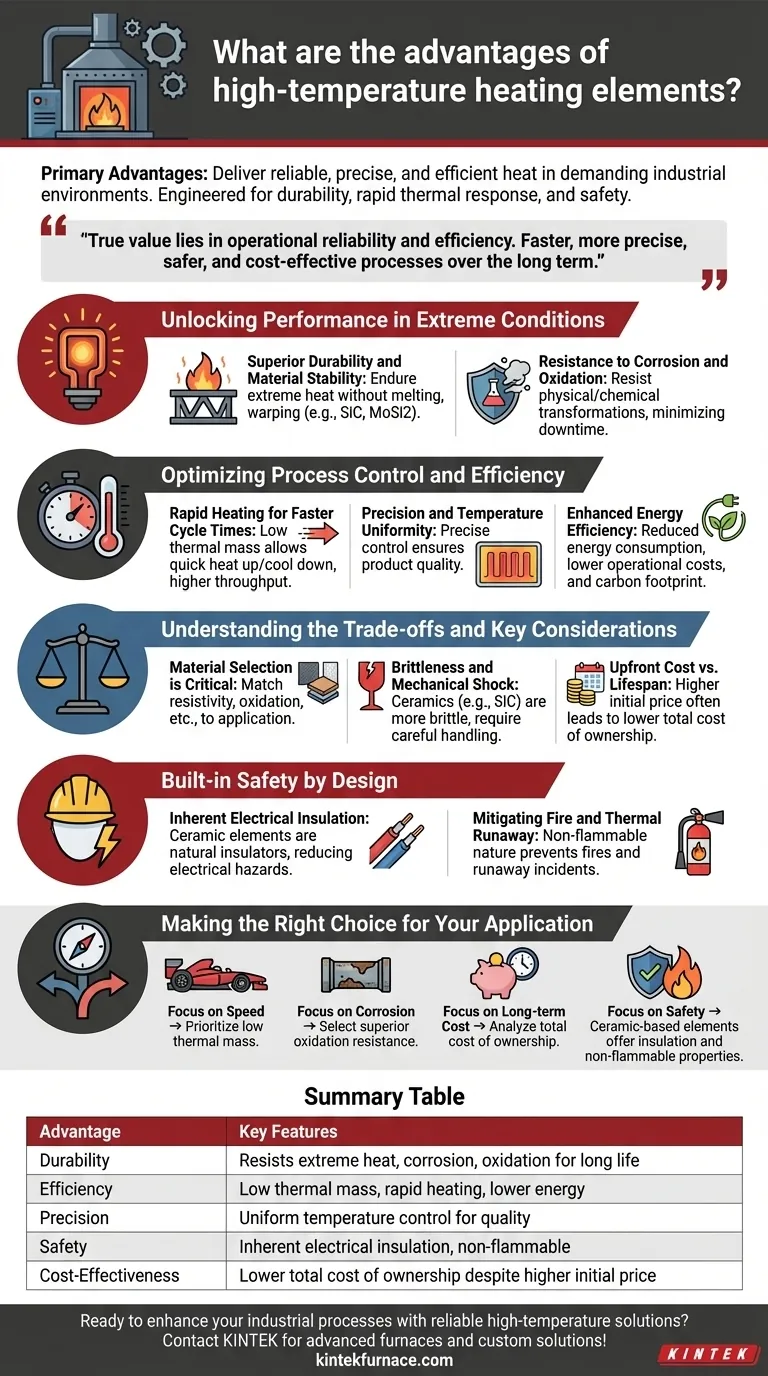
The primary advantages of high-temperature heating elements are their ability to deliver reliable, precise, and efficient heat in demanding industrial environments where conventional heaters would fail. These specialized components are engineered for exceptional durability, rapid thermal response, and enhanced operational safety, making them critical for advanced manufacturing and processing applications.
While the ability to reach extreme temperatures is their defining feature, the true value of these elements lies in their operational reliability and efficiency. They enable processes that are not only faster and more precise but also safer and more cost-effective over the long term.
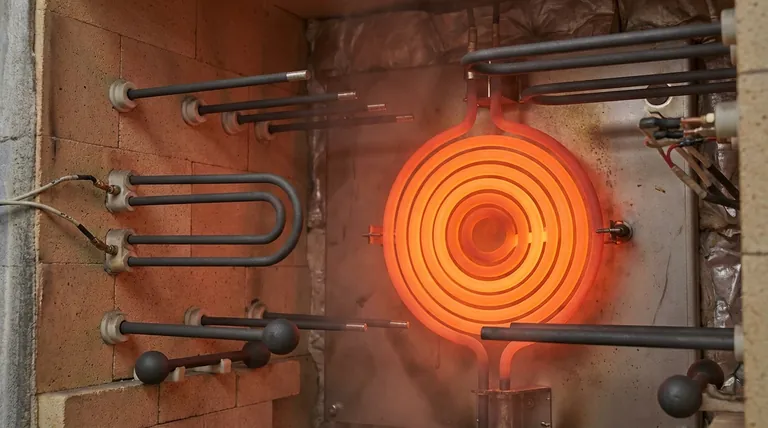
Unlocking Performance in Extreme Conditions
The core function of these elements is to perform consistently where others cannot. This reliability stems from their fundamental material properties.
Superior Durability and Material Stability
High-temperature elements are constructed from materials like silicon carbide (SiC), molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), or specific metallic alloys. These materials are chosen for their ability to endure extreme heat without melting, warping, or degrading. This ensures a long service life and consistent performance in processes like sintering, melting, or heat treatment.
Resistance to Corrosion and Oxidation
Many industrial processes involve chemically aggressive atmospheres. These heating elements are designed to resist physical and chemical transformations, including oxidation, which is a common failure point for standard metals at high temperatures. This resilience minimizes downtime and maintenance costs.
Optimizing Process Control and Efficiency
Beyond simple durability, high-temperature elements provide a level of control that directly impacts product quality and operational costs.
Rapid Heating for Faster Cycle Times
Many advanced elements, particularly ceramic types, feature a low thermal mass. This allows them to heat up and cool down very quickly, which significantly speeds up process cycle times. Faster cycles lead to higher throughput and productivity.
Precision and Temperature Uniformity
The materials used allow for precise control over the heating process. This capability is critical for applications that require consistent and uniform heat distribution to ensure product quality and prevent defects.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Rapid heating cycles directly contribute to reduced energy consumption, as less time is spent bringing the system to its target temperature. Furthermore, many ceramic materials hold heat very effectively, requiring less energy to maintain a stable temperature, which lowers operational costs and reduces the overall carbon footprint.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
While highly advantageous, these elements are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to successful implementation.
Material Selection is Critical
The performance of an element is dictated by its material composition. Factors like resistivity, oxidation resistance, and the temperature coefficient of resistance must be carefully matched to the specific application's environment and temperature requirements.
Brittleness and Mechanical Shock
Many high-performance ceramic elements, like SiC, are significantly more brittle than their metallic counterparts. They are more susceptible to damage from mechanical shock or vibration, requiring careful handling and installation design.
Upfront Cost vs. Lifespan
Specialized high-temperature elements typically have a higher initial purchase price than standard heaters. This cost must be weighed against their extended lifespan, lower energy use, and reduced maintenance needs, which often result in a lower total cost of ownership.
Built-in Safety by Design
Operating at extreme temperatures introduces significant safety challenges. High-temperature elements are designed with features to mitigate these risks.
Inherent Electrical Insulation
Ceramic heating elements are natural electrical insulators. This property drastically reduces the risk of electrical shorts and other hazards, creating a safer operating environment, especially in comparison to metallic elements that require separate insulation layers.
Mitigating Fire and Thermal Runaway
The non-flammable nature of materials like ceramics minimizes the risk of fire. Their stable thermal properties also help prevent thermal runaway incidents, where a feedback loop can cause temperatures to rise uncontrollably.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element requires aligning its specific advantages with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is process speed: Prioritize elements with low thermal mass for the most rapid heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is a corrosive environment: Select elements with superior oxidation resistance, such as silicon carbide or those with protective sheaths.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost efficiency: Analyze the total cost of ownership, factoring in the element's lifespan and energy consumption, not just its initial price.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Ceramic-based elements offer significant advantages due to their inherent electrical insulation and non-flammable properties.
Choosing the right high-temperature element is an investment in the reliability, efficiency, and safety of your entire process.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Durability | Resists extreme heat, corrosion, and oxidation for long service life |
| Efficiency | Low thermal mass enables rapid heating, reducing energy consumption |
| Precision | Ensures uniform temperature control for high-quality outcomes |
| Safety | Inherent electrical insulation and non-flammable properties minimize risks |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower total cost of ownership despite higher initial investment |
Ready to enhance your industrial processes with reliable high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our heating elements can boost your efficiency, safety, and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















