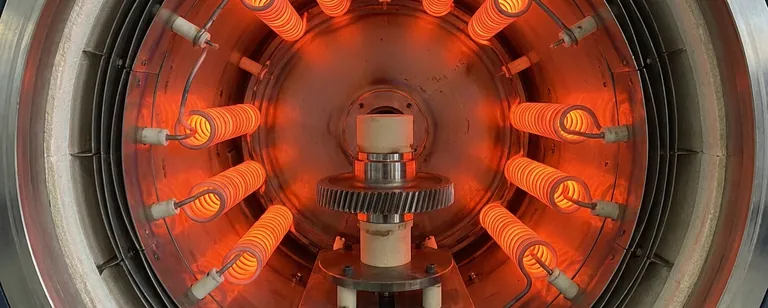
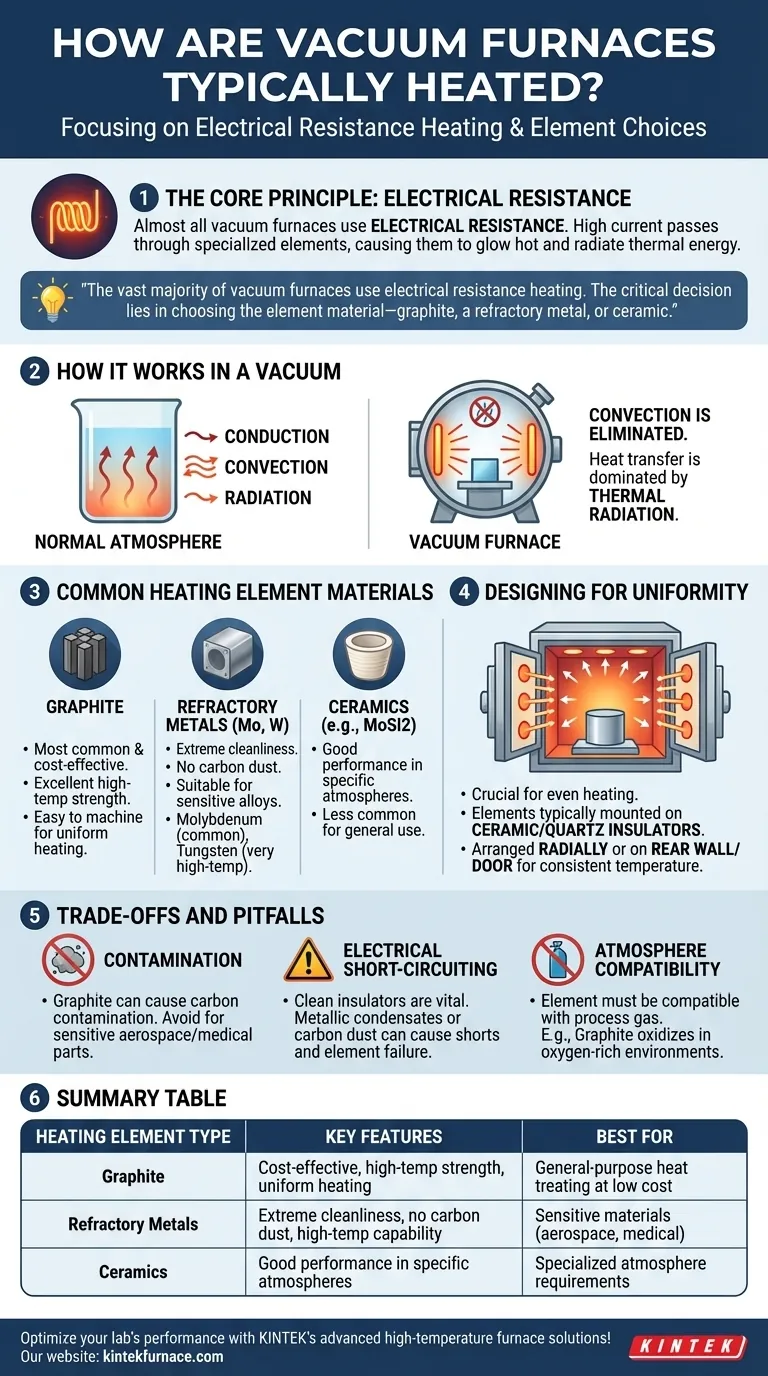
In a vacuum furnace, heating is almost always accomplished using electrical resistance. These systems pass a high electrical current through specialized heating elements, which glow hot and radiate thermal energy to the workpiece within the vacuum chamber.
The core principle is straightforward: the vast majority of vacuum furnaces use electrical resistance heating. The critical decision lies in choosing the element material—typically graphite, a refractory metal like molybdenum, or a ceramic—as this choice dictates the furnace's temperature capabilities, cleanliness, and operational costs.
The Dominant Method: Electrical Resistance
Nearly all modern vacuum furnaces rely on the principle of resistive heating, also known as Joule heating. An electrical current is forced through a material with high resistance, causing that material to heat up significantly.
How It Works in a Vacuum
In a normal atmosphere, heat transfers through conduction, convection, and radiation. Because a vacuum furnace removes air, convection is eliminated.
Heat transfer is therefore dominated by thermal radiation. The hot elements emit infrared energy, which travels through the vacuum and is absorbed by the workpiece, raising its temperature.
Common Heating Element Materials
The choice of material for the heating elements is the most critical design factor.
Graphite: This is the most common and cost-effective material. It has excellent high-temperature strength and is easy to machine into complex shapes for uniform heating.
Refractory Metals: Materials like molybdenum and tungsten are used for applications requiring extreme cleanliness. They do not produce carbon dust and are suitable for processing sensitive alloys. Molybdenum is common, while tungsten is reserved for very high-temperature applications.
Ceramics: Certain ceramic composites, like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), can also be used. They offer good performance in specific atmospheres but are less common in general-purpose vacuum furnaces.
Designing the Heating Zone for Uniformity
The physical arrangement of the heating elements is crucial for ensuring the part is heated evenly from all sides, preventing distortion or inconsistent material properties.
Element Placement
Heating elements are typically mounted on robust ceramic or quartz insulators. This prevents the high current from short-circuiting to the furnace's metal frame.
To achieve uniform temperature, elements may be arranged radially (in a cylinder around the workload) or placed on the furnace's rear wall and interior door.
Element Connections
Graphite elements are often connected using bolted graphite bridges, creating a continuous electrical circuit. Metallic elements are welded or mechanically fastened.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While reliable, resistive heating systems require careful management to ensure longevity and process quality. Understanding their limitations is key to successful operation.
Contamination and Cleanliness
Graphite elements, while economical, can be a source of carbon contamination. Over time, fine carbon dust can settle on surfaces, which is unacceptable for certain aerospace or medical applications. This is the primary reason for choosing more expensive metallic elements.
The Risk of Electrical Short-Circuiting
The insulators holding the elements must be kept impeccably clean. Metallic condensates (from brazing filler metal, for instance) or carbon dust can create a conductive path on an insulator's surface, causing a short circuit that can destroy the element and halt production.
Atmosphere Compatibility
The heating element material must be compatible with any process gas used. For example, using graphite elements in an oxygen-rich environment, even at trace levels, would cause them to rapidly oxidize and fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your process goals directly determine the ideal heating system configuration for your vacuum furnace.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating at a low cost: A furnace with graphite heating elements is the industry standard and most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute cleanliness for sensitive materials (e.g., medical implants or aerospace alloys): A furnace with molybdenum or tungsten heating elements is necessary to prevent carbon contamination.
- If your primary focus is direct and rapid heating of the conductive part itself: A specialized induction heating system, which heats the part directly via an electromagnetic field, may be the most efficient solution.
Ultimately, understanding the heating mechanism is fundamental to controlling your process and achieving repeatable, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Cost-effective, high-temperature strength, uniform heating | General-purpose heat treating at low cost |
| Refractory Metals (e.g., Molybdenum, Tungsten) | Extreme cleanliness, no carbon dust, high-temperature capability | Sensitive materials like aerospace alloys or medical implants |
| Ceramics (e.g., MoSi2) | Good performance in specific atmospheres | Specialized applications with specific atmosphere requirements |
Optimize your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Whether you need precise heating for sensitive materials or cost-effective general-purpose systems, our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems are backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. Leverage our deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes and deliver reliable, high-quality results tailored to your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















