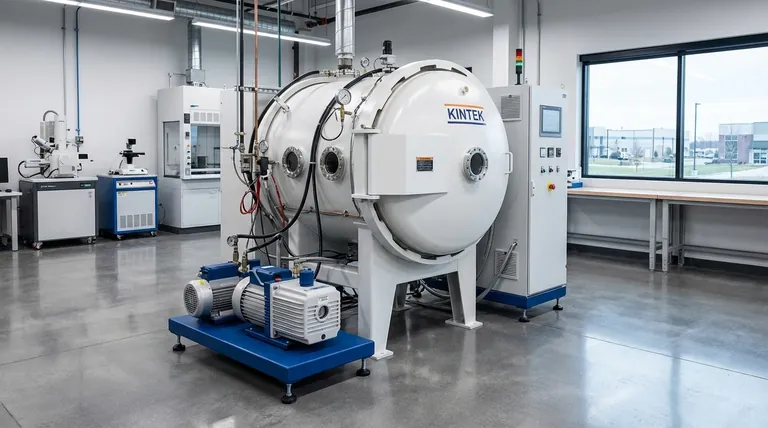
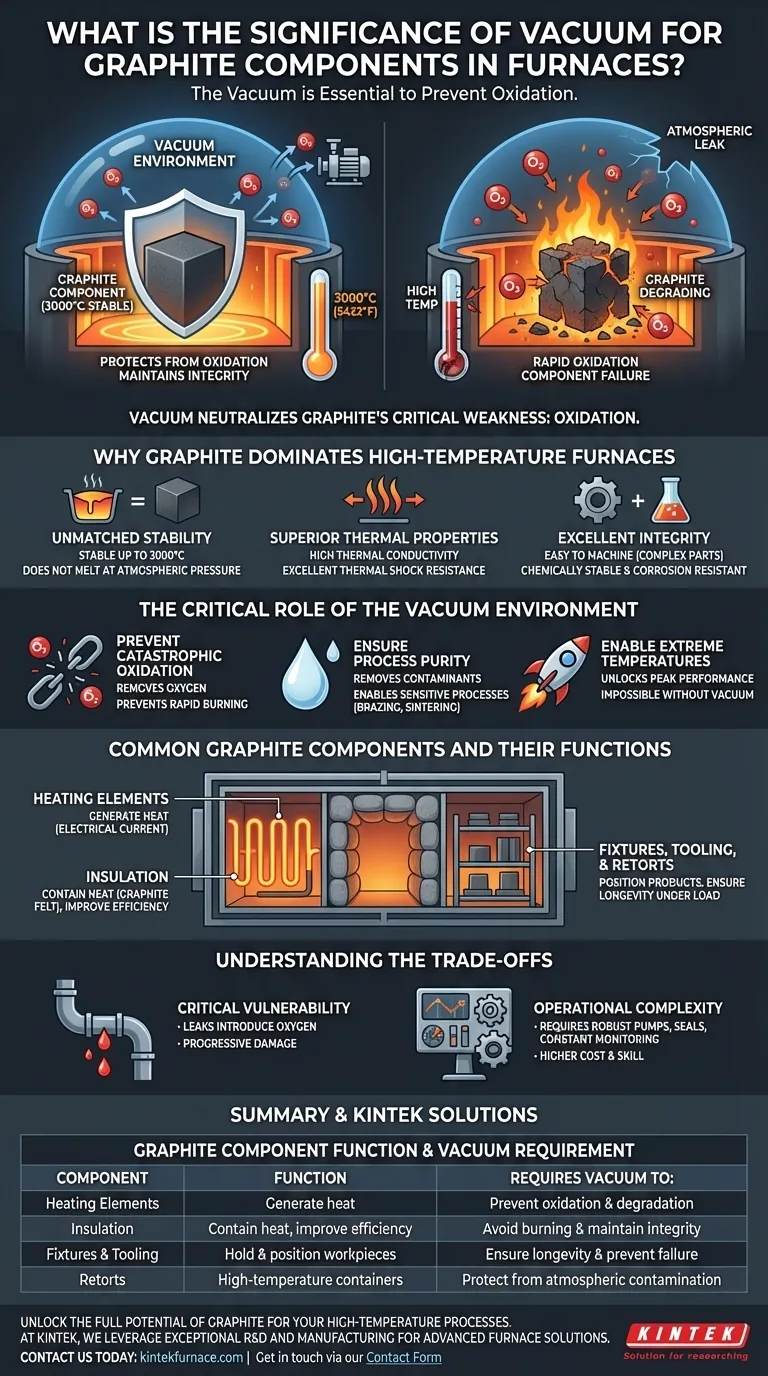
In short, a vacuum is essential because it protects graphite furnace components from being destroyed by oxidation. At the extreme temperatures inside a furnace, graphite reacts aggressively with oxygen, causing it to rapidly degrade and fail. A vacuum removes the oxygen, allowing the graphite to maintain its structural integrity and perform its function.
The relationship is simple: graphite is an exceptional high-temperature material with one critical weakness—oxidation. A vacuum environment neutralizes this weakness, unlocking graphite's full potential for extreme temperature applications.

Why Graphite Dominates High-Temperature Furnaces
To understand the significance of the vacuum, we must first appreciate why graphite is the material of choice for the hottest parts of a furnace. Its properties make it uniquely suited for these demanding environments.
Unmatched High-Temperature Stability
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; it sublimes. It can stably withstand temperatures up to 3000°C (5432°F) in a vacuum or inert atmosphere, far surpassing the limits of most metals.
Superior Thermal Properties
Graphite possesses high thermal conductivity, allowing it to distribute heat evenly. This is critical for heating elements and ensures uniform temperature within the furnace's hot zone.
It also has an exceptionally strong resistance to thermal shock, meaning it can endure rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or failing.
Excellent Mechanical and Chemical Integrity
Graphite is relatively easy to machine, allowing for the creation of complex components like fixtures, supports, and specialized heating elements. It is also chemically stable and resistant to corrosion from many substances.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum Environment
While graphite is nearly perfect for the heat, it is vulnerable to the atmosphere. This is where the vacuum becomes the indispensable partner.
Preventing Catastrophic Oxidation
The primary function of the vacuum is to remove oxygen. At high temperatures, graphite reacts with oxygen in a process of rapid oxidation—in simple terms, it burns away.
A failure to maintain a proper vacuum will lead to the swift destruction of expensive graphite heating elements, insulation, and fixtures.
Ensuring Process Purity
Beyond protecting the furnace components, a vacuum also removes other atmospheric gases and contaminants. This creates a pure environment, which is critical for sensitive metallurgical processes like brazing, sintering, and heat treating, preventing unwanted reactions with the workpiece.
Enabling Extreme Temperatures
The combination of graphite and vacuum enables furnaces to reach temperatures that would be impossible otherwise. Without the vacuum, the graphite components would oxidize and fail long before reaching their peak temperature capabilities.
Common Graphite Components and Their Functions
You will find graphite used for several key parts inside a vacuum furnace, each leveraging its unique properties.
Heating Elements
These components generate the heat when an electrical current is passed through them. Graphite's low resistivity and high-temperature stability make it an ideal material.
Insulation
Packs of graphite felt are used as high-performance insulation. They surround the hot zone, containing the intense heat and improving the furnace's energy efficiency.
Fixtures, Tooling, and Retorts
These are the racks, holders, and containers that position the product being heat-treated. Graphite's strength at high temperatures ensures these fixtures do not warp or fail under load.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The graphite-vacuum system is powerful, but its effectiveness is dependent on maintaining a delicate balance.
The Critical Vulnerability to Leaks
The entire system's integrity hinges on the quality of the vacuum. Even a small air leak can introduce enough oxygen to cause significant, progressive damage to the graphite components, especially during high-temperature cycles.
Operational Complexity
Operating and maintaining a vacuum furnace is more complex than an atmospheric furnace. It requires robust vacuum pumps, precise seals, and constant monitoring to ensure the environment remains free of oxygen. This adds a layer of operational cost and requires specific technical skill.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding this relationship between material and environment is key to operational success.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (above 2000°C): A graphite vacuum furnace is essential, as the material's integrity is entirely dependent on the oxygen-free environment.
- If your primary focus is component longevity and cost-effectiveness: Maintaining a high-quality vacuum is the single most important factor in preserving your graphite components and avoiding costly replacements.
- If your primary focus is process purity and repeatability: A vacuum is non-negotiable for removing atmospheric contaminants that can compromise sensitive applications like aerospace brazing or medical implant sintering.
Mastering your vacuum system is the key to unlocking the unparalleled high-temperature performance of graphite.
Summary Table:
| Graphite Component | Function | Requires Vacuum To: |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Generate heat via electrical current | Prevent oxidation and rapid degradation |
| Insulation (Graphite Felt) | Contain heat, improve efficiency | Avoid burning and maintain integrity |
| Fixtures & Tooling | Hold and position workpieces | Ensure longevity and prevent failure |
| Retorts | Act as high-temperature containers | Protect from atmospheric contamination |
Unlock the full potential of graphite for your high-temperature processes. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by deep customization capabilities to ensure your graphite components operate reliably at extreme temperatures. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and process purity. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness



















