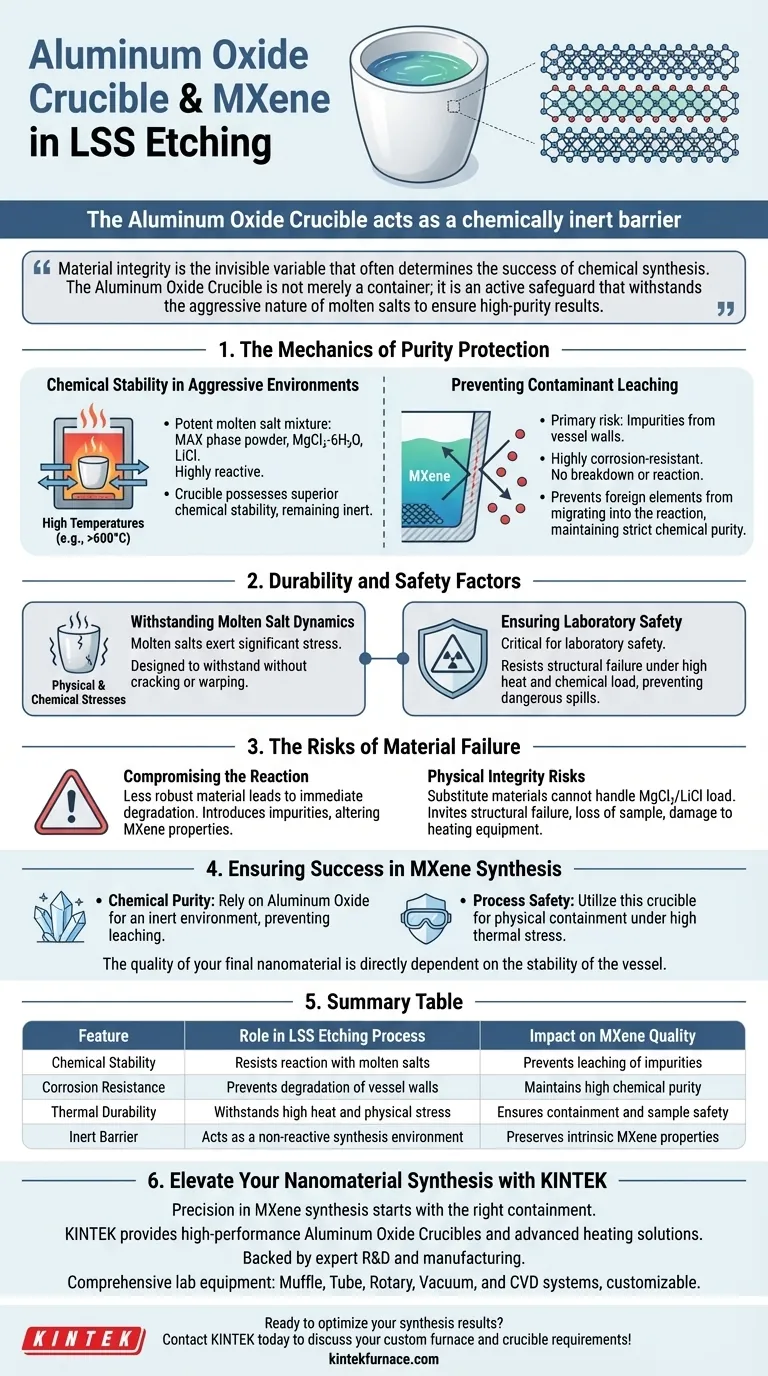
The Aluminum Oxide Crucible acts as a chemically inert barrier that is fundamental to preserving the purity of MXene during synthesis. By leveraging superior chemical stability and corrosion resistance, it prevents the reaction vessel itself from degrading and leaching contaminants into the aggressive molten salt mixture used in the Low-temperature Shielding Salt (LSS) process.
Material integrity is the invisible variable that often determines the success of chemical synthesis. The Aluminum Oxide Crucible is not merely a container; it is an active safeguard that withstands the aggressive nature of molten salts to ensure high-purity results.

The Mechanics of Purity Protection
To understand the crucible's role, one must look at how it interacts with the harsh environment inside the vessel.
Chemical Stability in Aggressive Environments
The LSS etching process utilizes a potent mixture of MAX phase powder, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, and lithium chloride.
At the high temperatures required for this reaction, these salts become molten and highly reactive.
The Aluminum Oxide Crucible possesses superior chemical stability, allowing it to remain inert despite constant exposure to this corrosive environment.
Preventing Contaminant Leaching
The primary risk in this type of synthesis is the introduction of unwanted impurities from the vessel walls.
Because Aluminum Oxide is highly corrosion-resistant, it does not break down or react with the salt mixture.
This ensures that no foreign elements migrate from the crucible into the reaction, maintaining the strict chemical purity required for the final MXene product.
Durability and Safety Factors
Beyond chemical inertness, the physical structural integrity of the vessel contributes to the overall success of the procedure.
Withstanding Molten Salt Dynamics
Molten salts exert significant physical and chemical stresses on their containment vessels.
The Aluminum Oxide Crucible is specifically designed to withstand these stresses without cracking or warping.
Ensuring Laboratory Safety
The durability of the crucible is critical not just for the product, but for the safety of the laboratory environment.
By resisting structural failure under high heat and chemical load, the crucible contains the hazardous reaction safely, preventing dangerous spills or containment breaches.
The Risks of Material Failure
It is vital to understand the trade-offs involved if a less robust material were used.
Compromising the Reaction
If a vessel lacks the specific resistance of Aluminum Oxide, the "trade-off" is an immediate degradation of the synthesis quality.
A degrading vessel introduces impurities that can fundamentally alter the electronic or physical properties of the MXene.
Physical Integrity Risks
Using a substitute material that cannot handle the specific thermal and chemical load of the $MgCl_2/LiCl$ mixture invites structural failure.
This can lead to the loss of the entire sample or potential damage to the heating equipment due to molten salt leakage.
Ensuring Success in MXene Synthesis
Selecting the correct reaction vessel is as critical as measuring the reactants themselves.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Rely on Aluminum Oxide to provide an inert environment that prevents the leaching of vessel material into your MXene lattice.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Utilize this crucible material to ensure the physical containment of hazardous molten salts under high thermal stress.
The quality of your final nanomaterial is directly dependent on the stability of the vessel in which it is born.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in LSS Etching Process | Impact on MXene Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Stability | Resists reaction with molten salts (MgCl₂/LiCl) | Prevents leaching of impurities |
| Corrosion Resistance | Prevents degradation of vessel walls | Maintains high chemical purity |
| Thermal Durability | Withstands high heat and physical stress | Ensures containment and sample safety |
| Inert Barrier | Acts as a non-reactive synthesis environment | Preserves intrinsic MXene properties |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in MXene synthesis starts with the right containment. KINTEK provides high-performance Aluminum Oxide Crucibles and advanced heating solutions tailored for aggressive chemical processes.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab equipment including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to your unique research needs. Ensure maximum chemical purity and laboratory safety by choosing materials designed for the most demanding environments.
Ready to optimize your synthesis results? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace and crucible requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Sin‐Yi Pang, Jianhua Hao. Fluoride‐Free Molten Salt Hydrate‐Assisted Synthesis of MXene in Air Down to 150 °C. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202504864
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity alumina (Al2O3) crucible required for the melting of nickel-based superalloys?
- What advanced material processing applications use graphite crucible furnaces? Unlock Precision in Nanomaterial Synthesis and More
- What are the advantages of using an infrared thermograph over traditional thermocouples in Plasma Flash Sintering (PFS)?
- How does a laboratory drying oven contribute to the preparation of C@TiC/SiO2 xerogels? Ensure Structural Integrity
- Why are high-alumina crucibles required for static immersion corrosion tests? Ensure Data Purity at 1000°C
- Why is an alundum crucible necessary for the melting and casting of FeAl alloys? Ensure Maximum Purity and Stability
- Why are high-purity ceramic boats used for V2O5 and VSe2 deposition? Ensure Film Purity and Thermal Stability
- How are quartz tubes applied in optics and pharmaceuticals? Unlock Purity and Performance in Critical Applications



















