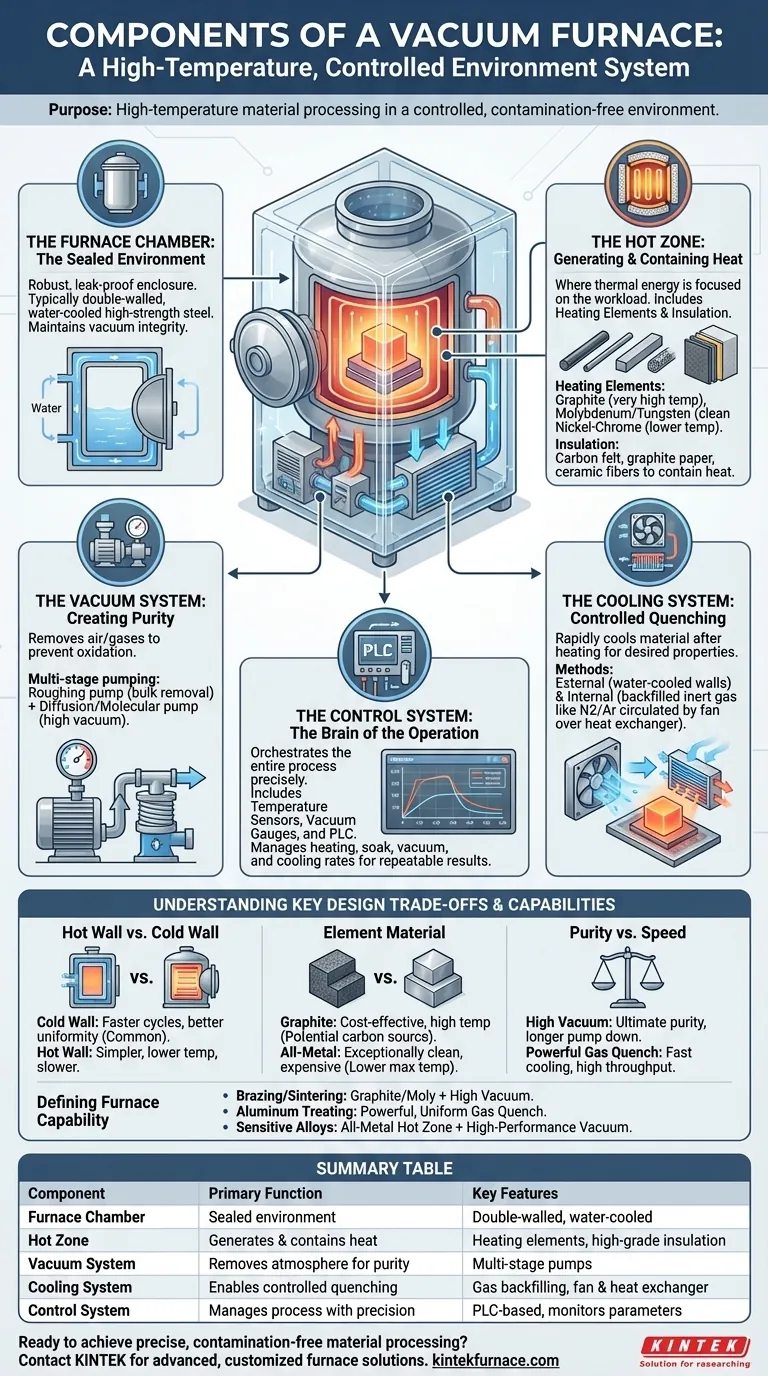
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a system of interconnected components designed for one purpose: high-temperature material processing in a controlled, contamination-free environment. Its primary components are the airtight furnace chamber which contains the process, a heating system to reach target temperatures, a vacuum system to remove the atmosphere, a control system to manage the process with precision, and a cooling system to bring the material back to a safe temperature.
A vacuum furnace is not merely a hot box. It is an integrated system where each component—from the vacuum pumps to the insulation—plays a critical role in creating an environment that enables metallurgical processes impossible to achieve in open air.

The Anatomy of a Vacuum Furnace: Core Systems
To understand how a vacuum furnace functions, it's best to think of it as a collection of purpose-built systems working in concert. Each system is responsible for one phase of the heat-treating cycle.
The Furnace Chamber: The Sealed Environment
The foundation of any vacuum furnace is its chamber, also known as the vessel or furnace body. This component's sole function is to provide a robust, leak-proof enclosure.
It is typically a double-walled, water-cooled structure made from high-strength steel or stainless steel. The water circulating between the walls keeps the exterior of the furnace cool and safe to the touch, even when the interior is at thousands of degrees.
A large, sealed door provides access for loading and unloading materials. The integrity of the chamber and its seals is paramount to achieving and maintaining the required vacuum level.
The Hot Zone: Generating and Containing Heat
Inside the chamber lies the "hot zone," which consists of the heating elements and the insulation package. This is where the thermal energy is generated and focused on the workload.
Heating elements are the source of the heat. Their material dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature. Common materials include:
- Graphite: Used for very high temperatures (up to and beyond 2200°C) in non-oxidizing vacuum environments.
- Molybdenum and Tungsten: High-temperature metals used for clean processing applications where carbon from graphite would be a contaminant.
- Nickel-Chrome (NiCr): A resistance wire used for lower-temperature applications like tempering (below 750°C).
Insulation surrounds the heating elements to prevent heat from escaping to the water-cooled chamber walls. This improves thermal efficiency and temperature uniformity. Materials like high-grade carbon felt, graphite paper, and ceramic fibers are used to reflect and contain the immense heat.
The Vacuum System: Creating Purity
The vacuum system is what separates a vacuum furnace from any other type of furnace. Its job is to remove air and other gases from the chamber before and during heating. This prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions on the material's surface.
A typical system uses multiple types of pumps working in stages. A mechanical "roughing" pump removes the bulk of the air, after which a diffusion, molecular, or "booster" pump takes over to achieve the much lower pressures required for high-vacuum processing.
The Cooling System: Controlled Quenching
After the heating cycle is complete, the material must be cooled in a rapid and controlled manner. This process, often called quenching, is critical for locking in the desired metallurgical properties.
Most modern "cold wall" furnaces use a combination of two cooling methods:
- External Cooling: The water circulating in the chamber's double walls continuously removes heat from the overall system.
- Internal Cooling: The furnace is rapidly backfilled with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon. A powerful fan circulates this gas through the hot zone and over a heat exchanger (typically water-cooled) to quickly and evenly cool the workload.
The Control System: The Brain of the Operation
The entire process is orchestrated by a sophisticated control system. This system includes temperature sensors (thermocouples), vacuum gauges, and a central processor (often a PLC, or Programmable Logic Controller).
The control system precisely manages the heating rate, soak time, temperature, vacuum level, and cooling rate according to a pre-programmed recipe. This ensures that every cycle is identical, guaranteeing repeatable and predictable results.
Understanding Key Design Trade-offs
The specific components chosen for a vacuum furnace define its capabilities and limitations. Not all furnaces are created equal, and the design involves significant trade-offs.
Hot Wall vs. Cold Wall Design
Cold wall furnaces, where the heating elements are inside a water-cooled vacuum chamber, are the most common type for high-temperature applications. They offer faster heating and cooling cycles and greater temperature uniformity.
Hot wall furnaces, where the entire vacuum chamber is placed inside a separate, larger furnace, are simpler but limited. They are generally used for lower temperatures and are slower to heat and cool.
Heating Element Material Choice
The choice between graphite and an all-metal hot zone (molybdenum/tungsten) is critical. Graphite is cost-effective and excellent for high temperatures, but it can be a source of carbon contamination, which is unacceptable for certain alloys.
All-metal hot zones provide an exceptionally clean processing environment but are more expensive and may have lower maximum temperature limits than graphite.
Purity vs. Production Speed
The configuration of the vacuum and cooling systems creates a trade-off between process purity and cycle time. A furnace with a powerful, multi-stage vacuum system can achieve a very high vacuum for ultimate purity, but it takes longer to pump down.
Conversely, a furnace with a massive gas-quenching system can cool parts extremely fast, increasing throughput, but may be overkill for processes that don't require rapid quenching.
How Components Define Furnace Capability
When evaluating a vacuum furnace, understanding its components allows you to match its design to your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature brazing or sintering: You need a furnace with graphite or molybdenum heating elements capable of exceeding your target temperature and a vacuum system that prevents oxidation.
- If your primary focus is solution treating and age hardening aluminum: A furnace with a powerful, uniform gas quenching system is more critical than one that can achieve an extremely high vacuum.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive medical or aerospace alloys: You require an all-metal hot zone and a high-performance vacuum system to ensure absolute cleanliness and prevent any contamination.
Ultimately, understanding the function of each component transforms a complex piece of equipment into a predictable tool for achieving specific material outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Chamber | Provides a sealed, leak-proof environment | Double-walled, water-cooled structure; high-strength steel construction |
| Hot Zone | Generates and contains heat | Heating elements (graphite, molybdenum, NiCr); high-grade insulation |
| Vacuum System | Removes atmosphere for purity | Multi-stage pumps (roughing, diffusion/molecular); prevents oxidation |
| Cooling System | Enables controlled quenching | Gas backfilling (N2/Ar); fan and heat exchanger for rapid, uniform cooling |
| Control System | Manages the entire process with precision | PLC-based; monitors temperature, vacuum, and cycle parameters |
Ready to achieve precise, contamination-free material processing?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you require a standard Muffle or Tube Furnace, or a highly customized Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnace or CVD/PECVD System for sensitive aerospace or medical applications, our deep customization capability ensures your furnace is perfectly matched to your process requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnace expertise can enhance your lab's capabilities and deliver repeatable, high-quality results. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















