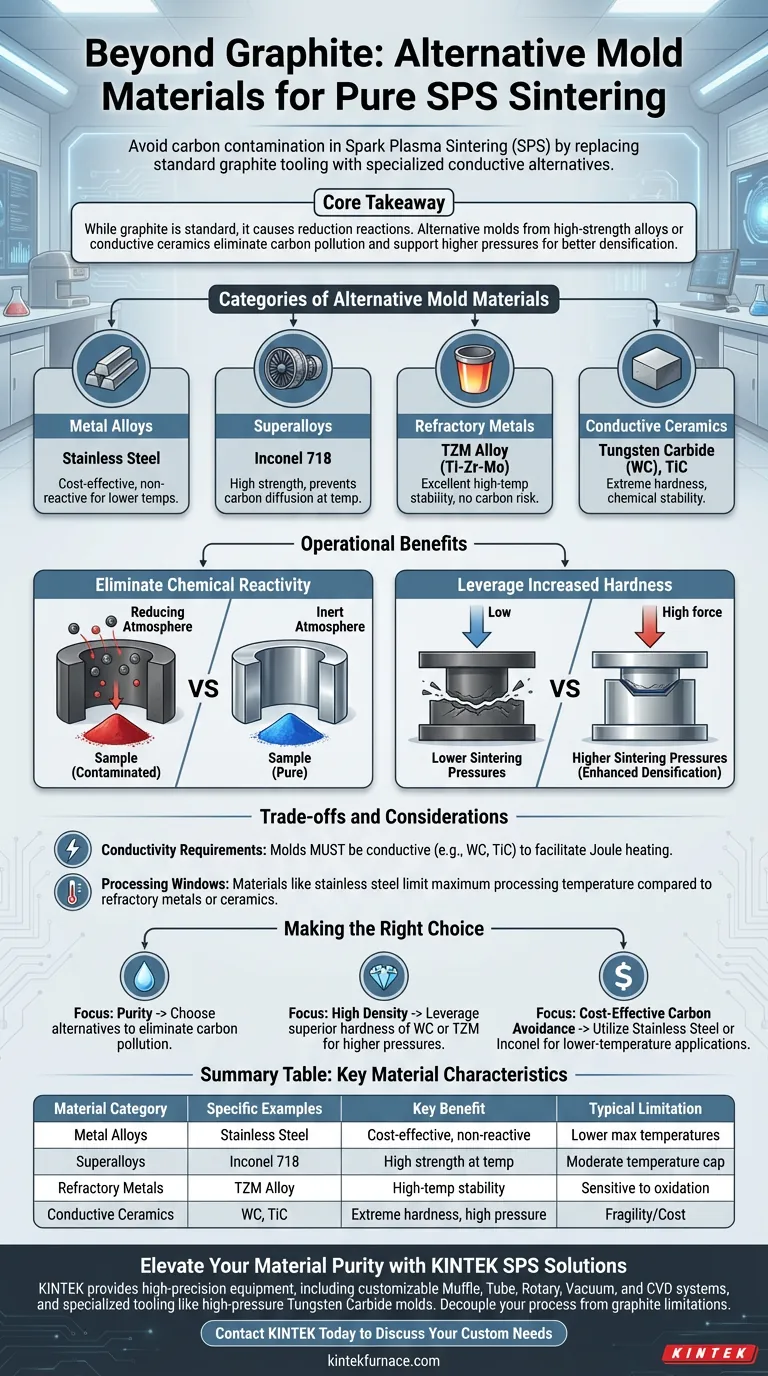
To avoid carbon contamination during Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), the standard graphite tooling is replaced with alternative mold materials including stainless steel, nickel-based superalloys (such as Inconel 718), refractory metals (like TZM alloy), or conductive ceramics like Tungsten Carbide (WC) and Titanium Carbide (TiC). These materials are chosen specifically for powders that react chemically with carbon or require higher sintering pressures.
Core Takeaway While graphite is the industry standard for SPS, it is unsuitable for materials prone to reduction reactions. Alternative molds made from high-strength alloys or conductive ceramics eliminate carbon pollution and offer the added benefit of supporting higher sintering pressures due to their superior hardness.
Categories of Alternative Mold Materials
When processing materials sensitive to carbon, you generally have three categories of conductive mold alternatives.
Metal Alloys
For lower temperature ranges where carbon interactions must be strictly avoided, standard metals are effective. Stainless steel provides a readily available, non-reactive option for many applications.
Nickel-Based Superalloys
For more demanding environments, Inconel 718 is a primary choice. This nickel-based superalloy maintains its strength at elevated temperatures better than standard steel while preventing carbon diffusion into the sample.
Refractory Metals
When high performance is required, TZM alloy (Titanium-Zirconium-Molybdenum) is utilized. TZM offers excellent high-temperature stability and conductivity without the carbon contamination risks associated with graphite.
Conductive Ceramics
Unlike standard insulating ceramics, these molds must conduct electricity to function in an SPS setup. Tungsten Carbide (WC) and Titanium Carbide (TiC) are the standard choices here, offering extreme hardness and chemical stability.
Understanding the Operational Benefits
Beyond simple chemical compatibility, switching to these materials alters the mechanical parameters of the sintering process.
Eliminating Chemical Reactivity
The primary driver for using these alternatives is to avoid reduction reactions. Graphite creates a reducing atmosphere which can strip oxygen from oxides or diffuse carbon into the sintering powder, altering its properties. Metal and ceramic molds are chemically inert regarding carbon, preserving the purity of the sample.
Leveraging Increased Hardness
Graphite is relatively soft, which limits the amount of uniaxial pressure you can apply during sintering.
Alternative materials like Inconel, TZM, and especially Tungsten Carbide are significantly harder. This allows for the application of higher sintering pressures, which can enhance densification and suppress grain growth in ways graphite tooling cannot.
Trade-offs and Considerations
While these materials solve the carbon problem, they introduce new constraints compared to standard graphite.
Conductivity Requirements
SPS relies on pulsed DC current passing through the mold to generate heat (Joule heating). Therefore, you cannot simply use any high-strength ceramic; it must be a conductive ceramic like WC or TiC to facilitate the heating process.
Processing Windows
While not explicitly detailed in the reference, utilizing metal alloys (like stainless steel) inherently limits your maximum processing temperature compared to refractory metals or ceramics. You must ensure the mold material does not soften or melt before your sample is fully sintered.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct mold material depends on the specific sensitivity of your powder and your densification requirements.
- If your primary focus is Purity: Choose these alternatives to completely eliminate the risk of carbon pollution and reduction reactions that occur with graphite.
- If your primary focus is High Density: Leverage the superior hardness of materials like Tungsten Carbide or TZM to apply higher pressures than graphite can withstand.
- If your primary focus is Cost-Effective Carbon Avoidance: Utilize stainless steel or Inconel 718 for lower-temperature applications where graphite is chemically incompatible.
Ultimately, the choice of mold material allows you to decouple the sintering process from the chemical limitations of standard graphite tooling.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Specific Examples | Key Benefit | Typical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Alloys | Stainless Steel | Cost-effective, non-reactive | Lower max temperatures |
| Superalloys | Inconel 718 | High strength at temp | Moderate temperature cap |
| Refractory Metals | TZM Alloy | High-temp stability | Sensitive to oxidation |
| Conductive Ceramics | Tungsten Carbide (WC), TiC | Extreme hardness, high pressure | Fragility/Cost |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK SPS Solutions
Don't let carbon contamination compromise your research or production. KINTEK provides high-precision laboratory equipment backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our team offers customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized tooling options for unique sintering needs.
Whether you require high-pressure Tungsten Carbide molds or specialized refractory metal setups, we help you decouple your process from the limitations of standard graphite.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature lab processes?
Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Needs
Visual Guide
References
- Alexander M. Laptev, Olivier Guillon. Tooling in Spark Plasma Sintering Technology: Design, Optimization, and Application. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202301391
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum press machine? Achieve Perfect, Void-Free Lamination and Densification
- How does temperature control in a vacuum hot pressing furnace influence the interface quality of Ti-Al composites?
- What are the technical advantages of using Pulsed Current Sintering (PCS) for Ag2S1-xTex? Optimize Your Microstructure
- What is the benefit of programmable multi-segment process control in hot press sintering furnaces for nano-copper?
- What is hot pressing sintering and how does vacuum hot pressing sintering improve the process? Achieve Superior Material Density and Purity
- What is the significance of using a high-temperature hot-press bonding furnace in MgO sensor heads? Expert Guide
- What core functions do high-purity graphite molds perform during the SPS of LaFeO3? Optimize Your Sintering Process
- Why are graphite molds necessary during the hot pressing sintering process of Fe-Cu-Ni-Sn-VN? Essential Sintering Tools

















