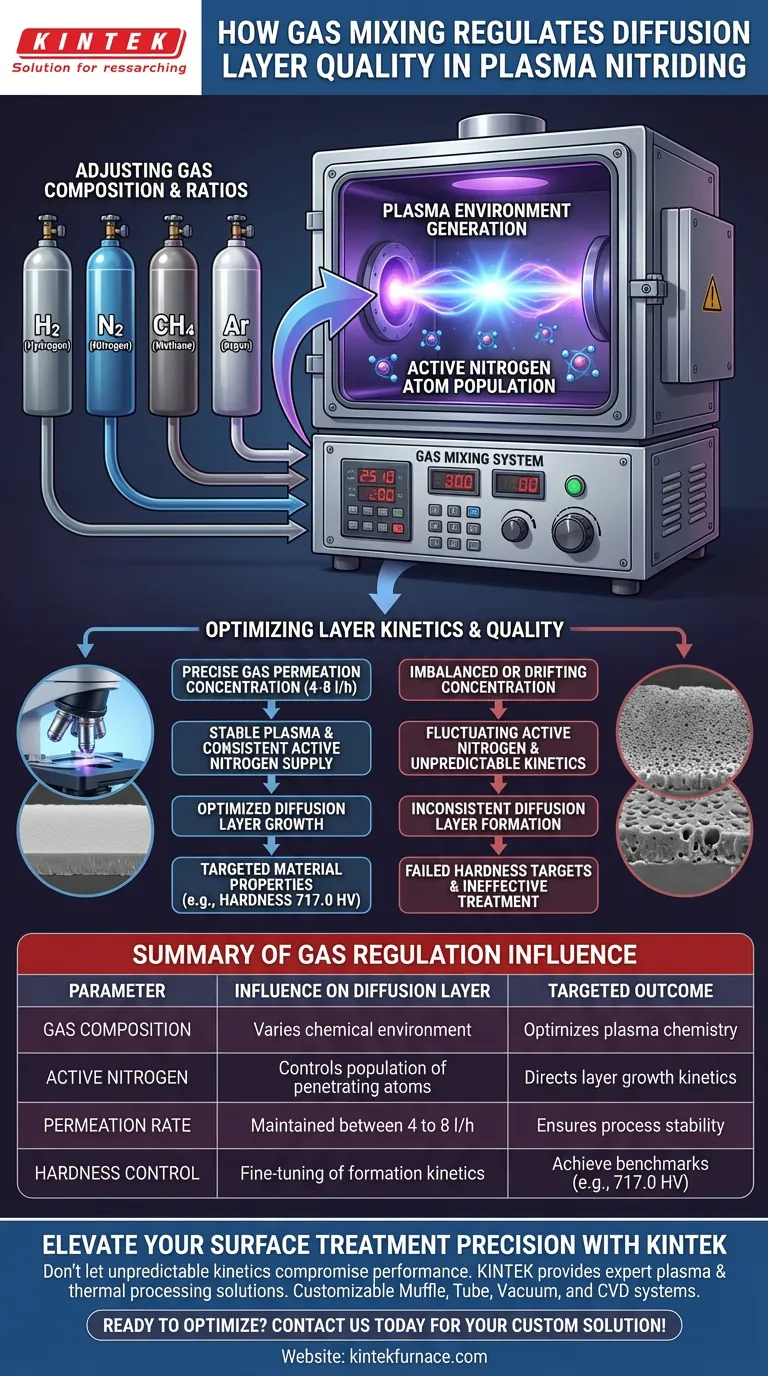
The gas mixing system acts as the primary regulator of metallurgical quality. It achieves this by precisely adjusting the flow rates and ratios of process gases, specifically hydrogen (H2), nitrogen (N2), methane (CH4), and argon (Ar). This regulation determines the concentration of active nitrogen atoms available in the plasma, which is the fundamental driver of diffusion layer formation.
The system controls gas permeation concentration to optimize the kinetics of the diffusion layer. This precision allows you to target specific material properties, such as a hardness of 717.0 HV, by directly managing the active nitrogen supply.

The Mechanics of Gas Regulation
Adjusting Gas Composition
The foundation of the process lies in the specific mixture of gases introduced into the chamber.
By varying the ratios of hydrogen, nitrogen, methane, and argon, the system alters the chemical environment of the plasma.
Regulating Active Nitrogen
The ultimate goal of mixing these gases is to control the population of active nitrogen atoms.
These atoms are responsible for penetrating the material surface. By manipulating the gas ratios, the system directly increases or decreases the concentration of these active species available for diffusion.
Optimizing Layer Kinetics
Controlling Permeation Concentration
The system manages the gas permeation concentration within a specific range, typically between 4 to 8 l/h.
Maintaining this flow rate is critical for stabilizing the plasma environment. It ensures a consistent supply of nitrogen without overwhelming the process or starving the surface of necessary reactants.
Meeting Hardness Requirements
The control of formation kinetics translates directly to physical properties.
By optimizing how the diffusion layer grows, the system ensures the final product meets exact specifications. For example, precise gas regulation allows the process to achieve specific hardness benchmarks, such as 717.0 HV.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Precision
The relationship between gas flow and layer quality is non-linear.
If the gas permeation concentration drifts outside the optimal range (e.g., outside 4 to 8 l/h), the concentration of active nitrogen will fluctuate.
Consequences of Imbalance
An imbalance in the gas mix leads to unpredictable diffusion kinetics.
This results in a diffusion layer that may fail to meet the required hardness targets, rendering the treatment ineffective for its intended application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve the best results with plasma nitriding, you must align your gas settings with your material targets.
- If your primary focus is specific hardness (e.g., 717.0 HV): Ensure the gas mixing system is calibrated to maintain a stable permeation concentration within the 4 to 8 l/h window to guarantee sufficient active nitrogen.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: Monitor the flow rates of H2, N2, CH4, and Ar closely to prevent fluctuations in diffusion layer formation kinetics.
Mastering the gas mix is not just about flow; it is about strictly managing the active nitrogen available to build your diffusion layer.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Influence on Diffusion Layer | Targeted Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Composition | Varies chemical environment (H2, N2, CH4, Ar) | Optimizes plasma chemistry |
| Active Nitrogen | Controls population of penetrating atoms | Directs layer growth kinetics |
| Permeation Rate | Maintained between 4 to 8 l/h | Ensures process stability |
| Hardness Control | Fine-tuning of formation kinetics | Achieve benchmarks (e.g., 717.0 HV) |
Elevate Your Surface Treatment Precision with KINTEK
Don't let unpredictable diffusion kinetics compromise your material performance. KINTEK provides industry-leading plasma and thermal processing solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our customizable Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems are designed to meet your exact metallurgical requirements, ensuring consistent hardness and superior layer quality for every application.
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes? Contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Nguyen Thai Van, Le Hong Ky. The Influence of Plasma Nitriding Technology Parameters on the Hardness of 18XГT Steel Parts. DOI: 10.48084/etasr.7089
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- How does the geometric design of a sample basket affect measurement accuracy in thermogravimetric analysis?
- What are the advantages of using a quartz glass reactor? Superior Visibility & Purity in Molten Salt Experiments
- How does the SOM method enhance titanium alloy purity? The Power of Solid Electrolyte Tubes
- What are the common uses for Alumina ceramic tubes? Ideal for High-Temp, Insulation, and Corrosion Resistance
- What is the role of a Teflon-lined autoclave in CeO2 synthesis? Achieve Pure, Monodisperse Nanomaterials
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during the SPS sintering process of Al2O3-TiC? Unlock Process Efficiency
- Why must the reaction containers be sealed within a fused quartz tube? Protect Your Crystal Growth Integrity
- Why is a high vacuum pumping system necessary for carbon nanotube peapods? Achieve Precise Molecular Encapsulation



















