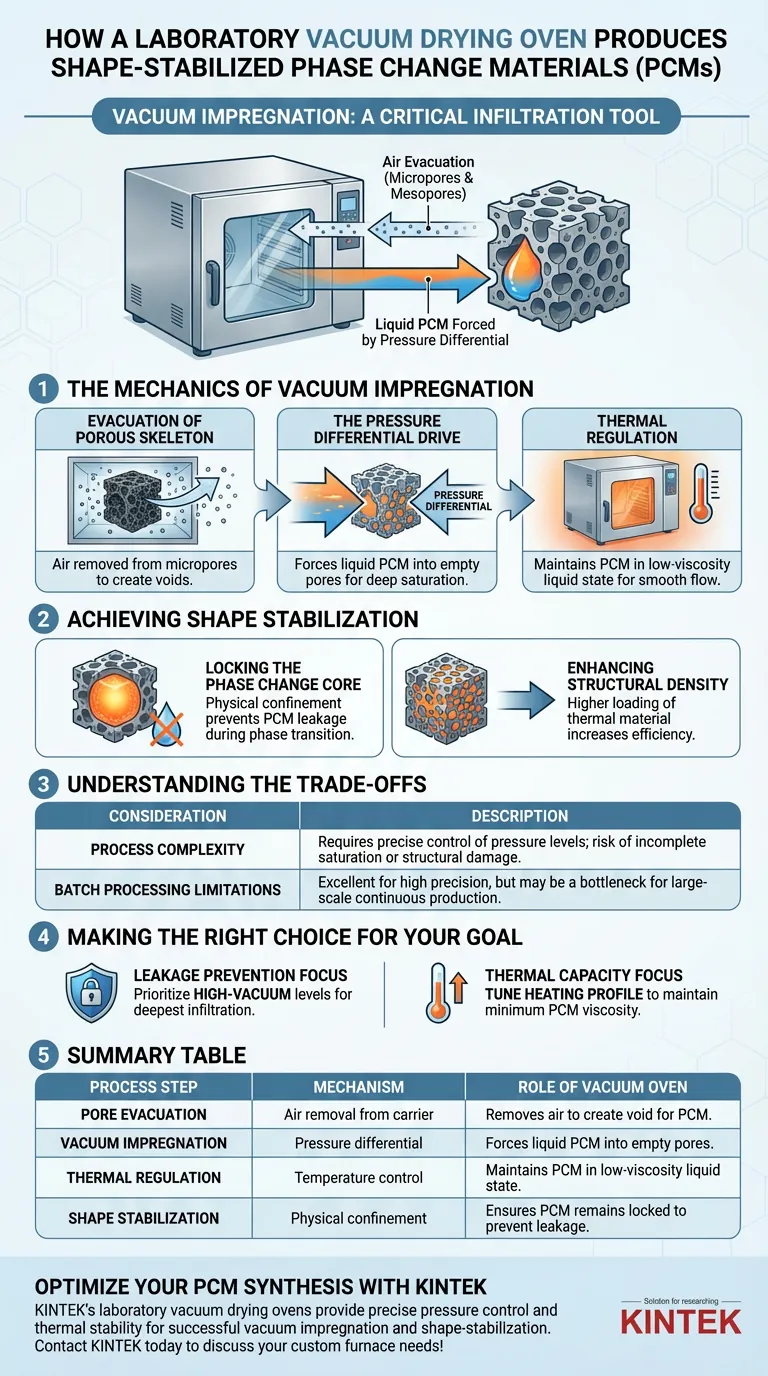
In the production of shape-stabilized phase change materials (PCMs), a laboratory vacuum drying oven acts as a critical infiltration tool rather than a simple drying device. Its primary function is to execute vacuum impregnation, a process where air is evacuated from the pores of a porous carrier (such as biochar) to allow liquid phase change materials (like polyethylene glycol) to deeply penetrate and occupy the material's internal structure.
The vacuum oven utilizes pressure differentials to force liquid PCMs into the microscopic framework of the carrier, locking the thermal storage material inside to effectively prevent leakage during phase transitions.
The Mechanics of Vacuum Impregnation
To create a stable composite material that holds heat without leaking liquid, the vacuum oven manipulates pressure and temperature simultaneously.
Evacuation of the Porous Skeleton
The process begins by placing the porous carrier material—often a carbon-based framework like biochar—into the oven.
The vacuum pump removes air trapped within the carrier's micropores and mesopores. This is the most critical step; without removing this air, the liquid PCM cannot enter the tiny voids.
The Pressure Differential Drive
Once the air is removed, the system introduces the liquid phase change material (PCM).
Because the pores are in a vacuum state (negative pressure), a strong pressure differential is created. This physical force drives the liquid PCM to rush into the empty pores, ensuring complete saturation of the internal volume.
Thermal Regulation
Throughout this process, the oven maintains constant heating.
This thermal control ensures the PCM remains in a liquid state with low viscosity during impregnation. It facilitates a smoother flow into the intricate porous structure of the skeleton.
Achieving Shape Stabilization
The ultimate goal of using a vacuum oven in this context is "shape stabilization"—ensuring the material stays solid macroscopically even when the internal chemical melts.
Locking the Phase Change Core
By forcing the PCM deep into the framework, the vacuum process maximizes the contact area between the core material and the skeleton.
This creates a strong interaction between the phase change core and the porous walls. This physical confinement is what prevents the PCM from leaking out when it turns to liquid during heat absorption.
Enhancing Structural Density
Vacuum impregnation leads to a denser final product compared to simple immersion.
Because the vacuum pulls the fluid into the smallest mesopores, the final composite has a higher loading of thermal material, increasing its efficiency as a heat storage medium.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum impregnation is superior for stability, it presents specific operational considerations.
Process Complexity
Unlike simple soaking or mixing, vacuum impregnation requires precise control of pressure levels.
If the vacuum is too weak, air pockets remain, leading to lower thermal capacity. If the pressure changes too rapidly, it can damage the delicate porous structure of the carrier.
Batch Processing Limitations
Vacuum drying ovens are typically batch-processing tools.
This makes them excellent for high-precision laboratory synthesis or small-scale production, but they may represent a bottleneck compared to continuous flow processes used in large-scale industrial manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When setting up your synthesis protocol, consider your specific performance targets.
- If your primary focus is Leakage Prevention: Prioritize high-vacuum levels to ensure the deepest possible infiltration into the mesopores, creating the strongest physical confinement.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Capacity: Ensure the heating profile is perfectly tuned to the PCM's melting point to maintain minimum viscosity, allowing the maximum amount of material to enter the voids.
The vacuum drying oven is not just for removing moisture; it is the engine that physically integrates the thermal core into the structural shell.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Mechanism | Role of Vacuum Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Pore Evacuation | Air removal from carrier | Removes air from micropores to create a void for the PCM. |
| Vacuum Impregnation | Pressure differential | Forces liquid PCM into empty pores for deep, uniform saturation. |
| Thermal Regulation | Temperature control | Maintains PCM in a low-viscosity liquid state for easier flow. |
| Shape Stabilization | Physical confinement | Ensures PCM remains locked in the skeleton to prevent leakage. |
Optimize Your PCM Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision thermal storage requires equipment that goes beyond simple heating. KINTEK’s laboratory vacuum drying ovens provide the precise pressure control and thermal stability essential for successful vacuum impregnation and shape-stabilization.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique research or production requirements. Whether you are developing biochar composites or advanced thermal frameworks, our high-performance systems ensure maximum loading and zero leakage.
Ready to enhance your material performance? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Ziming Wang, Hui Cao. Multistage Porous Carbon Derived from Enzyme-Treated Waste Walnut Green Husk and Polyethylene Glycol for Phase Change Energy Storage. DOI: 10.3390/ma17061379
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum annealing furnace play in AlCoCrFeNi2.1 joints? Ensure Microstructural Stability & Pure Diffusion
- How are vacuum furnaces typically heated? Discover Efficient, Clean Heating Solutions
- What role does a vacuum annealing furnace play in evaluating Ag2S1-xTex phase stability? Map Material Limits Precisely
- What are the steps involved in a typical vacuum brazing treatment? Master the Process for Strong, Clean Joints
- What types of pumps are used for vacuum brazing? Master the Staged System for High-Purity Brazing
- What is the function of a laboratory vacuum drying oven in catalyst and electrode treatment? Ensure Material Integrity
- What are the core functions of a vacuum thermal reduction furnace? Efficiently Extract Pure Magnesium
- What types of heat treatment processes can a vacuum furnace support? Achieve Purity and Precision in Material Processing



















