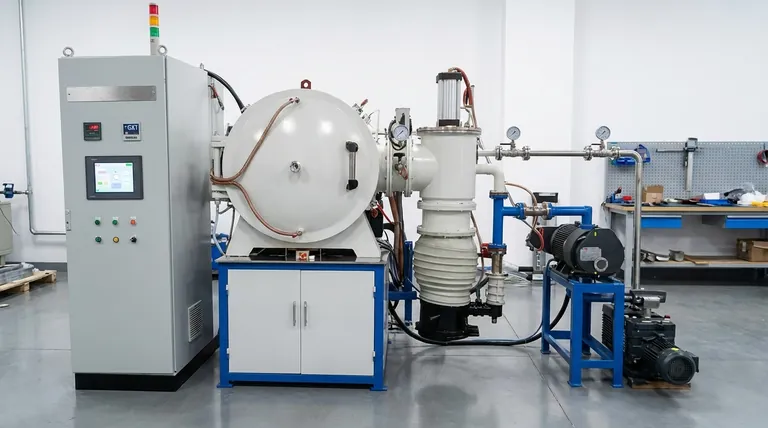
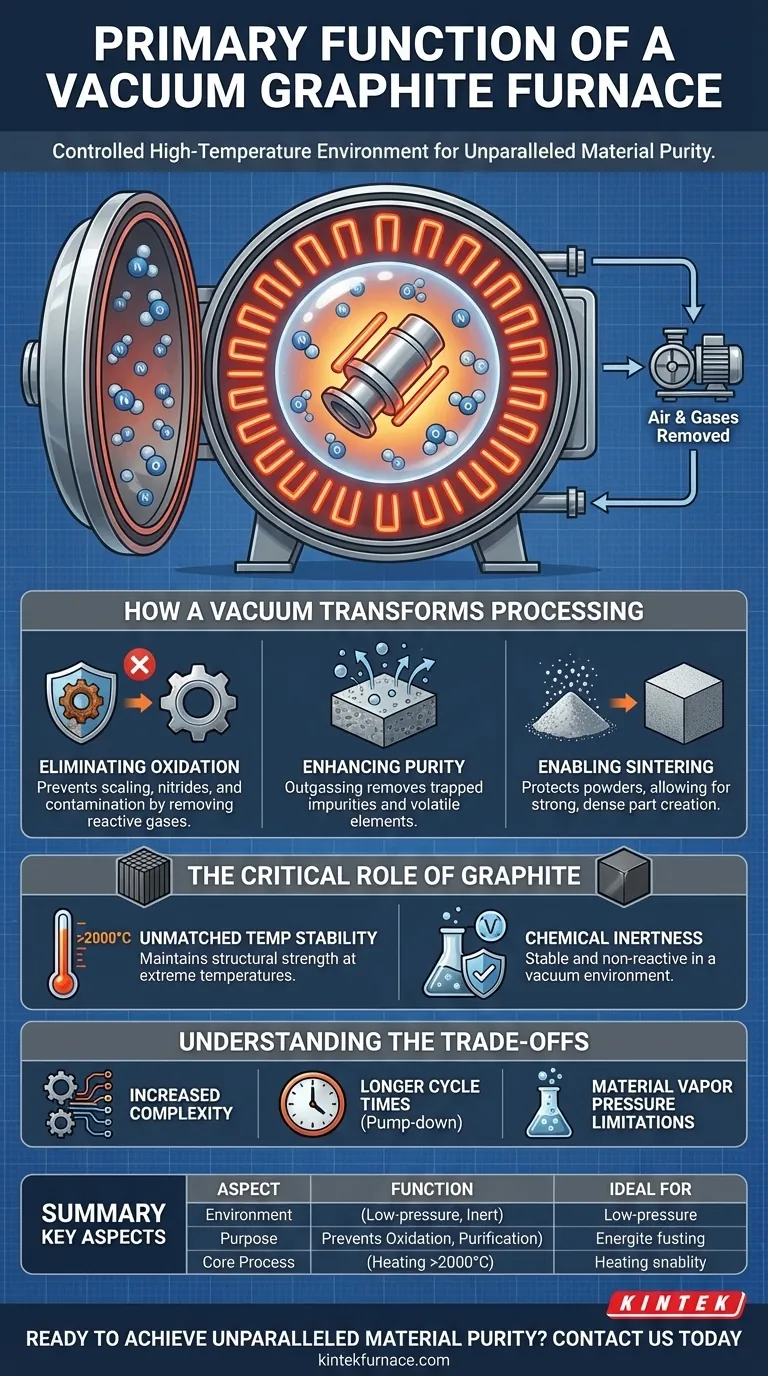
At its core, a vacuum graphite furnace is a specialized high-temperature chamber that heats materials in a controlled, low-pressure environment. Its primary function is to create a chemically pure atmosphere by removing air and other gases, thereby preventing unwanted reactions like oxidation and contamination during the heating process.
The crucial insight is that a vacuum furnace isn't just about getting things hot; it's about controlling the chemical environment while they are hot. This control allows for the processing of sensitive materials and the achievement of properties that are impossible in a standard, air-filled furnace.

How a Vacuum Transforms High-Temperature Processing
Heating a material can fundamentally change its properties. Introducing a vacuum environment gives you precise control over these changes by eliminating the variable of atmospheric interference.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, most metals and many materials react aggressively with the oxygen and nitrogen present in the air. This causes oxidation (scaling or rust) and can form nitrides, which degrade the material's surface and structural integrity.
A vacuum furnace physically removes these reactive gases. By pumping the chamber down to a low pressure, you create an environment where there are too few oxygen molecules to cause harmful reactions, protecting the part's surface finish and chemistry.
Enhancing Material Purity
The vacuum does more than just prevent contaminants from entering; it can also pull existing impurities out of the material itself. This process, known as outgassing, removes trapped gases and volatile elements from deep within the material being heated.
This purification is critical in applications like refining specialty alloys or preparing materials for medical implants, where even trace amounts of impurities can cause failure.
Enabling Specific Chemical Processes
Certain advanced manufacturing processes are only possible in a vacuum. A key example is sintering, where fine metal powders are heated until their particles fuse together to form a solid object.
In the open air, each tiny powder particle would oxidize instantly, preventing them from bonding properly. A vacuum protects the particles, allowing for the creation of strong, dense parts from materials like tungsten carbide or specialty steel powders.
The Critical Role of Graphite
The "graphite" in the furnace's name refers to the material used for the internal components, including the heating elements and insulation. This choice is deliberate and essential.
Unmatched Temperature Stability
Graphite has an exceptionally high melting point and maintains its structural strength at temperatures that would cause most metals to melt or deform. This allows vacuum graphite furnaces to operate at extreme temperatures, often exceeding 2000°C (3632°F).
Chemical Inertness in a Vacuum
While graphite would burn away in an oxygen-rich atmosphere, it is extremely stable and non-reactive in a vacuum. This makes it the ideal material for containing and radiating heat without contaminating the high-purity environment inside the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. They introduce specific complexities that must be considered.
Increased Process Complexity
Operating a vacuum furnace requires managing pumps, seals, and sophisticated control systems to create and maintain the low-pressure environment. This adds a layer of operational complexity and maintenance compared to a simple atmospheric furnace.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping all the air out of the furnace chamber—the "pump-down" phase—takes time. This can extend the total cycle time for each batch, potentially impacting throughput.
Material Vapor Pressure
Not all materials are suitable for vacuum processing. Elements with a high vapor pressure (like zinc, magnesium, or cadmium) can begin to "boil" or evaporate under vacuum at high temperatures. This can damage the material and contaminate the furnace interior.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum purity and a contamination-free surface: A vacuum furnace is essential, particularly for reactive metals like titanium or for powder metallurgy applications.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment of non-reactive steels: A more conventional atmosphere furnace might be a faster and more cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures for sintering, brazing, or graphitization: The graphite construction and vacuum environment make this furnace type the definitive choice.
By understanding the fundamental role of the vacuum, you can select the precise tool needed to achieve unparalleled material quality and performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Environment | Creates a low-pressure, chemically inert atmosphere. |
| Purpose | Prevents oxidation & contamination; enables material purification. |
| Core Process | Heating materials to extreme temperatures (>2000°C) with precision. |
| Ideal For | Processing reactive metals, sintering powders, and high-purity applications. |
Ready to Achieve Unparalleled Material Purity and Performance?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether your project involves sintering, brazing, graphitization, or processing reactive metals, our vacuum graphite furnaces are engineered to deliver the extreme-temperature purity and control you need. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating



















