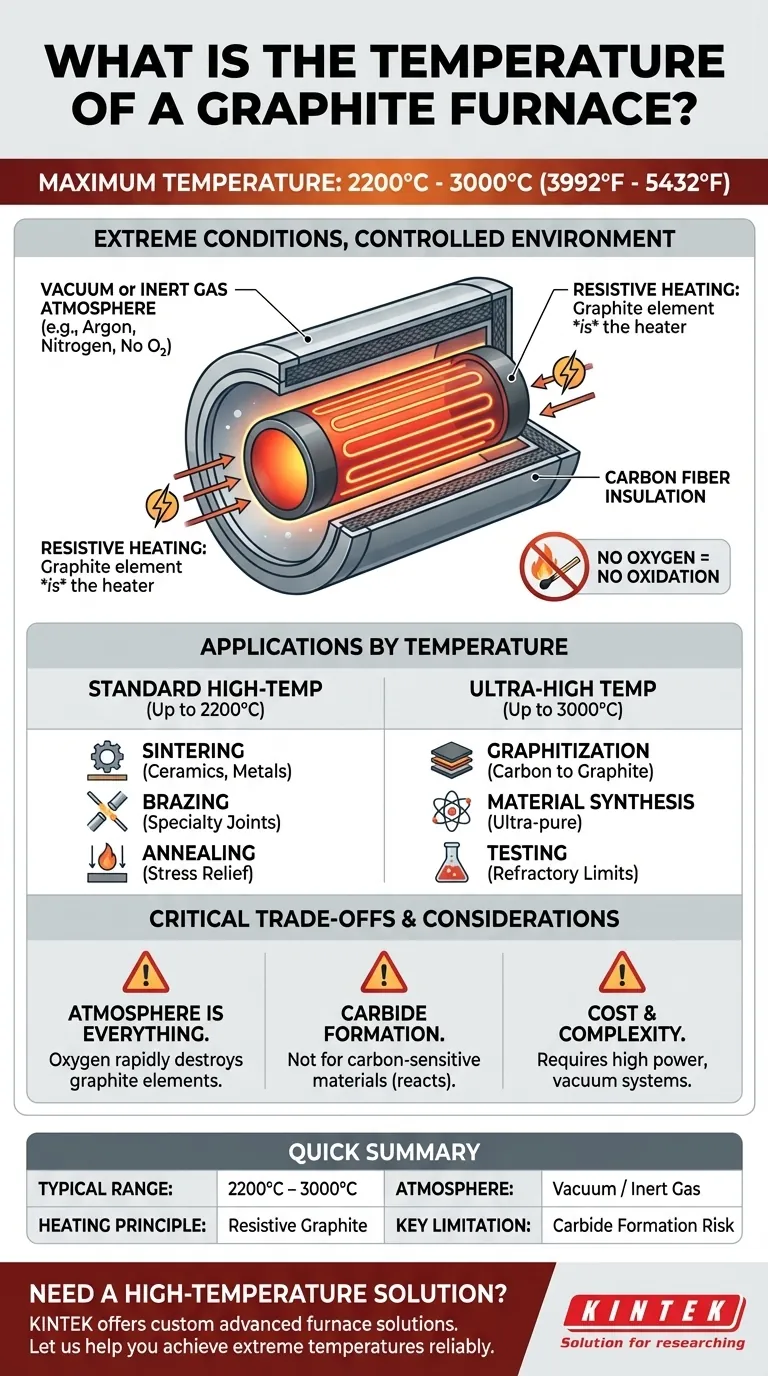
The maximum temperature of a graphite furnace typically ranges from 2200 °C to 3000 °C (3992 °F to 5432 °F). These furnaces are not defined by a single operating temperature, but rather by their capability to achieve these extreme conditions. This performance is possible because the furnace uses graphite itself as the heating element in a tightly controlled, oxygen-free environment.
A graphite furnace's high temperature capability is a direct consequence of its design. By using graphite as a resistive heater within a vacuum or inert gas, it bypasses the oxidation limits of conventional metallic elements, enabling processes that are otherwise impossible.

How Graphite Furnaces Achieve Extreme Temperatures
A graphite furnace is not simply a box lined with graphite. The material is integral to its function, acting as the very source of heat. Understanding this principle is key to understanding its capabilities.
The Role of Graphite as a Heating Element
A large electric current is passed directly through the furnace's graphite components (often a tube or series of rods). Due to its natural electrical resistance, the graphite heats up intensely, a principle known as resistive heating.
This design is fundamentally different from most furnaces, where a separate metallic or ceramic element heats the chamber. Here, the chamber is the heating element.
The Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Graphite readily burns away in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures, a process called oxidation. To prevent the furnace from destroying itself, the heated "hot zone" must be completely free of air.
This is achieved by operating the furnace under a deep vacuum or by filling the chamber with a non-reactive inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen. This controlled atmosphere is non-negotiable for furnace longevity and process purity.
Thermal Insulation and Efficiency
To manage the immense heat, the graphite heating element is surrounded by layers of high-purity carbon fiber insulation. This material is an exceptional insulator at high temperatures and is stable in a vacuum or inert gas, creating a highly efficient thermal system that directs energy to the workload.
Understanding the Temperature Range (2200°C to 3000°C)
The specific temperature used depends entirely on the industrial or scientific process being performed.
Standard High-Temp Operations (Up to 2200°C)
This is the workhorse range for many advanced applications. Common processes include the sintering of ceramics, brazing of specialty metals, annealing to relieve material stress, and creating carbon composite materials.
Ultra-High Temperature Applications (Up to 3000°C)
Temperatures approaching 3000 °C are reserved for the most demanding applications. These include graphitization (converting amorphous carbon into crystalline graphite), synthesizing ultra-pure materials, and testing the limits of refractory metals and ceramics for aerospace or nuclear applications.
Critical Trade-offs of Graphite Furnaces
While incredibly powerful, graphite furnaces have specific limitations that make them unsuitable for certain tasks. Ignoring these trade-offs can lead to failed processes and damaged equipment.
Atmosphere is Everything
The sensitivity to oxygen cannot be overstated. An air leak or improper gas purging will rapidly destroy the graphite heating elements and insulation. This requires robust vacuum systems and careful operational procedures.
Material Compatibility and Carbide Formation
Carbon is reactive at high temperatures. Certain elements and compounds will react with the graphite furnace atmosphere or components to form carbides. This can contaminate or destroy the material being processed. If your material is sensitive to carbon, a graphite furnace is the wrong choice.
Cost and Complexity
These are not simple ovens. Graphite furnaces are sophisticated systems requiring high-power electrical supplies, complex gas or vacuum handling systems, and advanced process controllers. Their acquisition and operational costs are significantly higher than standard air furnaces.
Is a Graphite Furnace Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right furnace technology depends entirely on your material, atmosphere, and temperature requirements.
- If your primary focus is processing above 2000°C in a non-oxidizing environment: A graphite furnace is one of the few, and often best, technologies capable of meeting your needs.
- If your materials are sensitive to carbon or form unwanted carbides: You must consider furnaces with refractory metal hot zones (molybdenum, tungsten) or advanced ceramic heaters.
- If your process runs below 1800°C and can tolerate an air atmosphere: A conventional furnace with metallic or silicon carbide heating elements is a far more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, understanding that a graphite furnace is a specialized "carbon system" is the key to leveraging its immense power for the right application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Typical Temperature Range | 2200 °C to 3000 °C (3992 °F to 5432 °F) |
| Heating Principle | Resistive heating of graphite elements |
| Required Atmosphere | Vacuum or Inert Gas (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen) |
| Common Applications | Sintering, Brazing, Graphitization, Annealing |
| Key Limitation | Not suitable for materials sensitive to carbon (risk of carbide formation) |
Need a High-Temperature Solution Tailored to Your Unique Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Let us help you achieve extreme temperatures reliably. Contact our experts today to discuss how our graphite furnace solutions can power your most demanding applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity



















