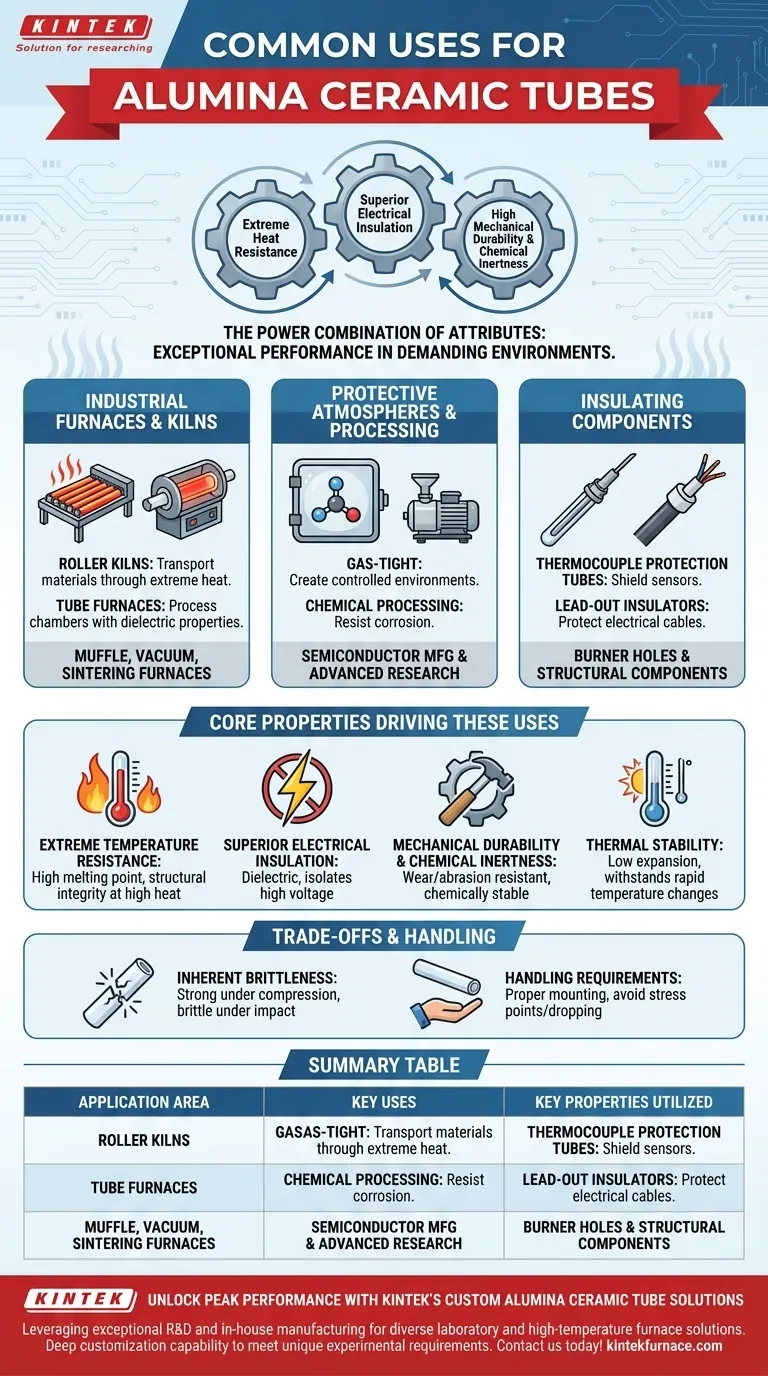
In essence, alumina ceramic tubes are primarily used in applications that demand exceptional performance in high-temperature, chemically harsh, or high-voltage environments where most other materials would fail. Their common applications range from industrial furnace linings and kiln rollers to protective sheaths for sensors and insulators for electrical heating elements.
The true value of alumina ceramic tubes lies not in a single property, but in their powerful combination of attributes. They simultaneously provide extreme heat resistance, excellent electrical insulation, and high mechanical durability, making them the go-to solution for the most demanding industrial and laboratory settings.

Why Alumina Dominates High-Temperature Applications
The use of alumina ceramics is concentrated in areas where conventional metals or polymers cannot survive. Their properties make them uniquely suited for containing and managing extreme heat and electricity.
In Industrial Furnaces and Kilns
Alumina tubes are fundamental components in various types of high-temperature furnaces. In roller kilns, they serve as rollers that transport materials through extreme heat, demanding resistance to both high temperatures and wear.
In tube furnaces, the alumina tube forms the central process chamber. Its ability to withstand high heat is critical, but its dielectric properties (electrical insulation) are equally important, safely separating the heated sample from the external electrical heating elements.
Other furnace applications include muffle furnaces, vacuum furnaces, and sintering furnaces used in manufacturing, metallurgy, and the glass industry.
For Protective Atmospheres and Processing
Because alumina can be manufactured to be gas-tight, it is ideal for creating controlled environments. This is essential in vacuum furnaces or in processes that require a specific protective atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
This property makes it invaluable for chemical processing, semiconductor manufacturing, and advanced materials research where purity and environmental control are paramount.
As Critical Insulating Components
Alumina's excellent electrical insulation makes it a superior choice for protecting sensitive components. It is commonly used for thermocouple protection tubes, shielding temperature sensors from corrosive environments or electrical interference.
They also serve as lead-out insulators for electrical cables and as structural components like burner holes in gas-fired kilns, where both heat and electrical resistance are needed.
The Core Properties Driving These Uses
The widespread adoption of alumina tubes is not accidental. It is a direct result of a specific set of inherent material properties.
Extreme Temperature Resistance
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) has a very high melting point and maintains its structural integrity and strength at temperatures where even high-performance metal alloys would weaken and fail.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Alumina is a dielectric material, meaning it does not conduct electricity. This allows it to act as a barrier, safely containing high-voltage heating elements or isolating sensitive electronic sensors from electrical noise.
Mechanical Durability and Chemical Inertness
Alumina exhibits high compression resistance and is highly resistant to wear and abrasion, ensuring a long service life. It is also chemically stable and resists corrosion from most acids and alkalis, even at high temperatures.
Thermal Stability
With low thermal expansion and good thermal shock resistance, alumina tubes can better withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking compared to many other ceramics. This is critical in applications involving fast heating or cooling cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly capable, alumina is not without its limitations. Acknowledging these is key to successful implementation.
Inherent Brittleness
Like most ceramics, alumina is strong under compression but brittle. It can fracture under sudden mechanical impact or tensile stress. This requires careful design and handling protocols to avoid breakage during installation or operation.
Handling and Installation Requirements
The material's brittleness means that proper mounting and support are critical. Tubes must be installed without creating stress points, and users must avoid dropping or striking them. Specialized preparation, such as ultrasonic cleaning, may also be required for high-purity applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material comes down to matching its properties to your primary challenge.
- If your primary focus is containing extreme heat: Alumina's ability to remain stable at very high temperatures makes it a leading candidate.
- If you need to electrically isolate a high-temperature component: Its combination of thermal resistance and dielectric strength is unmatched.
- If your application involves a vacuum or corrosive chemicals: Alumina's gas-tight nature and chemical inertness provide a reliable and durable solution.
By understanding these core properties and limitations, you can confidently specify alumina ceramic tubes for applications where performance in extreme conditions is non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Key Properties Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Furnaces and Kilns | Rollers, process chambers in tube furnaces, muffle furnaces | High-temperature resistance, electrical insulation, mechanical durability |
| Protective Atmospheres and Processing | Vacuum furnaces, chemical processing, semiconductor manufacturing | Gas-tight nature, chemical inertness, thermal stability |
| Insulating Components | Thermocouple protection tubes, lead-out insulators, burner holes | Electrical insulation, corrosion resistance, thermal shock resistance |
Unlock Peak Performance with KINTEK's Custom Alumina Ceramic Tube Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need reliable insulation, high-temperature resistance, or corrosion protection, we deliver tailored alumina ceramic tubes that enhance durability and efficiency in your demanding applications.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can address your specific challenges and elevate your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs



















