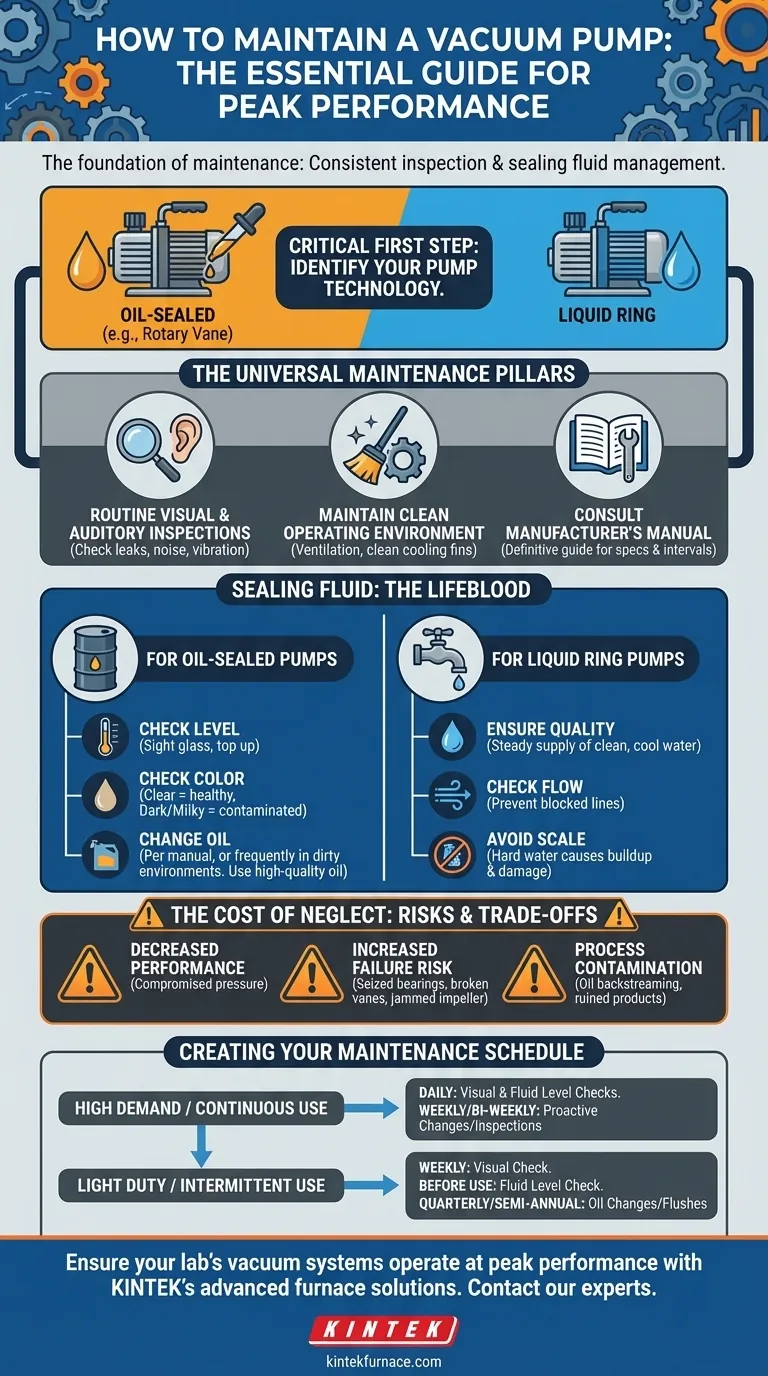
The foundation of vacuum pump maintenance is built on two universal practices: consistent, diligent inspection and the proper management of the pump's sealing fluid. This involves regularly checking for leaks, listening for unusual noises, and ensuring the oil or water that allows the pump to function is clean and at the correct level.
The most critical aspect of maintenance is first identifying your specific pump technology. The procedures for an oil-sealed rotary vane pump are completely different from those for a water-based liquid ring pump. Applying the wrong maintenance can cause poor performance and irreversible damage.
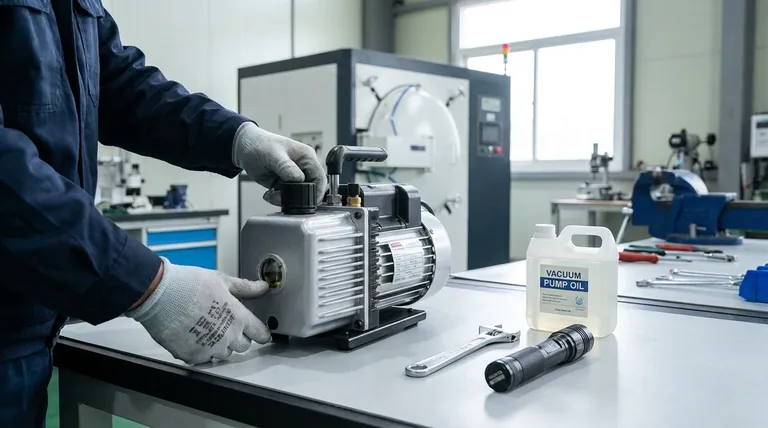

The Universal Maintenance Pillars
Regardless of your pump's specific type, a few foundational checks are always required. These form the baseline of any effective preventative maintenance program.
Routine Visual & Auditory Inspections
You can identify many potential issues before they become critical failures. Make it a habit to perform a quick check before starting the pump.
Look for any signs of oil or water leaks around fittings, seals, and gaskets. Check for physical damage or excessive vibration. Most importantly, listen for any new or unusual noises, such as grinding, rattling, or knocking, which often indicate internal wear.
Maintaining a Clean Operating Environment
The environment around the pump directly impacts its health. A pump caked in dust and debris cannot cool itself effectively, leading to overheating and premature wear on its components.
Ensure the pump has adequate ventilation and that cooling fins are kept clean. This simple step is one of the most effective ways to extend the life of the motor and internal pump elements.
The Manufacturer's Manual is Your Definitive Guide
Every pump is designed with specific tolerances and requirements. Your pump's instruction manual is the single most important document for its care.
It contains the exact specifications for fluid types, service intervals, and troubleshooting procedures. Always defer to the manufacturer's recommendations over any generic advice.
Sealing Fluid: The Lifeblood of Your Pump
The fluid inside your pump—whether it's oil or water—is not just a lubricant; it's a core functional component. Its condition directly determines the pump's ability to create a vacuum.
For Oil-Sealed Pumps (e.g., Rotary Vane)
In these common pumps, a specialized oil creates the vacuum seal, lubricates all moving parts, and transfers heat away from the mechanism. Neglecting the oil is the fastest way to destroy the pump.
Regularly check the oil level via the sight glass and top it up as needed. The oil's color indicates its health; clean oil is typically light and clear, while contaminated oil becomes dark and milky. Change the oil according to the manual's schedule, or more frequently if the pump is used in a dirty or humid environment. Always use high-quality vacuum pump oil specified for your model.
For Liquid Ring Pumps
These pumps use a rotating impeller to form a ring of liquid (typically water) against the pump's housing. This liquid ring is what traps and compresses the gas, creating the vacuum.
Maintenance focuses on the quality and flow of this sealing liquid. You must ensure a steady supply of clean, cool water as specified by the manufacturer. Blocked water lines or the use of hard water that can cause mineral buildup (scale) will severely degrade performance and can damage the impeller.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Cost of Neglect
Skipping maintenance might seem to save time in the short term, but it introduces significant risks and long-term costs.
Decreased Vacuum Performance
The ultimate vacuum level a pump can achieve is directly tied to the condition of its sealing fluid. Contaminated oil or an unstable water ring prevents the pump from reaching its specified pressure, which can compromise your entire process.
Increased Risk of Catastrophic Failure
Poor lubrication from degraded oil causes metal-on-metal contact, leading to seized bearings or broken vanes. Mineral buildup from a poor water supply in a liquid ring pump can cause the impeller to jam, resulting in a complete and often irreparable failure.
Process Contamination
In an oil-sealed pump, old oil can "backstream," sending oil vapor back into your vacuum chamber and contaminating your product or experiment. This is a critical failure in sensitive applications like semiconductor manufacturing or mass spectrometry.
Creating Your Maintenance Schedule
The right maintenance frequency depends entirely on your application's demands. Use the manufacturer's manual as a baseline and adjust from there.
- If your primary focus is uptime in a demanding, continuous-use environment: Perform daily visual and fluid-level checks. Plan for proactive oil changes or water system inspections on a weekly or bi-weekly basis, even if the fluid appears clean.
- If your primary focus is reliability for intermittent or light-duty work: A weekly visual check is sufficient. Schedule fluid level checks before each use and plan for oil changes or water system flushes on a quarterly or semi-annual basis.
Consistent maintenance is the most effective investment you can make in your pump's long-term performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| Visual & Auditory Inspection | Daily/Weekly | Check for leaks, noise, vibration |
| Sealing Fluid Level Check | Before use/Weekly | Top up oil or ensure water flow |
| Sealing Fluid Quality Check | Per manual/As needed | Change oil or flush water system |
| Environment Cleanliness | Ongoing | Keep pump and cooling fins clean |
Ensure your lab's vacuum systems operate at peak performance with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions. Our expertise in high-temperature technology, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is backed by exceptional R&D and deep customization capabilities. Whether you need reliable vacuum environments for materials processing or specialized thermal solutions, we can help. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can meet your unique experimental requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Performance Vacuum Bellows for Efficient Connection and Stable Vacuum in Systems
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















