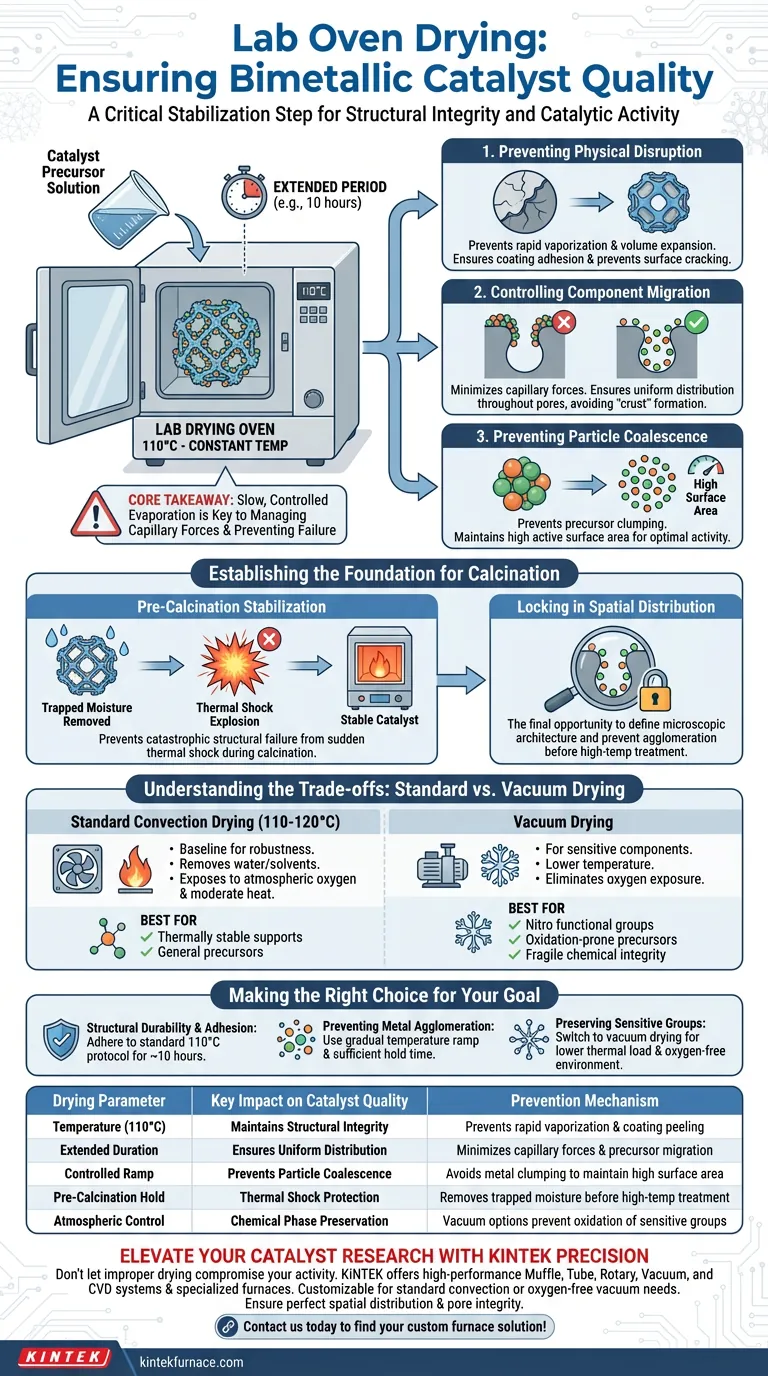
The lab oven drying process acts as a critical stabilization step, typically utilizing a constant temperature around 110°C for extended periods (e.g., 10 hours) to slowly evaporate moisture and solvents from catalyst pores. By controlling the rate of vaporization, this process prevents physical disruptions—such as coating peeling or the uneven distribution of active components—that occur when moisture escapes too rapidly, thereby ensuring the structural integrity required for subsequent calcination.
Core Takeaway Rushing the removal of solvents is a leading cause of catalyst failure before the reaction even begins. The drying oven’s primary function is to manage capillary forces inside the support structure, locking metal precursors in place to prevent migration and particle coalescence before high-temperature treatment makes those structures permanent.
Regulating Solvent Removal and Pore Integrity
Preventing Physical Disruption
The immediate danger during catalyst preparation is rapid vaporization. If the solvent within the porous support turns to steam too quickly, the resulting volume expansion can physically damage the catalyst structure.
This often manifests as coating peeling or surface cracking. By maintaining a steady temperature (typically 110°C–120°C), the oven ensures moisture is released gradually, preserving the physical coating on the support.
Controlling Component Migration
As solvents evaporate, they generate capillary forces that can drag dissolved metal precursors toward the surface of the pore.
If this process is uncontrolled, it leads to uneven distribution or "crust" formation. Slow, constant-temperature drying minimizes this migration, ensuring the active bimetallic components remain uniformly dispersed throughout the internal pore structure.
Preventing Particle Coalescence
When metal precursors are forced together by rapid evaporation, they tend to clump or coalesce.
This reduces the active surface area of the final catalyst. Extended drying times allow the solvent to recede without forcing these particles together, maintaining the high dispersion necessary for catalytic activity.
Establishing the Foundation for Phase Formation
Pre-Calcination Stabilization
The drying phase creates a sound physical foundation for the next step: high-temperature calcination.
If moisture remains trapped deep within the pores when the catalyst enters the calcination furnace, the sudden thermal shock can cause catastrophic structural failure. Thorough drying ensures the catalyst is physically stable before chemical phase changes occur.
Locking in Spatial Distribution
The spatial arrangement of the bimetallic components is defined during the drying stage, not the calcination stage.
Once the catalyst enters high-temperature treatment, the metal particles are essentially fixed in place. Therefore, the oven drying process is the final opportunity to influence component distribution and prevent the agglomeration of active sites.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Standard vs. Vacuum Drying
While standard oven drying at 110°C is the baseline for general robustness, it is not universally applicable to all catalyst types.
Standard Convection Drying (110°C - 120°C)
This is the standard approach for thermally stable supports and precursors. It effectively removes water and common solvents. However, it exposes the catalyst to atmospheric oxygen and moderate heat, which can be detrimental to highly sensitive functional groups.
Vacuum Drying Limitations
For catalysts containing sensitive components (such as nitro functional groups) or those prone to oxidation, standard drying may cause premature decomposition.
In these specific cases, a vacuum drying oven is required. This allows for solvent removal at reduced temperatures and eliminates oxygen exposure, preserving the chemical integrity of fragile precursors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the highest quality bimetallic catalyst, tailor your drying protocol to the specific stability of your precursors.
- If your primary focus is structural durability and coating adhesion: Adhere to the standard protocol of 110°C for approximately 10 hours to prevent peeling and ensure complete moisture removal.
- If your primary focus is preventing metal agglomeration: Ensure the temperature ramp is gradual and the hold time is sufficient to prevent capillary forces from causing particle migration.
- If your primary focus is preserving sensitive functional groups: Switch to vacuum drying to lower the thermal load and remove atmospheric oxygen from the process.
A disciplined drying phase is not merely about removing water; it is the primary control point for defining the microscopic architecture of your final catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Drying Parameter | Key Impact on Catalyst Quality | Prevention Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (110°C) | Maintains Structural Integrity | Prevents rapid vaporization and coating peeling |
| Extended Duration | Ensures Uniform Distribution | Minimizes capillary forces and precursor migration |
| Controlled Ramp | Prevents Particle Coalescence | Avoids metal clumping to maintain high surface area |
| Pre-Calcination Hold | Thermal Shock Protection | Removes trapped moisture before high-temp treatment |
| Atmospheric Control | Chemical Phase Preservation | Vacuum options prevent oxidation of sensitive groups |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let improper drying compromise your catalytic activity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique preparation needs. Whether you require standard convection stability or oxygen-free vacuum environments, our equipment ensures perfect spatial distribution and pore integrity for your bimetallic catalysts.
Ready to optimize your lab's drying and calcination protocols? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Xiaojian Wang, Hao Huang. Synergistic oxidation of toluene through bimetal/cordierite monolithic catalysts with ozone. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58026-6
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the synergistic effect of industrial fly ash in beet pulp porous carbons? Enhance 3D Structural Performance
- How do you maintain a vacuum pump? Ensure peak performance and longevity for your lab
- Why is a vacuum sealing process necessary for the synthesis of TaAs2 single crystals? Ensuring Purity in CVT Method
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Unlock Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What is the core role of a high-pressure autoclave in the synthesis of LTA zeolites? Achieve Precise Crystal Growth
- What is the firing temperature for sintering? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges
- Why is the precision of a temperature control system critical in copper brazing? Ensure Perfect Joints Every Time
- What is the primary purpose of introducing reactive gases (SF6/CF4) in magnetron sputtering? Restore Film Stoichiometry

















