In the extreme environment of a vacuum furnace, graphite fixtures and holders are indispensable. Their primary importance lies in their unique ability to securely position workpieces while remaining dimensionally stable at temperatures that would cause most metals to warp, melt, or deform. This structural integrity under intense heat is critical for ensuring the precision and success of processes like brazing, sintering, and annealing.
The core reason graphite dominates this application is not just one property, but a unique combination of thermal and mechanical traits. While its resistance to heat is paramount, its low thermal expansion is the true hero, ensuring it doesn't change shape and compromise the workpiece it is designed to hold.
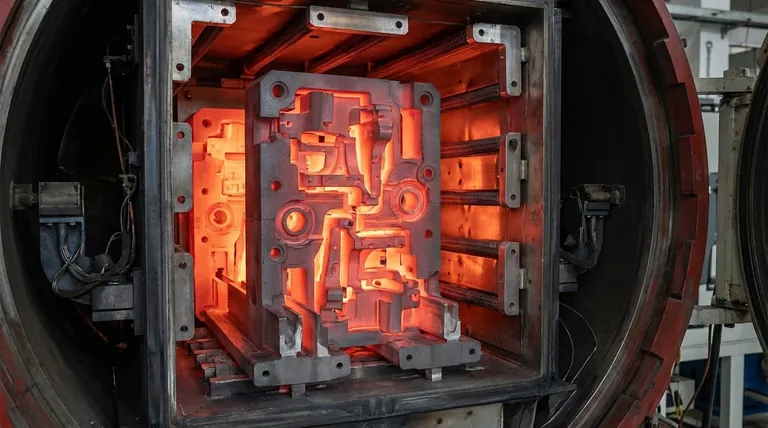
The Critical Role of Thermal Stability
A vacuum furnace environment is defined by radical temperature changes. Graphite's behavior under these conditions makes it the ideal material for internal tooling.
Resisting Extreme Temperatures
Graphite does not have a melting point at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimates (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at an incredibly high temperature, around 3,600°C.
This means that within the operational range of nearly all vacuum furnaces, graphite fixtures remain solid and rigid, providing a reliable platform for the materials being treated.
Unmatched Dimensional Stability
The most critical property for a fixture is its ability to maintain its shape. Graphite has a very low coefficient ofthermal expansion (CTE).
This means that as the furnace temperature soars, the graphite fixture or holder barely expands. This prevents it from warping, cracking, or exerting stress on the workpiece it is holding, which is essential for manufacturing high-precision components.
Surviving Thermal Shock
Furnace cycles often involve rapid heating and cooling. Graphite has excellent resistance to thermal shock, meaning it can withstand these quick temperature changes without cracking or failing.
This durability makes it a reliable and long-lasting material for tooling that is used across countless production cycles.
Key Mechanical and Chemical Advantages
Beyond its thermal properties, graphite's physical and chemical nature provides significant operational benefits.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Despite being very strong, graphite is also lightweight. This makes fixtures easier for operators to handle and install.
Lighter tooling also reduces the wear and tear on furnace support structures and can lower the energy costs required to heat the furnace load.
Superior Machinability
Graphite is relatively easy to machine into complex and precise shapes. This allows for the creation of custom-designed fixtures that can securely hold even the most intricate workpieces.
This machinability makes graphite a cost-effective solution for producing specialized, low-volume tooling.
Chemical Inertness
In the oxygen-free environment of a vacuum furnace, graphite is chemically stable and will not react with or contaminate the parts being heat-treated. This ensures the purity and integrity of the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Need for Vacuum
Graphite's remarkable properties come with one significant operational requirement.
The Enemy: Oxidation
Graphite's only major vulnerability is oxidation. In the presence of oxygen at high temperatures, graphite will rapidly burn away, much like charcoal.
This is precisely why these fixtures are used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere. The absence of oxygen is what protects the graphite and allows it to function.
Implications for Furnace Operation
Maintaining a high-quality vacuum is not only for the benefit of the workpiece but is absolutely essential for preserving the furnace's graphite components.
Even a small atmospheric leak can lead to the rapid degradation and failure of expensive graphite fixtures, insulation, and heating elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
When specifying or using graphite fixtures, your operational priorities will guide your focus.
- If your primary focus is process reliability: Prioritize graphite's low thermal expansion and high sublimation point, as these guarantee your fixtures will not deform and cause a process failure.
- If your primary focus is operational cost: Leverage graphite's high strength-to-weight ratio and machinability, which reduce handling labor and allow for affordable custom tooling.
- If your primary focus is furnace longevity: Pay strict attention to preventing oxidation by ensuring a high-quality vacuum, as this is the single most critical factor in extending the life of your graphite components.
Understanding these properties empowers you to leverage graphite not just as a material, but as a strategic tool for achieving precise and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|
| High Sublimation Point (~3600°C) | Remains solid at extreme temperatures |
| Low Thermal Expansion (CTE) | Maintains shape, prevents workpiece stress |
| Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating/cooling cycles |
| High Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Easy handling, reduces furnace wear |
| Superior Machinability | Enables custom, precise fixture designs |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination of workpieces |
Ready to enhance your vacuum furnace performance with precision graphite fixtures?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our expertise in graphite tooling ensures your brazing, sintering, and annealing processes achieve unmatched precision and repeatability.
Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our durable, custom-designed graphite fixtures can optimize your furnace operations and extend component life!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability



















