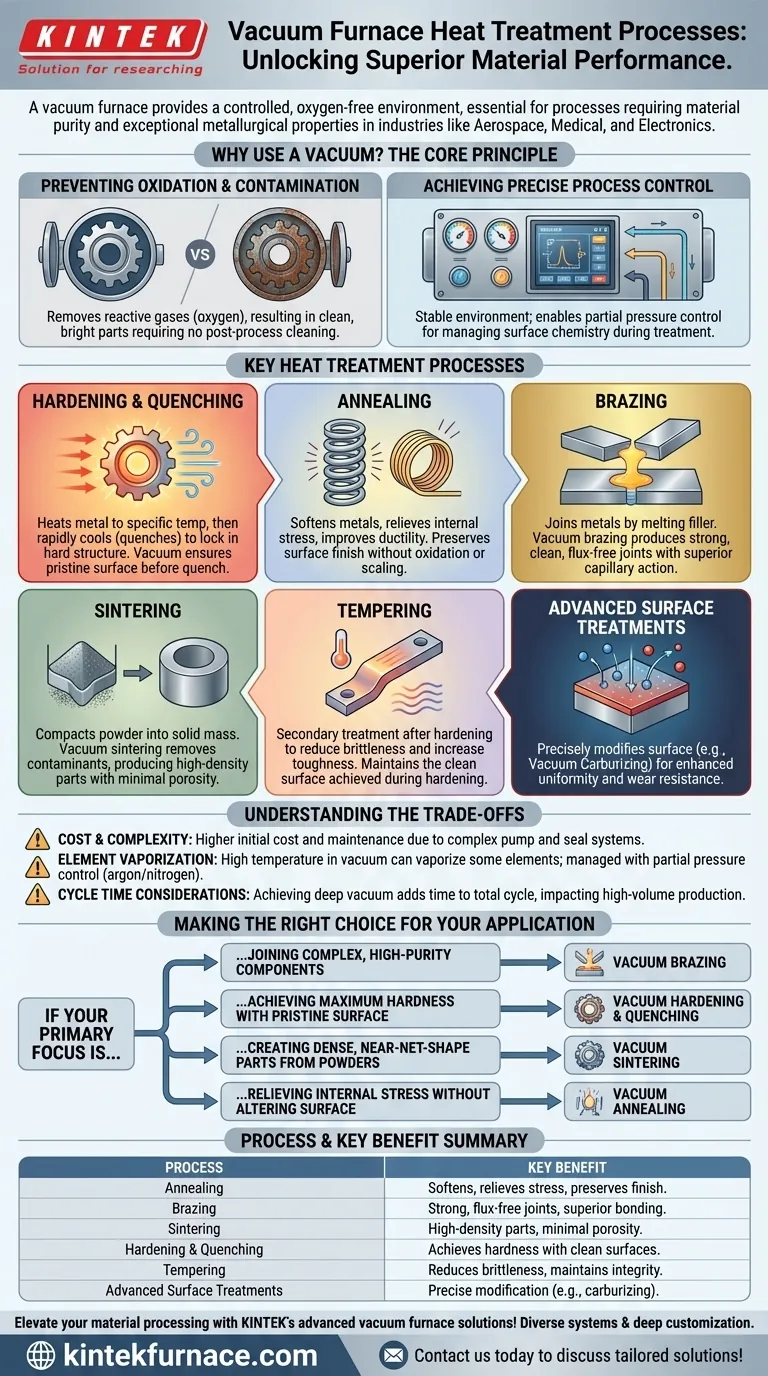
In short, a vacuum furnace supports a wide array of critical heat treatment processes, including annealing, brazing, sintering, tempering, and hardening. Its ability to operate in a controlled, oxygen-free environment makes it an essential tool for industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics where material purity and performance are non-negotiable.
The true value of a vacuum furnace isn't just the variety of processes it supports, but the high-purity, controlled environment it provides. This eliminates oxidation and contamination, enabling the creation of parts with exceptional strength, cleanliness, and metallurgical properties that are often impossible to achieve in a conventional atmosphere.
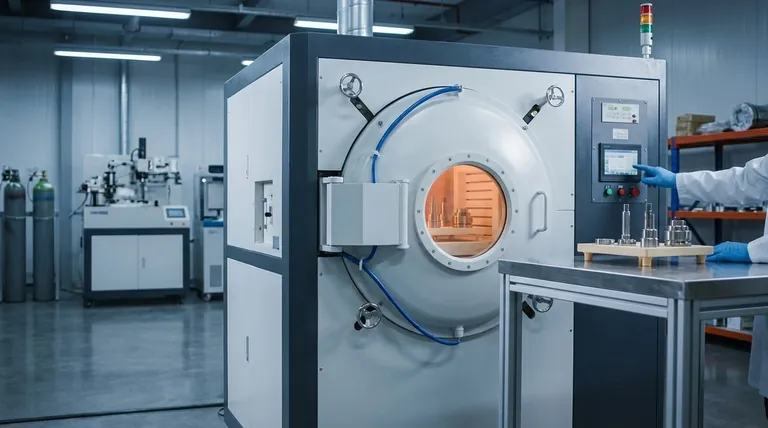

The Core Principle: Why Use a Vacuum?
Before detailing the specific processes, it's crucial to understand why a vacuum environment is so advantageous. The primary goal is to remove the reactive gases—primarily oxygen—that are present in a normal atmosphere.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
By removing the atmosphere, a vacuum furnace prevents the formation of oxides on the material's surface. This results in clean, bright parts that do not require post-process cleaning or machining to remove a discolored or scaled layer.
Achieving Precise Process Control
A vacuum provides an extremely stable and predictable environment. Advanced furnaces also allow for the introduction of specific gases at very low pressures, a technique known as partial pressure control. This allows engineers to precisely manage the surface chemistry of the material during treatment.
Key Heat Treatment Processes Explained
The vacuum environment enhances a range of standard thermal processes, each tailored for a specific metallurgical outcome.
Hardening & Quenching
Hardening involves heating a metal to a specific temperature and then cooling it rapidly (quenching) to lock in a hard, crystalline structure.
Using a vacuum ensures the part's surface is perfectly clean and free of oxides before the quench. Quenching can then be performed using high-pressure inert gas streams or, in some designs, by transferring the part to an integrated oil bath.
Annealing
Annealing is a process used to soften metals, relieve internal stresses, and improve their ductility.
When performed in a vacuum, annealing ensures the material's surface finish is preserved. There is no risk of the oxidation or scaling that commonly occurs during atmospheric annealing, which is critical for finished or near-finished parts.
Brazing
Brazing joins two or more metal items by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint.
Vacuum brazing is a standout application. It produces exceptionally strong, clean, and void-free joints without the use of corrosive flux. The vacuum pulls the filler metal deep into the joint capillaries, creating a superior bond essential for aerospace and high-performance components.
Sintering
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat, without melting it to the point of liquefaction. It's commonly used in powder metallurgy.
Vacuum sintering helps produce high-density components with minimal porosity. The vacuum environment is highly effective at removing trapped air and other contaminants from the powdered material before and during densification.
Tempering
Tempering is a secondary treatment performed after hardening to reduce brittleness and increase toughness.
While it's a lower-temperature process, performing it in a vacuum guarantees that the clean, bright surface achieved during the hardening phase is maintained.
Advanced Surface Treatments
A vacuum furnace is also the ideal environment for precisely modifying a material's surface. Processes like vacuum carburizing involve introducing a controlled, carbon-rich gas at low pressure to harden the surface layer of a part with exceptional uniformity and control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are more expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts. They require complex systems of pumps, seals, and instrumentation that demand regular, specialized maintenance to ensure performance.
Managing Element Vaporization
Under a deep vacuum, some alloying elements (like chromium in certain steels) can vaporize from the surface of the material at high temperatures. This is managed using partial pressure control, where a small, controlled amount of an inert gas like argon or nitrogen is introduced to suppress this effect.
Cycle Time Considerations
Achieving a deep vacuum takes time. The pump-down phase can add to the total cycle time compared to simply heating a part in an atmospheric furnace. This is a critical consideration for high-volume production environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a vacuum furnace process is driven by the final requirements of the component.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, high-purity components: Vacuum brazing provides superior joint strength without the need for corrosive fluxes.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness with a pristine surface: Vacuum hardening and quenching prevent oxidation, eliminating the need for post-process cleaning.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, near-net-shape parts from powders: Vacuum sintering is essential for removing contaminants and minimizing porosity.
- If your primary focus is relieving internal stress without altering surface finish: Vacuum annealing ensures the material is softened without any risk of discoloration or scaling.
Ultimately, leveraging a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize material integrity, cleanliness, and performance above all else.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Softens metals, relieves stress, preserves surface finish | Aerospace, medical components |
| Brazing | Creates strong, flux-free joints with superior bonding | High-performance assemblies, electronics |
| Sintering | Produces high-density parts with minimal porosity | Powder metallurgy, industrial parts |
| Hardening & Quenching | Achieves hardness with clean, oxide-free surfaces | Tool steels, automotive parts |
| Tempering | Reduces brittleness, maintains surface integrity | Post-hardening treatments |
| Advanced Surface Treatments | Enables precise surface modification (e.g., carburizing) | Wear-resistant components |
Elevate your material processing with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior purity, performance, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your specific applications in aerospace, medical, or electronics industries!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















