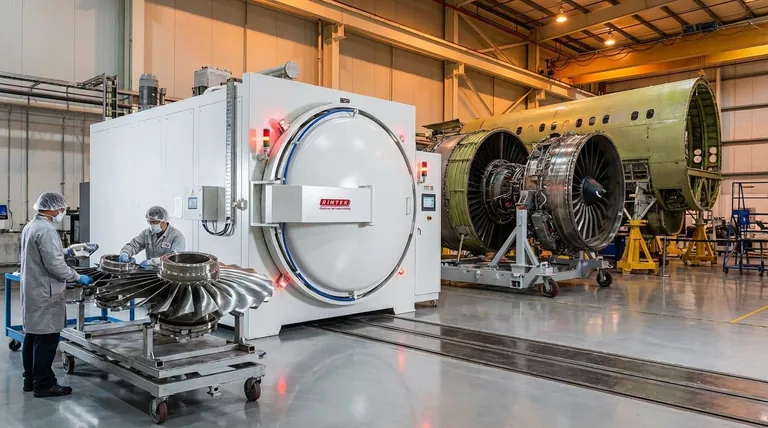
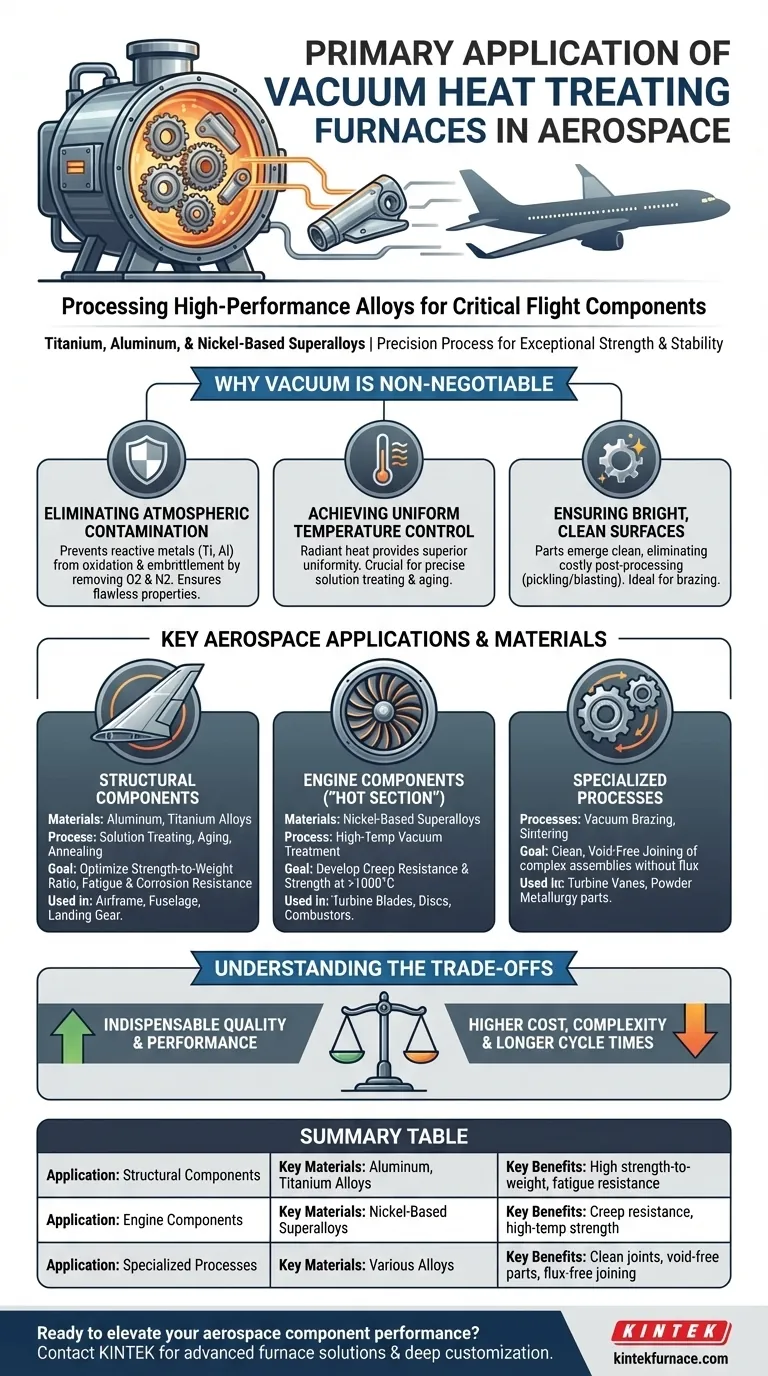
At its core, the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace is the processing of high-performance alloys—specifically titanium, aluminum, and nickel-based superalloys—for critical flight components. This treatment is not merely about heating metal; it is a precision process that develops the exceptional strength, fatigue resistance, and high-temperature stability required for engines, structural airframes, and landing gear to perform safely and reliably.
The fundamental value of vacuum heat treatment in aerospace is its ability to create a perfectly controlled, contamination-free environment. This prevents reactive metals from being compromised by atmospheric gases, ensuring the final component has the flawless metallurgical properties demanded by the industry's zero-failure tolerance.

Why Vacuum is Non-Negotiable in Aerospace
Heat treating is about modifying a metal's internal crystal structure to enhance its properties. In an industry as demanding as aerospace, the environment in which this happens is as critical as the process itself. Using a vacuum is a solution to fundamental chemical and physical challenges.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
High-performance aerospace alloys, particularly titanium and certain aluminum alloys, are highly reactive with oxygen and nitrogen at elevated temperatures.
Exposure to atmosphere during heat treatment can cause oxidation and embrittlement, creating a weak surface layer and compromising the integrity of the entire part. A vacuum removes these reactive gases, ensuring the material's inherent properties are fully realized.
Achieving Uniform Temperature Control
A vacuum environment provides superior temperature uniformity compared to convection-based atmospheric furnaces. Radiant heat transfers directly and evenly to the parts without interference from air currents.
This precise thermal control is crucial for complex processes like solution treating and aging, where even minor temperature deviations can result in inconsistent material properties and potential component failure.
Ensuring Bright, Clean Surfaces
Because vacuum processing prevents oxidation, parts emerge from the furnace with a bright, clean surface.
This eliminates the need for aggressive post-processing steps like acid pickling or blast cleaning, which can be costly, environmentally hazardous, and potentially damaging to the component's surface finish. This is especially vital for parts that will be subsequently brazed or welded.
Key Aerospace Applications and Materials
The need for a controlled vacuum environment directly maps to the most critical components on an aircraft. Different alloys are chosen for specific functions, and each relies on vacuum treatment to meet performance specifications.
Structural Components (Aluminum and Titanium Alloys)
The airframe, fuselage, wings, and landing gear depend on materials with an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.
Vacuum furnaces are used for the solution treatment and aging of high-strength aluminum alloys and the annealing of titanium alloys. This optimizes their strength, ductility, and resistance to fatigue and corrosion, which are essential for the structural longevity of the aircraft.
Engine Components (Nickel-Based Superalloys)
The "hot section" of a jet engine—including turbine blades, discs, and combustors—operates under extreme temperatures and mechanical stress. These parts are often made from nickel-based superalloys.
Vacuum heat treatment is essential to develop the creep resistance and high-temperature strength of these superalloys, preventing them from deforming under load at temperatures exceeding 1000°C (1832°F).
Specialized Processes (Brazing and Sintering)
Beyond strengthening, vacuum furnaces are used for joining and forming. Vacuum brazing uses a filler metal to join complex assemblies, like turbine vanes, without using corrosive flux. The vacuum ensures a strong, clean, and void-free joint.
Vacuum sintering is also used to fuse powdered metals into solid, near-net-shape parts, a process known as powder metallurgy, which is growing in importance for manufacturing complex aerospace components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, vacuum furnace technology is not without its specific challenges and considerations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to understanding its place in manufacturing.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnace systems are significantly more expensive to purchase and install than their atmospheric counterparts. They also require more complex control systems, vacuum pumps, and infrastructure.
Operation and maintenance demand a higher level of technical expertise to manage vacuum integrity and ensure process repeatability.
Longer Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum (pumping down the chamber) and cooling the workload in a vacuum environment can take longer than in an atmospheric furnace where fans can circulate inert gas.
This can result in lower throughput for certain high-volume applications, making it a deliberate choice for high-value parts where quality outweighs speed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven entirely by the material and the performance requirements of the final component. The process is chosen when the risks of atmospheric contamination are unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is airframe and structural integrity: You will rely on vacuum solution treating and aging for aluminum and titanium alloys to maximize strength-to-weight ratios and fatigue life.
- If your primary focus is engine performance and high-temperature durability: Vacuum heat treatment is the only viable option for developing the critical creep resistance and strength of nickel-based superalloys.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, high-value assemblies: Vacuum brazing provides the cleanest, strongest, and most reliable method for creating flux-free joints in mission-critical components.
Ultimately, vacuum heat treatment is the enabling technology that transforms advanced metal alloys into the safe, high-performance components that make modern flight possible.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Materials | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Components | Aluminum, Titanium Alloys | High strength-to-weight ratio, fatigue resistance |
| Engine Components | Nickel-Based Superalloys | Creep resistance, high-temperature strength |
| Specialized Processes (Brazing/Sintering) | Various Alloys | Clean joints, void-free parts, flux-free joining |
Ready to elevate your aerospace component performance with precision heat treatment? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for critical aerospace applications. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















