trapped gases between metal particles, a vacuum allows for better bonding and the formation of a more perfect crystalline structure. In semiconductor manufacturing, this is mandatory for creating defect-free silicon wafers with reliable electrical properties.
Ensuring Process Consistency
A vacuum provides a stable, repeatable environment. This minimizes variables and ensures that each part produced has uniform properties.
This level of control is vital for complex processes like Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD), where a consistent, contaminant-free environment is necessary for uniform surface coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Vacuum vs. Atmosphere Furnaces
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is not the only solution for controlling the processing environment. It's important to understand where it fits.
When to Use a Vacuum Furnace
A vacuum is the superior choice when maximum purity is non-negotiable. This applies to reactive metals, semiconductor wafers, and components for medical or aerospace use where even trace contamination can lead to failure. It is also the only choice for processes that rely on purification through degassing.
When an Atmosphere Furnace Suffices
For many common heat treatment processes like tempering or annealing standard steels, a full vacuum is overkill.
Atmosphere furnaces, which use a controlled flood of an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, are often sufficient to displace oxygen and prevent oxidation. They are generally less complex and more cost-effective for these applications.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are a significant investment. They require robust chambers, powerful pumps, and precise controls, making them more expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum, atmosphere, or open-air process depends entirely on the desired outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance: A vacuum furnace is the only way to eliminate nearly all reactive contaminants and purify the metal itself.
- If your primary focus is preventing basic oxidation on a budget: A controlled atmosphere furnace using inert gas is a highly effective and more economical solution.
- If your primary focus is removing volatile impurities from the metal: A vacuum environment is essential to enable the degassing process.
Ultimately, controlling the environment is the key to controlling your material's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit in Vacuum Environment |
|---|---|
| Oxidation Prevention | Eliminates oxygen to avoid surface degradation and brittleness. |
| Contamination Avoidance | Removes nitrogen, moisture, and gases for pure metal surfaces. |
| Material Purification | Enables vacuum degassing to remove volatile impurities like zinc. |
| Structural Integrity | Improves density and strength through processes like sintering. |
| Process Consistency | Provides stable conditions for uniform properties in applications like PECVD. |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Metal Processing with KINTEK
Are you working with reactive metals, aerospace components, or semiconductor materials that demand maximum purity and performance? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Vacuum Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, enhancing material properties and process efficiency.
Don't let contamination or inconsistent results hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our vacuum and atmosphere furnaces can transform your metal processing and deliver superior outcomes for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















